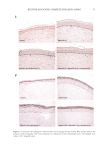
43 HyaluronicALURONIC acid water binding
which is 22,389. Experimental measurements of the number of water molecules bound
per disaccharide repeating unit discussed above gave ca. 14 (±5) waters per disaccharide
repeat unit. The only obvious way water would bind to a carbohydrate polymer is through
hydrogen bonding. However, each hyaluronic acid disaccharide repeating unit has only 12
atoms capable of hydrogen bonding, and each of those can only bind to a maximum of 3
water molecules, for a theoretical maximum of 36 hydrogen-bonded water molecules per
disaccharide. Because the molecular weight of water is 18 and that of the repeating unit
in the HA polymer (N-acetylglucosamine-D-glucuronic acid) is 403, the theoretical mass
ratio for a water-HA hydrogen-bonded complex would be 36 × 18 =648 per 403 amu.
That ratio works out to be 1.61 times the weight of the HA polymer.
While the foregoing seriously compromises the idea that HA binds 1,000 times its weight
in water, there are other synthetic polymers that do bind large amounts of water per unit
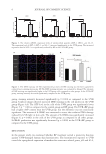
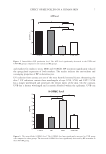
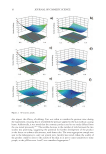
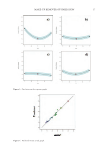
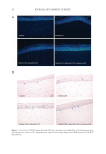
Figure 3. DSC data for 10% solution of glycerol scanned from 20 to −40 to 20°C in triplicate.
Figure 4. DSC data for pure water scanned from 20 to −40 to 150°C (control).
which is 22,389. Experimental measurements of the number of water molecules bound
per disaccharide repeating unit discussed above gave ca. 14 (±5) waters per disaccharide
repeat unit. The only obvious way water would bind to a carbohydrate polymer is through
hydrogen bonding. However, each hyaluronic acid disaccharide repeating unit has only 12
atoms capable of hydrogen bonding, and each of those can only bind to a maximum of 3
water molecules, for a theoretical maximum of 36 hydrogen-bonded water molecules per
disaccharide. Because the molecular weight of water is 18 and that of the repeating unit
in the HA polymer (N-acetylglucosamine-D-glucuronic acid) is 403, the theoretical mass
ratio for a water-HA hydrogen-bonded complex would be 36 × 18 =648 per 403 amu.
That ratio works out to be 1.61 times the weight of the HA polymer.
While the foregoing seriously compromises the idea that HA binds 1,000 times its weight
in water, there are other synthetic polymers that do bind large amounts of water per unit
Figure 3. DSC data for 10% solution of glycerol scanned from 20 to −40 to 20°C in triplicate.
Figure 4. DSC data for pure water scanned from 20 to −40 to 150°C (control).