DIFFUSION OF PRESERVATIVES 247 20 15 methyl- ethyl- -p- hydroxybenzoate propyl- Figure 3. Comparative effect of different formulations on the in vitro diffusion of preservatives. Histograms represent the mean values (n = 6) + SD of log J,. Filled pattern: water-in-oil emulsion. Left diagonal lines pattern: oil-in-water emulsion. Criss-cross lines pattern: Pemulen gel. Right diagonal lines pattern: Car- bopol gel. alkyl acrylate (Pemulen) resin. The scarce attraction of Carbopol gel to parabens can suggest the use of acrylates/C10-30 alkyl acrylate crosspolymers (for instance carbomer 1342) instead of the carboxy vinyl polymer in order to produce well-preserved topical formulations, able to hold onto parabens. Different considerations should be made in the case of the emulsions that, being two- phase systems, can dissolve parabens part in the oil and part in the aqueous phases. In this regard, the water phase concentrations of parabens in the different emulsions were determined by HPLC analysis. It was found that the aqueous phase concentrations of parabens in the W/O emulsion were 2.54, 1.12, and 0.6 mg/ml for MP, EP, and PP, respectively, while in the aqueous phase of the O/W emulsion, paraben concentrations were 2.6, 1.08, and 0.48 for MP, EP, and PP, respectively. The trend of paraben diffusion On MP Jn EP Jn PP, Table III) is in agreement with the water solubility of parabens, both in the W/O and O/W emulsions. Considering diffusion of the different parabens, in the case of MP, Jn is higher in the O/W emulsion in comparison to the W/O emulsion (9.74 versus 6.96 cm/h x 103), probably because in the O/W emulsion, MP is mostly dissolved in the external aqueous phase and its diffusion in the receiving medium is faster. On the contrary, in the case of the more lipophilic EP and PP, Jn values are lower in the O/W emulsion (2.8 and 0.74 cm/h x 103 for EP and PP, respectively) in comparison to the W/O emulsion (6.74 and 2.16 cm/h x 103 for EP and PP, respectively). This trend can be related to the low solubilities in water of these parabens, mostly dissolved in the internal disperse phase of the O/W emulsion or in the continuous oil phase of the W/O emulsion. The different partition of parabens in the phases of the two emulsions can account for differences in J• values. In addition, one should consider the different compositions of the oil phases. In the O/W
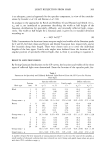
248 JOURNAL OF COSMETIC SCIENCE emulsion, capric/caprilic triglyceride can dissolve EP and PP better than petrolatum present in the oil phase of the W/O emulsion. The EP and PP attraction to the oil phase of the O/W emulsion can justify their lower diffusion coefficients with respect to the W/O emulsion. These last considerations suggest that the lipophilic components of the matrix could represent a mean to hold on to parabens, promoting their preservative action in the formulation. As an appendix to Table III, Table IIIa reports the results of a statistical analysis based on a paired t-test performed to compare the Jn of parabens for the different formulations. The results obtained with different formulations were significantly different (being Table IIIa Statistical Analysis (paired t-test) of the J,• Values of Parabens Incorporated in the Different Formulations Reported in Table III Aqueous W/O O/W Carbopol Pemulen Methylparaben solution emulsion emulsion gel gel Aqueous solution -- t = 45.42 t = 43.92 t = 39.3 p 0.0001 p 0.0001 p 0.0001 W/O emulsion t = 45.40 -- t = 9.55 t = 3.37 p 0.0001 p = 0.0002 p = 0.0198 O/W emulsion t = 43.90 t = 9.55 t = 13.11 p 0.0001 p = 0.0002 p 0.0001 Carbopol gel t = 39.30 t = 3.37 t = 13.11 -- p 0.0001 p = 0.0198 p 0.0001 Pemulen gel t = 54.58 t = 22.5 t = 73.55 t = 60.16 p 0.0001 p 0.0001 p 0.0001 p 0.0001 54.58 0.0001 22.50 0.0001 73.55 0.0001 60.16 0.0001 Ethylparaben Aqueous W/O O/W Carbopol Pemulen solution emulsion emulsion gel gel Aqueous solution -- t = 2.46.57 t = 119.30 t = 271.68 p 0.0001 p 0.0001 p 0.0001 W/O emulsion t = 246.57 -- t = 26.93 t = 297.87 p 0.0001 p 0.0001 p 0.0001 O/W emulsion t = 119.30 t = 26.93 t = 1.78 p 0.0001 p 0.0001 n.s. Carbopol gel t = 271.68 t = 297.87 t = 1.78 p 0.0001 p 0.0001 n.s. Pemulen gel t = 51.53 t = 66.15 t = 142.91 t = 101.46 p 0.0001 p = 0.0001 p 0.0001 p 0.0001 51.53 0.0001 66.15 0.0001 142.91 0.0001 101.46 0.0001 -- Propylparaben Aqueous W/O O/W Carbopol Pemulen solution emulsion emulsion gel gel Aqueous solution -- t = 8.81 t = 104.67 t = 13.24 p 0.0001 p 0.0001 p 0.0001 W/O emulsion t = 8,81 -- t = 7.37 t = 47.27 p 0.0001 p 0.0001 p 0.0001 O/W emulsion t = 104.67 t = 7.37 -- t = 50.76 p 0.0001 p 0.0001 p 0.0001 Carbopol gel t = 13.24 t = 47.27 t = 50.76 -- p 0.0001 p 0.0001 p 0.0001 Pemulen gel t = 105.61 t = 2.83 t = 10.23 t = 50.88 p 0.0001 p = 0.0178 p 0.0001 p 0.0001 105.61 0.0001 2.83 0.0001 10.23 0.0001 50.88 0.0001 --
Purchased for the exclusive use of nofirst nolast (unknown) From: SCC Media Library & Resource Center (library.scconline.org)