JOURNAL OF COSMETIC SCIENCE 322 spectrometry(HPLC-MS) (12), gas chromatography (GC) (13), gas chromatography-mass spectrometry (GC-MS) (14–16), capillary electrophoresis (CE) (17), and micellar electroki- netic chromatography (MEKC) (18,19). Usually, GC and CE have better separation ability than HPLC. However, GC has some restrictions for the determination of hydrophilic sub- stances in hair dyes due to their high polarity and low volatility, and CE is not suitable for quantitative determination because of low reproducibility. Therefore, only HPLC is the most convenient method for the determination of hair dye intermediates, which has high polarity, low volatility, and thermostability. Several studies contribute to improving the amount of oxidative hair dyes analyzed in a single HPLC run by optimizing the separation parameters (7–10) or prolonging the analysis time (11). Up to now, the best result achieved (11) is the separation of 22 oxidative hair dyes in 50 min. Usually, a HPLC runs less than 30 min and allows the simultaneous determination of two to eight oxidative hair dyes (7–10). Therefore, the aim of this work was to develop a reliable HPLC method to analyze the most commonly used hair dye intermediates, such as benzenediamines, aminophenols, benzenediols, naphthalenediol, and diaminopyridine, with less time. EXPERIMENTAL CHEMICALS AND REAGENTS Hydroquinone (99.5%), resorcinol (99.5%), p-aminophenol (99.0%), and phenol (99.5%) were purchased from Dr. Ehrenstorfer GmbH (Augsburg, Germany) o-phenylenediamine (99.5%), 1,5-naphthalenediol (99%), and 3,4-diaminetoluene (99.8%) from ChemService (West Chester, PA) N,N-diethyl-p-phenylenediamine sulfate (97%) from IL (South San Francisco, CA) m-aminophenol (99%), 4-methylaminophenol sulfate (99%), p-phenylenediamine (99%), 2,5-diaminotoluene sulfate (99%), and 2,6-diaminopyridine (98%) from ACROS (Geel, Belgium) 1-octanesulfonic acid sodium salt monohydrate (97%) from J&KCHEMICA (Beijing, China). Water (Milli-Q Purifi cation System, Millipore (Billerica, MA)), acetonitrile, and ethanol were of HPLC grade. Sodium dithionite and sodium sulfi te were of AR grade. Standard stock solutions of 13 dye intermediates each at a concentration of 2500 μg/ml was prepared in 50% (v/v) ethanol solution containing 0.1% sodium sulfi te in brown bottles, and stored at −10°C. A calibration curve was prepared by injecting eight diluted solutions, obtained from the stock solution, in the concentration range of 2–500 μg/ml. APPARATUS HPLC system was composed of a Waters 2695 pump equipped with a liquid autosam- pler, and a Waters 2996 diode array detector. Analysis was performed at 30°C on a ZORBAX SB-Aq C18 column (5 μm, 250 × 4.6 mm I.D., Agilent (Santa Clara, CA)) with a same packing precolumn (5 × 4.6 mm I.D.) through a gradient elution. The fl ow rate was 1.0 ml/min. Eluent A was a buffer solution (pH 2.6) containing 10 mmol/l citric acid and 10 mmol/l sodium 1-octanesulfonate. Eluent B was acetonitrile. Time program: 0–5 min, B 12% 5.01–15 min, B 12–20% 15.01–24 min, B 12%. Injection volume: 5 μl. Detection was performed by scanning from 190 to 400 nm. Quantitation was performed at 331 nm for 2,6-diaminopyridine and at 280 nm for all the other dye intermediates.
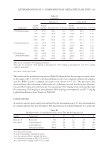
DETERMINATION OF 13 COMPONENTS IN OXIDATIVE HAIR DYES 323 SAMPLE PREPARATION About a 1.0 g sample was weighed and placed in a 25 ml calibrated fl ask, then 1 ml 1% sodium dithionite and 15 ml 50% (v/v) ethanol were added. The mixture was homoge- nized adequately by stirring before 15 min of the ultrasonic extraction process. Then the solution was diluted to volume with 50% (v/v) ethanol. About 1 ml aliquot of this solu- tion was fi ltered through a 0.45 μm membrane fi lter and ready for HPLC analysis. VALIDATION To evaluate the accuracy and precision of the method, standard recovery test was perfor med on real sample A (containing 536.6 mg/kg resorcinol) and sample B (con- taining 3528 mg/kg m-aminophenol, 6618 mg/kg p-aminophenol, and 8727 mg/kg p-phenylenediamine), with four addition levels of 1 time, 2 times, 10 times, and 20 or 100 times the LOQ (limit of quantifi cation) of target compounds. The method was also validated by fi ve different laboratories with real sample determination and standard recovery test. Figure 1. Chromatogram of dye intermediates at (a) 280 nm and (b) 331 nm. 1. Hydroquinone 2. resor- cinol 3. p-aminophenol 4. phenol 5. m-aminophenol 6. 4-methylaminophenol 7. o-phenylenediamine 8. p-phenylenediamine 9. 2,5-diaminotoluene 10. 1,5-naphthalenediol 11. 3,4-diaminetoluene 12. N,N-diethyl-p-phenylenediamine 13. 2,6-diaminopyridine.
Purchased for the exclusive use of nofirst nolast (unknown) From: SCC Media Library & Resource Center (library.scconline.org)