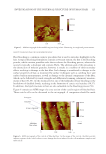
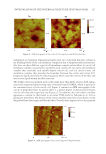
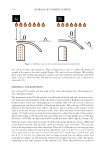
J. Cosmet. Sci., 71, 167–178 (May/June 2020) 167 Conformal Projection Printing Method to Increase the Accuracy of 3D Printed Nails CHAN JOUN PARK, ABHILASH ADITYA, and NAMSOO PETER KIM , Department of Mechanical Engineering, Center for Printable Materials Certifi cate, The University of Texas at El Paso, El Paso, Texas 79968 (C.J.P.), Department of Metallurgical Materials and Biomedical Engineering, Center for Printable Materials Certifi cate, The University of Texas at El Paso, El Paso, Texas 79968 (N.P.K., A.A.) Accepted for publication March 6, 2020. Synopsis Incorporating technologies such as 3D printers and the Internet of things (IoT) can improve the nail art industry by making it more effi cient, and, most importantly, safer. It eliminates the need for physical shops such as nail salons. Nail art by 3D printing technology can achieve higher resolution and accuracy than before with conformal projection printing method (CPPM). The conventional method of painting nails manually leads to acute exposure to ultraviolet (UV) light that can contribute to minor health hazards. This research illustrates the benefi ts of using 3D printing for nail art. This study uses the IoT system, which can be stationed in a distinct location from the customer. The product on the nail is printed at least once and up to three times within 5 μm to achieve precise resolution through laser marking and CPPM, which can increase the accuracy by repeated projection to attain the required settling ratio. The correlation between the numbers of printed layers and different incident angles of the printing head on the conformal surface is discussed. The ratio of projected weight to the ideal weight for high-defi nition printing condition is illustrated, and comparison studies with conventional nail art techniques are conducted to validate the results. I NTRODUCTION The integration of artifi cial intelligence (AI) in the industries of the 21st century increased the effi ciency of existing production and marketing processes. The amalgamation of 3D printers and Internet of things (IoT) systems puts forth the concept of digital manufac- turing (DM), which enables users to enter the relevant information and produce with minimal material input. Such improvement simplifi es the manufacturing processes and reduces the lead time, gaining consumer satisfaction and leading to the fourth industrial revolution (1). DM technology initiated with nano-inks where nanosized particles were dispersed in an aqueous solution through the direct injection method. This technology has drawn attention since 1990, because of not only various convergence technologies but Address all correspondence to Namsoo Peter Kim at nkim@utep.edu.
Purchased for the exclusive use of nofirst nolast (unknown) From: SCC Media Library & Resource Center (library.scconline.org)