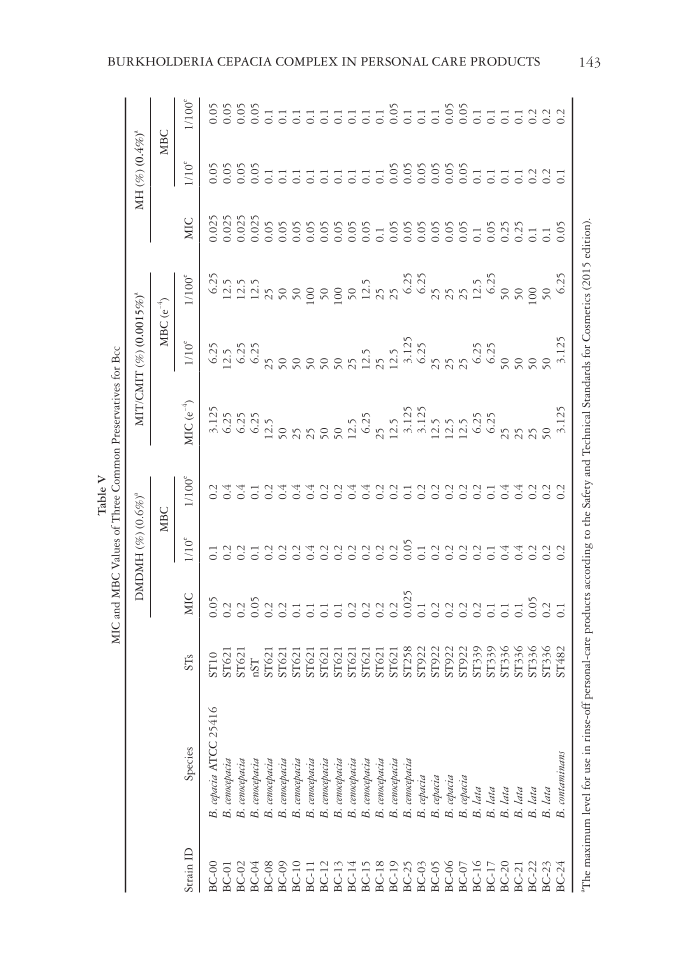
Table V MIC and MBC Values of Three Common Preservatives for Bcc Strain ID Species STs DMDMH (%) (0.6%) a MIT/CMIT (%) (0.0015%) a MH (%) (0.4%) a MIC MBC MIC (e-4) MBC (e-4) MIC MBC 1/10e 1/100 e 1/10 e 1/100 e 1/10e 1/100 e BC-00 B. cepacia ATCC 25416 ST10 0.05 0.1 0.2 3.125 6.25 6.25 0.025 0.05 0.05 BC-01 B. cenocepacia ST621 0.2 0.2 0.4 6.25 12.5 12.5 0.025 0.05 0.05 BC-02 B. cenocepacia ST621 0.2 0.2 0.4 6.25 6.25 12.5 0.025 0.05 0.05 BC-04 B. cenocepacia nST 0.05 0.1 0.1 6.25 6.25 12.5 0.025 0.05 0.05 BC-08 B. cenocepacia ST621 0.2 0.2 0.2 12.5 25 25 0.05 0.1 0.1 BC-09 B. cenocepacia ST621 0.2 0.2 0.4 50 50 50 0.05 0.1 0.1 BC-10 B. cenocepacia ST621 0.1 0.2 0.4 25 50 50 0.05 0.1 0.1 BC-11 B. cenocepacia ST621 0.1 0.4 0.4 25 50 100 0.05 0.1 0.1 BC-12 B. cenocepacia ST621 0.1 0.2 0.2 50 50 50 0.05 0.1 0.1 BC-13 B. cenocepacia ST621 0.1 0.2 0.2 50 50 100 0.05 0.1 0.1 BC-14 B. cenocepacia ST621 0.2 0.2 0.4 12.5 25 50 0.05 0.1 0.1 BC-15 B. cenocepacia ST621 0.2 0.2 0.4 6.25 12.5 12.5 0.05 0.1 0.1 BC-18 B. cenocepacia ST621 0.2 0.2 0.2 25 25 25 0.1 0.1 0.1 BC-19 B. cenocepacia ST621 0.2 0.2 0.2 12.5 12.5 25 0.05 0.05 0.05 BC-25 B. cenocepacia ST258 0.025 0.05 0.1 3.125 3.125 6.25 0.05 0.05 0.1 BC-03 B. cepacia ST922 0.1 0.1 0.2 3.125 6.25 6.25 0.05 0.05 0.1 BC-05 B. cepacia ST922 0.2 0.2 0.2 12.5 25 25 0.05 0.05 0.1 BC-06 B. cepacia ST922 0.2 0.2 0.2 12.5 25 25 0.05 0.05 0.05 BC-07 B. cepacia ST922 0.2 0.2 0.2 12.5 25 25 0.05 0.05 0.05 BC-16 B. lata ST339 0.2 0.2 