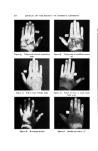
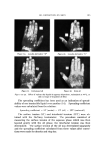
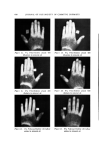
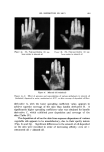
J. Soc. Cosmetic Chemists, 17, 575-579 (1966) Cosmetic Uses of a Antifungal Agent Ncw Synthetic F. GIALDI, PROF. ORD.,* A. BARUFFINI, PROF. INC.,* R. PONCI, PROF. $TRAORD.,'• and P. CACCIALANZA, PROF. ORD.$ Synopsis--It is shown that 2,2-dithiobis (N-butylbenzamide) is an effective topical anti- fungal agent for therapeutic, prophylactic, and cosmetic use. The results of clinical tests with cosmetic products containing this agent are detailed. INTRODUCTION For several years, studies have been carried out toward the syn- thesis of antifungal agents related to aromatic sulfides (1, 2). Among the new substances synthesized, 2,2-dithiobis [N-butylbenzamide] (OD- 507) has been found to be particularly interesting: This substance possesses high antifungal activity and is also active against some bacteria. Table 12 gives some data on minimum inhibitory concentrations of this compound. Comparative microbiological tests have demonstrated that OD-507 possesses activity equal or superior to that of the best known natural or synthetic antifungal agents (2). Pharmacological studies on the toxicity of OD-507 have revealed that this substance is very wall tolerated (3). Furthermore, a series of * Institute of Pharmaceutical Chemistry, Pavia University, Italy. t Institute of Pharmaceutical Chemistry, Parma University, Italy. ++ Dermatological Clinic, Perugia University, Italy. 575
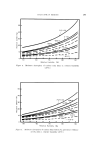
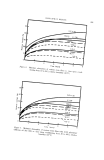
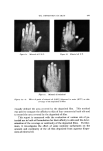
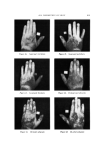
576 JOURNAL OF THE SOCIETY OF COSMETIC CHEMISTS Table I Minimum inhibitory Concentrations MIC M icroorgan ism (mcg./ml. ) Trichophyton mentagrophytes (ATCC 8757) Trichophyton xnentagrophytes (ATCC 9129) Epider•nophyton floccosum (ATCC 10227) Microsporum audouini (ATCC 9079) Microsporum gypscum (ATCC 11658) Microsporum canis (ATCC 10214) Candida albicans (ATCC 10231) Candida albieans (LCP) Candida tropicalis (ATCC 1369) Saccharomyces cerevisiae (ATCC 9763) Saccharomyces carlsbergensis (ATCC 9080) Kloeckera brevis (ATCC 977) Cryptococcus neoformans (SKF 1110) Nocardia asteroides (CBS) Staphylococcus aureus (ATCC 6,538) Streptococcus pyogenes (C-203) Streptococcus faecalis (ATCC 10541) Bacillus subtilis (ATCC 6633) Pseudomonas aeruginosa (ATCC 10145) Mycobacterium tuberculosis (H 37 RV) _ 1 1 2 5 5 2 10 5 1 10 0.5 2 5 2 1 5 2 20 1 experimental "patch tests" and "scratch tests" in humans indicated no irritation or sensitization reactions by this substance. In view of all these facts, the utility of OD-507 as an antifungal medication for dermatological use was studied in a preliminary clinical trial, and the results obtained have been reported (2). The substance has proved to be generally well tolerated both by healthy human skin and in areas of epidermomycotic lesions. The antifungal activity of OD-507 tested in various types of epidermomycotic infections (inguinal epidermophytosis, erythrasma, athlete's foot, etc.) has been found to be extensive and efficient, superior or comparable to that of the best-known modern therapeutic antifungal preparations. PURPOSE OF STUDY All the results of studies so far performed emphasize the fact that OD-507 is both highly active and always well tolerated. In fact, the rare cases of intolerances noted in the earlier clinical experiments (2) have turned out to be related to the composition of the vehicle, not to the active antifungal agent. The study of OD-507 has now been ex- tended to the cosmetic field. The basic requirement for the application of an active substance in cosmetics is its tolerance over prolonged periods
Purchased for the exclusive use of nofirst nolast (unknown) From: SCC Media Library & Resource Center (library.scconline.org)