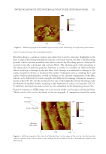
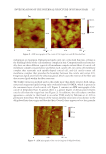
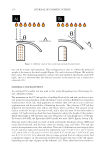
J. Cosmet. Sci., 71, 167–178 (May/June 2020) 167 Conformal Projection Printing Method to Increase the Accuracy of 3D Printed Nails CHAN JOUN PARK, ABHILASH ADITYA, and NAMSOO PETER KIM , Department of Mechanical Engineering, Center for Printable Materials Certifi cate, The University of Texas at El Paso, El Paso, Texas 79968 (C.J.P.), Department of Metallurgical Materials and Biomedical Engineering, Center for Printable Materials Certifi cate, The University of Texas at El Paso, El Paso, Texas 79968 (N.P.K., A.A.) Accepted for publication March 6, 2020. Synopsis Incorporating technologies such as 3D printers and the Internet of things (IoT) can improve the nail art industry by making it more effi cient, and, most importantly, safer. It eliminates the need for physical shops such as nail salons. Nail art by 3D printing technology can achieve higher resolution and accuracy than before with conformal projection printing method (CPPM). The conventional method of painting nails manually leads to acute exposure to ultraviolet (UV) light that can contribute to minor health hazards. This research illustrates the benefi ts of using 3D printing for nail art. This study uses the IoT system, which can be stationed in a distinct location from the customer. The product on the nail is printed at least once and up to three times within 5 μm to achieve precise resolution through laser marking and CPPM, which can increase the accuracy by repeated projection to attain the required settling ratio. The correlation between the numbers of printed layers and different incident angles of the printing head on the conformal surface is discussed. The ratio of projected weight to the ideal weight for high-defi nition printing condition is illustrated, and comparison studies with conventional nail art techniques are conducted to validate the results. I NTRODUCTION The integration of artifi cial intelligence (AI) in the industries of the 21st century increased the effi ciency of existing production and marketing processes. The amalgamation of 3D printers and Internet of things (IoT) systems puts forth the concept of digital manufac- turing (DM), which enables users to enter the relevant information and produce with minimal material input. Such improvement simplifi es the manufacturing processes and reduces the lead time, gaining consumer satisfaction and leading to the fourth industrial revolution (1). DM technology initiated with nano-inks where nanosized particles were dispersed in an aqueous solution through the direct injection method. This technology has drawn attention since 1990, because of not only various convergence technologies but Address all correspondence to Namsoo Peter Kim at nkim@utep.edu.
JOURNAL OF COSMETIC SCIENCE 168 also effi cient and effective economic advantages that can save material and time (2). The conventional printing method has grown as a leading technology in the 3D printing in- dustry, ranging from roll to roll, micro-dispensing deposition write, and inkjet. Further- more, it emphasized on standardization of materials and equipment, which are used in display printing (3). In addition to plastics, ceramics, metals, food, biomaterials, and medicines have been used and developed in various industries, including architecture, automobiles, dentistry, education, medicine, dietary life, drug delivery, and fashion (4–6). Furthermore, the specifi c fl exibility of 3D printing technology that can create unique, complex, and diverse shapes with the characteristics to be used in different materials depending on the user has gained popularity among scientists and technical workers because of its fl exibility and its unique characteristics (7). Wohlers Associates and the Journal of Science Policy & Governance predicted the growth of the global 3D printing market, which supports the emergence and rapid growth of several future industrial tech- nologies, which might increase to US$10.8 billion by 2021 (8). Because of the future direction of the automated industries, economic growth and the devel- opment of media through modernization affect the increase of people’s desire to express themselves freely and individually (9). In the beauty industry, along with the hair design and makeup sectors, the nail art industry has proliferated in recent years and has attracted attention by the fusion of material aesthetics with sophistication and smooth curves that give a smooth glossy surface from a material point of view (10). These positive changes in aesthetic perceptions are widely expressed beyond social class, genders, and ages. The nail art market, which has been developed mainly by women, is expected to expand to the area of tattoos with the development of 3D printing technology. In recent years, tattoos widely spread and became widespread among young people as a form of art (11). Therefore, the development of the nail art and tattoo industry can realize the recent rapid growth and changes in society through the convergence of art and engineering for per- sonal identity and the freedom of expression and aesthetic reasons. However, the nail art industry has recently received a red light in scalability as a challenge to solve the health problems caused by exposure to chemical toxic substances and UV process during gel nail formation. Nail art contains harmful chemicals such as acetone, ethyl acetic acid, toluene, and butyl acetic acid, and other various chemical dust that occur during the abrasion process, which is the essential task of smoothing nails. These can cause respiratory disor- ders to customers and operators (12). In California, a survey of 201 nail art workers in 74 different branches of nail shops found that 62% of workers complained of general health problems and 47% of them had skin irritation, respiratory disease, and paralysis related to the eyes and neck (13). The UV lamp rays that are used to cure acrylic gel in the nail polish process have similar properties to UV suntans that which most emit UV-A radia- tion (14). The UV exposure that accompanies the nail curing process has the potential of susceptible damage to the skin’s epidermis, which can be caused by UV rays. Thereby, the DNA cells called “P53” that inhibit the occurrence of apoptosis or mutation of DNA cells can lose their function. This means the possibility of causing skin cancer (15). UV exposure is known to be a severe risk factor for skin cancers such as cutaneous melanoma and nonmelanoma (16). The emotional conversation between the customer and the nail art practitioner was the impetus for the development of the nail art industry rather than technical advancement. If any error is found in the fi nal product in the fi eld, it can be immediately corrected, and it could lead to emotional satisfaction, which cannot be quantifi ed. It has evolved to
Purchased for the exclusive use of nofirst nolast (unknown) From: SCC Media Library & Resource Center (library.scconline.org)