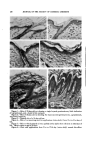
USE OF PENETROMETER WITH PETROLEUM JELLY 237 the same source. The B.P. specification for melting point range for both white and yellow jelly lies between 38 and 56øC. and, even though you ob- tain supplies with a melting point with a much smaller range, say 4øC., considerable differences may be felt between samples when handled. Later in this talk, I shall attempt to show you that, although a number of samples of petroleum jelly can have melting points lying within 3øC. of each other, a very considerable difference can exist in the consistency of the samples. In fact, samples having a melting point varying by only 0.2øC. can have a difference in consistency of 2.8 min. At this point, it may be as well to attempt a definition of consistency. Briefly it is the degree of firmness or solidity of the sample and is defined by the penetration of a standard cone into the sample, the depth of penetra- tion being measured in 1/10 ram., this measurement being the numerical value reported. The consistency of a sample of petroleum jelly will vary somewhat, depending on conditions to which the sample has been sub- jected. It is therefore important that samples shall always be subjected to the same set of conditions when being compared for a consistency deter- mination by the penetrometer. The containers for holding the sample to be tested should be cylindrical with a flat bottom and constructed from metal of sufficient gauge to prevent any give at the side of the container when handled. It is preferable for the container to have a well-fitting, slip-on cover. The size specified by the Institute of Petroleum is 2a/16 in. internal diameter X l a/8 or 2•/4 in. in depth (the deeper vessel being used for samples with a consistency of over 225), whereas A.S.T.M. specified 4 4- •/4 in. diameter and 21/2 in. or greater depth. In my opinion, the larger container is to be preferred because of the greater number of tests which can be carried out on the one sample. The coded containers should be heated to 180øF., filled to a level just be- low the top rim with petroleum jelly which has been melted in a constant temperature oven at 180øF., and the filled samples allowed to cool naturally on a level bench free from vibration. The samples should be shielded from direct sunlight or draught and if possible should be in a temperature main- tained at 77 q- 5øF. After the samples have solidified, they should be allowed to age for not less than sixteen hours before testing and during at least six hours of this time the sample should be in air maintained at 77 m IøF., or the lids sealed and the container completely immersed in a water bath maintained at 77 4- IøF. It is preferable that the sample be tested without disturbance of the surface but if it is found, as is sometimes the case, that the surface is depressed toward the centre, the surface may be carefully cut level with a sharp blade, care being taken not to work the surface during this operation. If the surface is badly depressed at the centre, the sample is best discarded. If the cone temperature varies by more than 3 ø from 77øF., its temperature should be adjusted to 77 m 1 øF.,
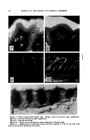
238 JOURNAL OF THE SOCIETY OF COSMETIC CHEMISTS as also should be the blade if this is used to cut the surface of the sample. The penetrometer itself should be of robust construction and operated in a manner that will not transmit vibration or shock to the samples at the time of impact and contact between the cone and sample. The instru- ment shown here is the type usually met with but may vary slightly. The cone should be preferably of stainless steel or hardened steel, as this is less liable to damage than one made from brass or stainless with stainless or hardened steel tip. It is essential that the cone be fabricated to the exter- nal dimensions specified and that the total moving weight, that is the weight of the cone plus the plunger, shall be 150 gm. If a light cone is used, a weight must be attached to bring the total weight to 150 gin. The speci- fied dimensions of the cone may be obtained from the "Standard Methods for Testing Petroleum and Its Prod- ucts," I.P. 50/48. The release mecha- nism should be perfectly smooth in action and the cone and attached shaft should be free to drop on release with- out appreciable friction. With samples and penetrometer pre- pared, the tests should be carried out without loss of time and if possible in a room in which the temperature is maintained within reasonable limits. The penetrometer should be set on a level bench free from vibration and the instrument adjusted until the sample platform is level, using the level gauge mounted on the base of the instrument. Place the sample on the penetrometer table, adjust the upper assembly so that the tip of the cone is 1 •/= in. from the side of the rim of the container, the tip being sited just above the surface of the sample. If the sample should have a consistency greater than 200, only one test should be carried out with the cone tip sited centrally over the container. Adjust the bottom platform until the tip of the cone is just touching the surface of the sample (adjustment is simple if a light is placed behind the cone to throw the shadow of the tip on to the surface of the jelly when the correct adjust- ment is arrived at by making the tip of the cone coincident with the tip of
Purchased for the exclusive use of nofirst nolast (unknown) From: SCC Media Library & Resource Center (library.scconline.org)