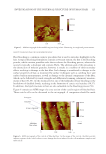
BURKHOLDERIA CEPACIA COMPLEX IN PERSONAL CARE PRODUCTS 141 Figure 1. Phylogenetic tree of the B. cepacia complex based on the complete recA gene sequence. Bootstrap values are shown on each horizontal limb of the tree. The tree was rooted with the B. xenovorans strain TCo-26 recA gene as a representative member of a species outside the Bcc group. Different symbols represent different ST types: : ST621 : novel ST : ST922 : ST336 : ST482 : ST339 : ST258.
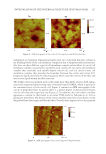
JOURNAL OF COSMETIC SCIENCE 142 protocol involved performing MIC/MBC testing in 2-fold dilutions, and the MIC and MBC values were highly reproducible across three separate experiments, as indicated by low standard deviations. Growth curves were also performed in this study to determine the su sceptibility of all Bcc in the presence of three preservatives (DMDMH, MIT/cMIT, and MH). Part of the growth curves of four different types of Bcc and the standard strain are shown in Figure 3. When the concentration of MIT/cMIT was 0.00015625% and 0.003125%, the B. cepacia ATCC 25416 could grow well except for 0.005%, other low concentrations of MIT/cMIT could not inhibit the growth of BC12 (B. cenocepacia) the MIT/cMIT MIC to BC12 was 8-fold greater than it to B. cepacia ATCC 25416. For BC05 (B. cepacia), the MIT/cMIT MIC was 0.0025%. For BC16 (B. lata) and BC04 (B. contaminans), the OD600 values of the wells were unchanged, except for the positive control wells after 16 h of incubation. When cultured to 24 h, MIT concentration of 0.0003125% and 0.00015625% could not in- hibit the growth of BC16, and 0.00015625% MIT could not prevent the reproduction of BC24. Overall, the MBC values for three preservatives were higher than or equal to those of MIC for all strains, and MBC dilutions at 1/100e were higher than or equal to that dilution at 1/10e. For DMDMH and MH, the maximum permitted concentrations according to the safety specifi cation of cosmetics (0.6% and 0.4%) were able to inhibit or kill all strains. Regarding the MIT/cMIT, the MIC values for 10 strains (BC09-13, BC18, and BC20- 23), belonging to B. cenocepacia (ST621) and B. lata (ST336), were higher than the maxi- mum permitted concentrations (0.0015%) the MBC values even reached 0.005% or 0.01% (Table V) and these Bcc strains were mainly isolated from cosmetics containing the preservatives of MIT/cMIT. DISCUSSION Bcc members consist of multiple closely related species that are ub iquitous in nature. Phenotypic variation can occur in all Bcc species, even within sequential clinical isolates of the same strain (41). There have also been reports of morphological differences based Figure 2. Morphological differences of Bcc bacteria grown on TSA.
Purchased for the exclusive use of nofirst nolast (unknown) From: SCC Media Library & Resource Center (library.scconline.org)