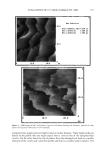
236 JOURNAL OF COSMETIC SCIENCE 1121.001 0 103 I I•1 -1 I-I I•'1 c D Figure 5. Production of nitric oxide by UV-irradiated human dermal fibroblasts. The intracellular NO was measured using NO sensor dye and fluorescence-activated cell sorter. Black line: without UV irradiation. White line: with UV irradiation. A: control. B: 10 J/cm 2. C: 20 J/cm 2. D: 30 J/cm 2. various NOS inhibitors in the presence of UV irradiation (30 J/cm2). AG, NAME, NAL, and BAC are NOS inhibitors that inhibit both the constitutive and inducible NOS. The extract of Scutellaria root is plentiful in various iNOS inhibitors including wogonin, baicalin, and baicalein (22). The enhancement of MMP production by UV irradiation was partially but significantly (p 0.05) blocked by iNOS inhibitors such as AG and BAC, but not by NAME and NAL. Figure 6 shows that the enhanced production of MMP-1 or MMP-2 by UV irradiation was downregulated by the addition of AG and BAC. When 20 microM of BAC was added to the culture media, only 40% of MMP-1 and 42% of MMP-2 were produced, compared to the untreated case. These findings suggest that NO affects MMP-1 and -2 production through the cGMP pathway and is an important signal mediator in regulating the production of MMP by UV-irradiated HDF. CONCLUSIONS The effect of NO and iNOS inhibitors on the production of MMP-1 and -2 by UV- irradiated or non-irradiated HDF was studied. The addition of a NO donor, SNP, to the culture medium of HDF enhanced the production of MMP-1 and -2, while the addition of iNOS inhibitors such as AG and BAC downregulated the production of MMP-1 and -2 by UV-irradiated HDF. Although the production of NO by UV-irradiated HDF was not significant statistically, the influence of NO on HDF might not be negligible, considering the NO produced by UV-irradiated keratinocytes. From these results, we
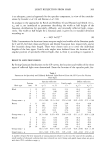
INHIBITION OF MATRIX METALLOPROTEINASES 237 0.7 •0.6 -.0.5 o ,mo. 4 00.3 o 00.2 mO. 1 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 _ ,m•'M•P2::•/ ! B no UV UV AG NAME NAL BAC ESC Figure 6. The effect of various NOS inhibitors on the production of MMP-1 and MMP-2 by UV-irradiated human dermal fibroblasts. (A) Zymography of MMP-2. 1. no UV. 2. UV (30 J/cm2). 3. UV + AG (25 microM). 4. UV + NAME (50 microM). 5. UV + NAL (50 microM). 6. UV + BAC (20 microM). 7. UV + ESC (200 microg). (B) Proteins of MMP-1 and -2. AG: arninoguanidine. NAME: nitro-L-arginine methyl ester. NAL: nitro-L-arginine. BAC: baicalein. ESC: extract of Scutellaria root. *n = 4. p 0.05 vs no treatment. conclude that the production of MMP-1 and -2 by UV-irradiated HDF is regulated through the signaling pathway involving NO and can be downregulated using NOS inhibitors. ACKNOWLEDGMENTS The authors acknowledge the financial support of the Konkuk University Research Foundation made in the 2000 program year. REFERENCES (1) K. Scharffetter, M. Wlaschek, A. Hogg, K. Bolsen, A. Schothorst, G. Goerz, and G. Piewig, UVA irradiation induces collagenase in human derreal fibroblasts in vitro and in vivo, Arch. Dermatol. Res., 283, 509-511 (1991). (2) M.J. Petersen, C. Hansen, and S. Craig, Ultraviolet A irradiation stimulates collagenase production in cultured human fibroblasts, J. Invest. Dermatol., 99, 440-444 (1992).
Purchased for the exclusive use of nofirst nolast (unknown) From: SCC Media Library & Resource Center (library.scconline.org)