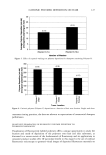
96 JOURNAL OF COSMETIC SCIENCE • 20 --D-B 10 ........................ 0 10 20 30 40 50 Days Figure 5. Sun exposure: evolution of the stratum corneum thickness following one-week sun exposure in subjects A and B. anticipated since the Raleigh-limit formula predicts better resolution for shorter wave- lengths. Nevertheless, other technical features could also be responsible for the unprec- edented quality of the images. The use of a coherent light instead of white light can be considered, even though it has already been demonstrated that the laser source used generates side lobe effects (14) that may degrade resolution. This effect is not encoun- tered with incoherent white light sources. The rather unusual high numerical aperture .. .... ... ...•. ß . ... Figure 6. Sun exposure: condensation of the chromatin. (a) Presence of bright inclusions in numerous nuclei of granular and spinous keratinocytes subject B, T20. Image size: 168 x 168 pro. (b) Zoomed image of four nuclei showing several bright inclusions in each subject B, T12. Image size: 42 x 42 pm.
IN VIVO CONFOCAL MICROSCOPY 97 Figure 7. Sun exposure: migration of melanosomes. Two pictures showing the presence of bright spotted filaments in the intercellular spaces of the epidermal spinous layers. (a) Upper layers. (b) Lower layers. Subject B, T12. Image size: 168 x 168 pm. of 1.30 for a x40 objective lens certainly plays a role in increasing the axial and lateral resolution. Other lenses have been tested, in particular infinity-corrected objectives that introduced unexpected and unfortunate back reflections. Even though the laser power was limited to 2 mW at the objective lens, it provided a much larger light budget than the 1% of the light transmitted by the Nipkow disk of the TSM. There were also improvements made in the design of the contact stabilization device. By providing the axial displacement of the objective lens with a long-stroke piezoelectric translator with 0.1-pro precision, as opposed to moving the contact tip with a stepping motor of 1-pro step, a gain in precision was added to a gain in stability at the fixed skin surface. The Figure 8. Sun exposure: the lack of melanosome caps. (a) Before exposure, basal cells exhibit bright melanosome clusters. (b) After exposure, bright caps are almost missing a few are indicated by the white arrow. Subject B, T20. Image size: 168 x 168 pro.
Purchased for the exclusive use of nofirst nolast (unknown) From: SCC Media Library & Resource Center (library.scconline.org)