0.2 6.25 6.25 12.5 0.1 0.1 0.1 BC-17 B. lata ST339 0.1 0.1 0.1 6.25 6.25 6.25 0.05 0.1 0.1 BC-20 B. lata ST336 0.1 0.4 0.4 25 50 50 0.25 0.1 0.1 BC-21 B. lata ST336 0.1 0.4 0.4 25 50 50 0.25 0.1 0.1 BC-22 B. lata ST336 0.05 0.2 0.2 25 50 100 0.1 0.2 0.2 BC-23 B. lata ST336 0.2 0.2 0.2 50 50 50 0.1 0.2 0.2 BC-24 B. contaminans ST482 0.1 0.2 0.2 3.125 3.125 6.25 0.05 0.1 0.2 a The maximum level for use in rinse-off personal-care products according to the Safety and Technical Standards for Cosmetics (2015 edition). BURKHOLDERIA CEPACIA COMPLEX IN PERSONAL CARE PRODUCTS 143
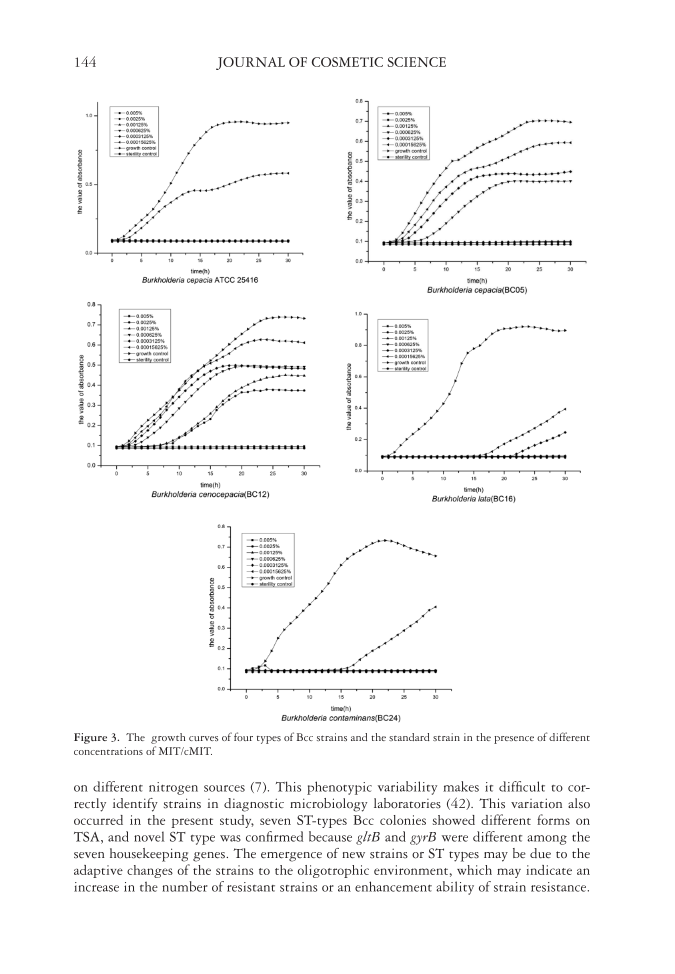
JOURNAL OF COSMETIC SCIENCE 144 Figure 3. The growth curves of four types of Bcc strains and the standard strain in the presence of different concentrations of MIT/cMIT. on different nitrogen sources (7). This phenotypic variability makes it diffi cult to cor- rectly identify strains in diagnostic microbiology laboratories (42). This variation also occurred in the present study, seven ST-types Bcc colonies showed different forms on TSA, and novel ST type was confi rmed because gltB and gyrB were different among the seven housekeeping genes. The emergence of new strains or ST types may be due to the adaptive changes of the strains to the oligotrophic environment, which may indicate an increase in the number of resistant strains or an enhancement ability of strain resistance.
Purchased for the exclusive use of nofirst nolast (unknown) From: SCC Media Library & Resource Center (library.scconline.org)