134 JOURNAL OF COSMETIC SCIENCE
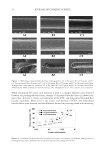
Figure 2. DTA curves of AVB and its binary mixtures 1:1 (m/m) with lipid-based excipients: (A) solid
lipids, (B) liquid lipids, and (C) surfactants. Samples were analyzed under nitrogen atmosphere (50 mL/min−1),
heating rate of 10°C/min−1, and temperature range of 25–500°C.
Figure 2. DTA curves of AVB and its binary mixtures 1:1 (m/m) with lipid-based excipients: (A) solid
lipids, (B) liquid lipids, and (C) surfactants. Samples were analyzed under nitrogen atmosphere (50 mL/min−1),
heating rate of 10°C/min−1, and temperature range of 25–500°C.