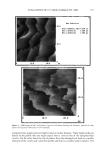
256 JOURNAL OF COSMETIC SCIENCE •5 .•4 •2 6.33 6.23 5.92 6.13 Baseline 8 hrs 12 hrs 24 hrs 48 hrs [] 0.3% Tdclosan ß Placebo Control Baseline 8 Hours 12 Hours Triclosan Control Triclosan Control Triclosan Control Mean Odor Score 6.33 6,23 5.18 5.43 5.37 5.67 Mean Sample Diff. +CI • --- 0,25 + 0.46 0.30 + 0.54 Signed Rank p-value: -- 0.2797 2 0.3513 2 Estimates % Differences --- 4.60% 5,29% Panel Size 15 15 15 24 Hours 48 Hours Triclosan Control Triclosan Control Mean Odor Score 5.52 5.92 6.13 6.45 Mean Sample Diff. +CI • 0.40 + 0.42 0.32 + 0.55 Signed Rank p-value: 0.0706 2 0.3265 2 Estimates % Differences 6.76% 4.91% Panel Size 15 15 , , Analysis of Variance Results Treatment Effect 0.1276 2 Interaction 0.5000 3 Overall Treatment Means ,Triclosan-5.55 Control-5.87 • - 95% Confidence Intervals • - No Significant Difference Between Treatments 3 _ No Significant Interaction of Treatment and Time Figure 4. Comparison of malodor scores (0.3% Triclosan vs placebo control). Deofix TM were related to its acting as an electron donor as do classical antioxidants. Mea- surements were made over the pH range of 3-10 (12). In a typical experiment, a potassium ion-free pH 7 buffer was prepared with 29 ml of 0.1 M NaOH and 50 ml of 0.1 M sodium dihydrogen phosphate. To this buffer was added 0.1 M NaC1 to insure high electrolyte conductivity. Deofix TM was added to a 4-mM concentration. A platinum electrode was used in the cyclic voltametry measurements. The results are presented in Figure 6. As seen in Figure 6, Deofix TM at a 4-mM concentration is electrochemically inactive at pH 7. At the potential scanned of 0.2 to 0.6 V versus Ag/AgCI, no activity is seen other
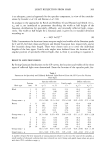
USE OF DEOFIX TM IN DEODORANT PRODUCTS 257 O,8OO 0.800, ...... 20 4O 60 80 100 120 140 '-•--BHA Control '-•'- Deofix TM --•--Ethanol Control Time (min) Figure 5. The antioxidant activity of Deofix TM and BHA were compared to an alcohol control by measuring their effect on the coupled oxidation of carotene with linoleic acid. Decrease in the 470-nm absorption indicates a coupled oxidation is occurring between carotene and linoleic acid. 2.0 1.5 1.0 0.5 o.o -o,5 -1.o - !.o I , I , I . I ' ,I 0.2 0.3 0.4 0.5 0.6 Potential vs AgtAgCI, V Figure 6. Cyclic voltametry of DeofixTM in pH 7 buffer. than baseline response. Similar results were observed for the other pHs (pH 3-10). The results indicate that Deofix TM is not an active oxidant or reductant and that the mecha- nism of action for the antioxidant effect observed above is not related to its ease of oxidation as with classical antioxidants. SAFETY DATA The cytotoxity of Deofix TM is very low. Testing in the National Cancer Institute's revised anticancer screen (13) against neoplastic cell lines at five concentrations of ten- fold dilution was performed. A 48-hour continuous exposure protocol was used, and a sulforhodamine B (SRB) protein assay was used to estimate cell viability or growth. The
Purchased for the exclusive use of nofirst nolast (unknown) From: SCC Media Library & Resource Center (library.scconline.org)