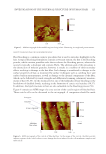
JOURNAL OF COSMETIC SCIENCE 170 area can be accurate and consistent. This settling ratio is close to 1 when the projected weight is the same as the ideal weight (Figure 1A), and it decreases (Figure 1B) with the theta value. The dispensing pigments contain color and solidifi ers that harden under UV light, and it is observed that the density increases as the particle size is reduced to nanoscale (21). MATERI A LS AND EQUIPMENT An oil -based UV-curable ink was used in this study (Hongkong Liyu Technology Co., Ltd., Shenzhen, China). The mo nomers in the UV ink produce a building block of the ink and can devote a spe- cifi c property such as hardness of the ink when it cured, as well as fl exibility or elongation characteristics of the ink. And pigments are smaller than 200 nm in size to prevent agglomeration and the possibility of hindering the nozzle. The colorants of UV ink that applied in the experiment were yellow, red, black, white, and blue. The amount of ink used at a time for 10 tips is less than 10 mL, and it takes less than 10 min from order to output. UV light emitting diode has been designed to adjust the height of the product, which emits light at 3W intensity and cures the product of 5 μm height up to 1,000 μm. To obtain 4,000 DPI, the Epson head L805 model was used. (L805 Epson, Carson, CA) Nail tips used in this study are made of both acrylonitrile butadiene styrene (ABS) and acrylic-based material, and the basic colors are natural, clear, and white. The nail tips used in the experiment were clear and white. There are 10 different tip sizes ranging from 0 to 9, and seven types were used in this experiment. (size 2: 0.46 × 1.15 size 3: 0.44 × 1.07 size 4: 0.41 × 1.05 size 5: 0.41 × 1.03 size 6: 0.37 × 0.99 size 7: 0.34 × 0.97 and size 8: 0.31 × 0.91). It is observed that an image printed from an inkjet printer had a signifi cant impact on the printing modulation transfer function of the ink image, depending on the type of paper on the substrate (22). Thus, there have been studies to Figure 1. Different values of theta on the nail tip from the printer head.
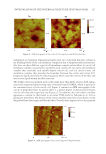
CONFORMAL PROJECTION PRINTING METHOD FOR 3D NAIL ART PRINTING 171 solve the problem that these factors can infl uence the print result by using various methods such as measuring the horizontality of output and the bed, including surface tension (23). As the degree of curvature of the conformal surface varied according to the nail tip size, the different injection frequencies were simulated and empirically tested with three zones that, according to the incidence angle (theta), range on the nonhorizontal plane. To minimize the infl uence of such external conditions and to increase precision, a laser treatment process was incorporated that precisely removes the hydrophilic or hydrophobic coating of the output, preventing the spread and diffusion of the ink on the surface. It is reported that the equipment used in this study can be operated at 3W through which the energy consumption is reduced by less than 1/10 times when compared with existing UV lamps (24). The equipment used in the experiment is an A4 UV printer (A4 UV printer Taicang Vevor Machinery Equipment Co., Taicang, China) that outputs only by XYZ movement without rotation axis, and the method of stacking is 2D–2.5D layers on the plane. Figure 2 shows the overall schematic of the mechanical processing of an order for printing. The concept of nail printing and its material chain verifi cation experiment is explained in Figure 2D–F. By combining IoT system and AI, the operator selects the design remotely and the customer can choose by using a system that separates the space between the customer and the operator (Figure 2A). Once the data to be printed are delivered to the Raspberry Pi, which is the central processing unit for processing information (Figure 2B), ink is dispensed through the print head (Figure 2C). The surface was etched with a 3W precision laser (Figure 2D) for surface modifi cation, and repeated printing (Figure 2E) is Figure 2. Basic concept of nail printing and the fl ow of material chain.
Purchased for the exclusive use of nofirst nolast (unknown) From: SCC Media Library & Resource Center (library.scconline.org)