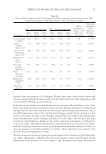
JOURNAL OF COSMETIC SCIENCE 32 in preliminary experiments based on the concentrations of DMSO that are nontoxic for the types of cells used. To prepare the stock solution for cell staining according to the protocol for this assay (7), 5 mg of DAPI was dissolved in 1 ml of dimethylformamide and allowed to stand until the dissolution was complete. For the working solution, 4 μl of the stock solution was added to 50 ml of phosphate buffer solution (PBS) and stored at 4°C, protected from light before the time of staining. METABOLIC ACTIVATION SYSTEM Inclusion of a metabolic activation system in the genotoxicity assay enables the detection of mutagenic activity for carcinogens and/or mutagens that require such transformation (i.e., cyclophosphamide). The metabolic activation system was prepared according to the method described in references (7) and (8). Aroclor-1254-induced rat liver S9 fraction was purchased from Moltox. The following chemicals were added in the order listed to get a total volume of 3 ml of S9 mix: sterile double-distilled H2O (840 μl) sodium phosphate buffer (0.1 M), pH 7.4 (1.5 ml) 4 mM NADP (150 μl) 120 mM glucose-6-phosphate (22 μl) potassium magnesium salt solution, 8 mM–33 mM (60 μl) and rat liver fraction (3.00 μl) to give a fi nal concentration of 10% (v/v). The fi nal concentration of the meta- bolic activator used for each test fl ask was 1% (v/v). In contrast to cyclophosphamide, EMS does not require metabolic activation and therefore the metabolic activation system was not used in the experiments involving EMS. CELL LINE Chinese hamster ovary (CHO-K1) cells were used as recommended in the OECD protocol (3) and were bought from American Type Culture Collection (ATCC, Manassas, VA). Cells were cultured in ATCC-formulated F-12K medium supplemented with 10% fetal bovine serum (Fisher Chemicals, Fairlawn, NJ) and penicillin-streptomycin (100 UI/ ml–100 ug/ml). Cells were grown at 37°C in a humidifi ed atmosphere of 5% CO2 (v/v) in air. All experiments were performed on cells in the exponential growth phase. EXPERIMENTAL SERIES AND CONDITIONS About 300,000 cells were cultured with the media in each 25-cm2 fl ask and held 24 hours before treatment. They were then incubated with the substances as indicated in Figure 1. For the series with metabolic activation, the cells were treated for three hours after which the media were replaced with fresh media and the cells were incubated for 24 hours. For the groups without S9 activation, the cells were incubated for 24 hours. All the cells were harvested at the end of 24 hours and stained to detect the presence of micronuclei. The following series of experiments was carried out: (1) media only (negative control) (2) DMSO (100 μl) (negative control) (3) cyclophosphamide + S9 mix (10 μg/ml) (positive control) (4) ethyl methanesulfonate (400 μg/ml) (positive control) (5) OB (0.2 mg/ml) (6) OB (0.3 mg/ml) (7) OB (0.2 mg/ml) + S9 mix and (8) OB (0.3 mg/ml) + S9 mix.
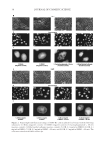
TEST FOR GENOTOXIC POTENTIAL BY MICRONUCLEI ASSAY 33 All the treatment groups were set up as duplicates the determination of cellular toxicity was made in eight independent measurements. After the end of all treatments, the cells were harvested for staining. Cell staining. After 24 hours of incubation with the aforementioned substances, the media from all the fl asks were removed. The cells were fi xed by slowly adding a cold solution of 100% methanol and allowing the mixture to stand for fi ve minutes. The methanol was removed and the cells were washed with phosphate buffer solution two times for two minutes. The cells’ nuclei were then stained with 600 nM DAPI (2 ml) (4,6 diamidino- 2-phenylindole) for eight minutes. This solution was removed and all the fl asks were washed with PBS containing 0.05 % Tween 20 (Sigma Aldrich). The cells were kept moist by adding PBS at the end. The cells were then observed under a microscope. Counting of micronuclei. For each experimental series, the formation of micronuclei was determined as described (9) by counting the number of micronuclei per 1000 cells using light and a fl uorescent microscope (Olympus I×71, New York. Cell viability and proliferation. A modifi ed MTT (3-(4, 5-dimethylthiazol-2-yl)-2,5-diphe- nyltetrazolium bromide) assay was used to assess the cytotoxicity of the studied substances as previously described (10). To measure cytotoxicity, cells were separately incubated in a Figure 1. Scheme of experimental series and conditions. The shaded areas represent the treatment periods with tested substances or media. At the beginning of the experiments, the cells were incubated with media within 24 h. For the series with metabolic activation, the cells were treated for three hours after which the media were replaced with fresh media and the cells were incubated for 24 hours. For the groups without S9 activation, the cells were incubated for 24 hours.
Purchased for the exclusive use of nofirst nolast (unknown) From: SCC Media Library & Resource Center (library.scconline.org)