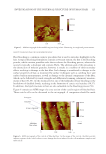
JOURNAL OF COSMETIC SCIENCE 158 P otential shift in the λmax was also studied. Having a shift in λmax could affect UV fi lter’s effi cacy and ability to provide optimal protection to the skin against UV rays. An ingre- dient may be a good booster or photostabilizer, but if it negatively affects the effi cacy of a UV fi lter, it is not recommended to be used. The λmax for homosalate and ethylhexyl salicylate was at 311 nm, and for butyl methoxydibenzoylmethane at 357 nm (29). The UV fi lter blend was expected to have two peaks, one correlating with the UVB fi lters, and the other with the UVA fi lter. Three solvents, including butyloctyl salicylate, ethylhexyl methoxycrylene, and polyester-8 had an absorption peak at 311, 312, and 311 nm, re- spectively. This fi nding is in correlation with the aforementioned results, referring to the inherent UV-absorbing capacity of the solvents. Diethylhexyl 2,6-naphthalate had three main peaks: the highest at 297 nm, the second highest at 350 nm, and the third at 335 nm. Two s olvents shifted the λmax of homosalate signifi cantly (p 0.05) toward shorter wavelengths (hypsochromic shift), including shea butter ethyl esters and diethylhexyl Figure 1. Transmittance spectra. (A) Solvents alone. (B) Homosalate–solvent mixtures. (C) Ethylhexyl sa- licylate–solvent mixtures. (D) Butyl methoxydibenzoylmethane–solvent mixtures. (E) UV fi lter blend–sol- vent mixtures.
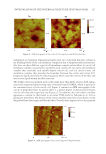
SOLVENT EFFECTS ON SPF AND BROAD-SPECTRUM PROTECTION 159 2,6-naphthalate (Table IV and Figure 2B). The rest of the solvents only caused a minimal shift (1–2 nm) toward either the shorter or longer wavelengths. In the case of ethylhexyl salicylate, shea butter ethyl esters, diethylhexyl 2,6-naphthalate, and tris(PPG-3 benzyl ether) citrate shifted the λmax signifi cantly toward shorter wavelengths (p 0.05, Table IV and Figure 2C), the rest of the solvents did not cause a signifi cant change. The mix- tures of diethylhexyl 2,6-naphthalate and the UVB fi lters had three absorption peaks, similar to diethylhexyl 2,6-naphthalate alone. All solvents except for diisopropyl adipate caused a signifi cant shift in butyl methoxydibenzoylmethane’s λmax (p 0.05) diethyl- hexyl 2,6-naphthalate shifted the λmax toward a shorter wavelength, whereas the rest of the solvents caused a bathochromic shift. Diethylhexyl 2,6-naphthalate, butyloctyl sa- licylate, and polyester-8 caused double peaks for butyl methoxydibenzoylmethane (Table IV and Figure 2D). In the case of the UV fi lter blend, diethylhexyl 2,6-naphthalate caused a signifi cant hypsochromic shift (p 0.05) the rest of the solvents did not cause a signifi cant change in the UVB region (Table IV and Figure 2E). Isopropyl myristate, ethylhexyl methoxycrylene, and polyester-8 did not cause a signifi cant change in the UVA range, whereas the rest of the solvents shifted the λmax (p 0.05) to either a shorter wavelength (diethylhexyl 2,6-naphthalate) or longer wavelength (rest of the solvents). Table III Critical Wavelength (nm) of the UV Filter–Solvent Mixtures INCI name 1:9 Mixture with H 1:9 Mixture with EHS 1:9 Mixture with BMDM 2.3:7.7 Mixture with UV fi lter blend 1 Isododecane 324 357 - - 2 Cyclotetrasiloxane and cyclopentasiloxane 322 354 - - 3 Olea europaea (olive) fruit oil 323 326 382 378 4 C12-15 alkyl benzoate 321 325 382 378 5 Shea butter ethyl esters 322 323 381 377 6 Mineral oil 323 324 7 Helianthus annuus (sunfl ower) seed oil 324 323 - - 8 Isopropyl isostearate 322 322 - - 9 Dimethicone 322 323 - - 10 Heptyl undecylenate 323 322 381 377 11 Isopropyl myristate 322 328 380 376 12 Caprylic/capric triglyceride 322 326 381 377 13 Ethanol 331 330 - - 14 Ricinus communis (castor) oil 325 321 - - 15 Propanediol dicaprylate/caprate 323 323 381 377 16 2-Ethylhexyl palmitate 322 323 - - 17 Diethylhexyl 2,6-naphthalate 353 353 383 377 18 Pentylene glycol 327 319 - - 19 PPG-3 benzyl ether ethylhexanoate 323 324 383 378 20 Tris(PPG-3 benzyl ether) citrate 323 328 384 380 21 Butyloctyl salicylate 330 329 382 377 22 Diisopropyl adipate 322 320 381 377 23 Ethylhexyl methoxycrylene 387 386 387 386 24 Polyester-8 356 356 384 379 H: homosalate, EHS: ethylhexyl salicylate, BMDM: butyl methoxydibenzoylmethane. - refers to solvents in which BMDM was insoluble.
Purchased for the exclusive use of nofirst nolast (unknown) From: SCC Media Library & Resource Center (library.scconline.org)