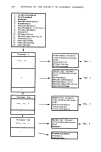
294 JOURNAL OF THE SOCIETY OF COSMETIC CHEMISTS Table II Agar Plate Screening Test of Antimicrobial Activity of N-fi-D-Glycosyl-5-ylidene Rhodanines O ROCH2 [ • C--C•CH--Ar .4•0 N / OR Compounds tested Ar R Organisms tested S. aureus E. coli P. aeruginosa C. albicans A. niger --• H OCH 3 --•OH H OC2H 5 -•)-OH H -•C1 H C1 CI I-•Br I• OCH• -•OH Acetyl O%H5 •OH Acetyl Rhodanine ++ -- _ + + +++ +++ +++ +++ +++ + + + Very active + + moderately active + slightly active - no activity. was disregarded, whereas a large cluster or growth or definite turbidity was considered evidence that the compound had failed to inhibit growth completely at that concentration (26). The minimal inhibitory concentrations for the compounds tested are shown in Table III. ACUTE TOXICITY DETERMINATIONS Compounds II, V, VIII, and IX were dissolved or suspended in normal saline and administered intraperitoneally to 20-25 g Charles River CD-1 male mice. Three mice
ANTIMICROBIAL ACTIVITY OF N-GLUCOSYLRHODANINES 295 Table III Minimal Inhibitory Concentrations of Compounds Tested by the Broth Dilution Method O HO--• S HO• C--C=CH--Ar •t•O $ / I o ! HO O• H OH OH No. M.I.C. (btg/ml) Compounds tested $. E. P. C. A. R or Ar aureus coli aeruginosa albicans niger I --N(CH3)2 2,633 II --NH(CH2)3CH3 333 33 333 III --NHCH2-•OCH 3 3,584 358 3,584 IV --NHCH2CH2- • 342 V --NHCH20 3,864 3,864 VI --NHCH2CH•H2 28 VII --NHN(CH3) 2 2,813 2,813 VIII --N•/---• 3,064 306 IX --NH2 24 238 2,383 X -• 383 XI -•C1 418 C1 XII -• 453 453 4,53 C1 XIII Rhodanine 133 133 133 133 1,332 were used for each compound, two animals receiving a dose of 1000 mg/kg and one animal receiving 2000 mg/kg. The mice were observed periodically for a week, at which time all animals appeared normal (34). RESULTS AND CONCLUSIONS A number of the compounds (Table III) showed inhibitory activities against $taphylo- coccus aureus N-/5-D-glucopyranosyl-N'-allylthiourea (VI) and N-/5-D-glucopyranosyl- thiourea (IX) proved to be the most active. All of the glycopyranosylthioureas which exhibited inhibitory activities were derivatives of primary amines except compounds I and VIII. This indicates that N', N'-disubstituted thioureas will in general show decreased antimicrobial activities.
Purchased for the exclusive use of nofirst nolast (unknown) From: SCC Media Library & Resource Center (library.scconline.org)