USE OF DEOFIX TM IN DEODORANT PRODUCTS 253 their standard protocol for evaluating deodorancy (9). A round-robin study was per- formed in which Deofix TM and Triclosan were each compared to a placebo treatment and also compared directly to each other. The normal use concentration for Triclosan in underarm deodorants is 0.15-0.30% (3). To represent the high end of the normal use concentration, 0.3% was chosen for testing. Based on preliminary uncontrolled labora- tory studies, 1.0% Deofix TM was chosen for testing (economic considerations did not allow for a more rigorous clinical dose-response study). Deofix TM was applied as a 1% solution in 50% ethanol/water. Since Deofix TM solutions are very acidic (it is a triphosphonic acid), the solution was adjusted to pH 5.5 with NaOH to avoid irritation. Triclosan was applied as a 0.3% solution in 50% ethanol/ water, and the placebo treatment was 50% ethanol/water. Axillary malodor evaluations were performed at 8, 12, 24, and 48 hours after the third daily application of the materials. Panel sizes consisted of 15 subjects on each panel. Summaries of the results are presented in Figures 2, 3, and 4. Results show that: 1. Deofix TM (1%) was found to be significantly better than the placebo treatment at reducing axillary malodor at 8, 12, 24, and 48 hours after the third day of application. (Figure 2). 2. Deofix TM (1%) was found to be directionally better than Triclosan (0.3%) at all measurement times and significantly better than Triclosan at reducing axillary malodor at 8 and 24 hours after the third day of application. (Figure 3). 3. The magnitude of axillary malodor difference between Deofix TM and the placebo- treated axilla became greater with time over the 48 hours of the study. This difference was greater than that observed in the Triclosan-treated axilla vs the placebo-treated axilla. These results indicate that the Deofix TM treatment is more effective than Triclosan treatment over 48 hours. (Figures 2, 4). ANTIMICROBIAL STUDIES The ability of Deofix TM to inhibit microbial growth by measuring minimum inhibitory concentrations (MIC) varies according to the microbial growth media employed. In large part this is related to the content and nature of first transition series elements contained in the growth media. Media containing large quantities of first transition series elements show evidence of "interference" with the activity of Deofix TM. Typical growth media used in our experiments were RPMI, 10% Muller-Hinton in RPMI, and 2% brain heart infusion in RPMI. Representative MICs for Deofix TM against a gram-positive organism, Staphylococc•s a•re•s, were in the range of 31-250 lag/ml for a gram-negative organism, Eschericchia co/i, the MIC range was 31-500 lag/ml and for a yeast, Candida albicans, the MIC range was 1-15 pg/ml. The Deofix TM chelator complex with Fe(III) showed essentially no antimicrobial properties. These observations are consistent with the mode of action of Deofix TM in lowering the concentration of first transition series elements to levels below that which is essential for microbial replication. A high concentration of any of these elements in a growth media would correspondingly require high concentrations of the chelator to complex with them.
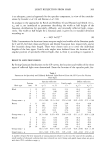
254 JOURNAL OF COSMETIC SCIENCE 6.2 6.43 6.23 5• • 5.05 5.18 Baseline 8 hrs 12 hrs 24 hrs 48 hrs [] 1% Deofix ß Placebo Control Baseline 8 Hours 12 Hours Deofix TM Control Deofix TM Control Deofix TM Control Mean Odor Score 6.2 6.43 4.58 5.05 4.77 5.4 Mean Sample Diff. +Cl • -- 0.47 + 0.37 0.63 + 0.44 Signed Rank p-value: -- 0.0122 2 0.0083 2 Estimates % Differences -- 9.24% 11.73% Panel Size 15 15 15 24 Hours 48 Hours Deofix TM Control Deofix TM Control Mean Odor Score 4.6 5.53 5.18 6.23 Mean Sample Diff. +Cl • 0.93 + 0.67 1.05 + 0.67 Signed Rank p-value: 0.0075 2 0.0079 2 Estimates % Differences 16.87% 16.84% Panel Size 15 15 Analysis of Variance Results Treatment Effect D.0010 3 Interaction D. 1841 Overall Treatment Means Deofix TM - 4.78 Control - 5.55 • - 95% Confidence Intervals 2 _ Significant Difference Favoring Deofix TM (Signed Rank Test) 3 _ Significant Overall Difference Favoring Deofix TM (Analysis of Variance) Figure 2. Comparison of malodor scores (1% Deofix TM vs placebo control). ANTIOXIDANT ACTIVITY The antioxidant activity of Deofix TM was determined by measuring its effect on the coupled oxidation of carotene with linoleic acid, using the method of Marco (10) with minor modifications. Approximately 0.1 mg of beta-carotene was dissolved in 10 ml of chloroform. Two tenths of a milliliter of the carotene-chloroform solution was pipetted into a boiling flask that contained 20 mg of purified linoleic acid and 200 mg of Tween-40. After removal of the chloroform with N2, 50 ml of double-distilled water was added to the flask with vigorous swirling. Five-milliliter aliquots of this emulsion were
Purchased for the exclusive use of nofirst nolast (unknown) From: SCC Media Library & Resource Center (library.scconline.org)