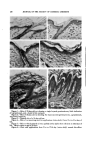
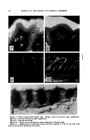
236 JOURNAL OF THE SOCIETY OF COSMETIC CHEMISTS REFERENCES (1) Butcher, E. O., "The Hair Cycles in the Albino Rat," dnat. Rec., 61, 5 (1934). (2) Butcher, E. O., "The Oxygen Consumption of the Skin During the Hair Cycle in the White Rat," rim. 7. Physiol., 138, 408 (1943). (3) Butcher, E. O., and Grokoest, A. W., "The Influence of Tissue Fluid on Hair Growth," Growth, 5, 175 (1941). (4) Butcher, E. O., "The Effects of Applications of Various Substances on the Epidermis of the Rat," it. Invest. Derrnatol., 16, 85 (1951). (5) Periman, A., "The Effect of Certain Lubricating Agents and Coarse Foods Upon the Cornification of the Oral Mucosa of the White Rat," 7. Dent. Res., 29, 1 (1950). (6) Harry, R. G., "Skin Penetration," Brit. 7. DermatoL & Syphilol., 53, 65 (1941). (7) Eller, J. J., and Wolff, S., "Permeability and Absorption of the Skin," drch. Dermatol. & Syphilol., 40, 900 (1939). (8) Calvery, H. O., Draize, J. H., and Lang, E. P., "The Metabolism and Permeability of Normal Skin," Phys. Reviews, 26, 495 (1946). (9) Butcher, E. O., "The Penetration of Fat and Fatty Acids Into the Skin of the Rat," 7. Invest. Dermatol., 21, 43 (1953). (10) MacKee, G. M., Sulzberger, M. B., Hermann, F., and Baker, R. L., "Histological Stud- ies on Percutaneous Penetration with Special Reference to the Effect of Vehicles," Ibid., 6, 43 (1945). (11) Johnston, G. W., and Lee, C. O., "A Radioactive Method of Testing Absorption from Ointment Bases," 7. rim. Pharm. dssoc., 32, 278 (1943). (12) Butcher, E. O., "Penetration of Radioactive Stearic Acid Into the Skin of the Rat," 7. Invest. DermatoL, 21, 243 (1953). (13) Burch, G. E., and Winsor, T., "Diffusion of Water Through Dead Plantar, Palmar, and Torsal Human Skin and Through the Nails," drch. Dermatol. & Syphilol., 53, 39 (1944). (14) Ralston, A. W., "Fatty Acids and Their Derivatives," New York, John Wiley & Sons, Inc. (1948), p. 78. (15) O'Brien, J.P., "The Effect of Lipoid Solvents on the Pores of the Skin," it. Invest. Der- matol., 15, 141 (1950). THE USE OF THE PENETROMETER IN THE DETERMINATION OF CONSISTENCY OF PETROLEUM JELLY* By R. T. DOBSON Chesebrough Manufacturing Co., Ltd., London, England THE OBJECT of this short talk is to explain to those not familiar with the penetrometer the working method to be employed with this apparatus and precautions which should be undertaken to ensure that repeatable and comparable results may be obtained which are indicative of differences in consistency between petroleum jellies from different sources. As many of you will be aware, the consistency of petroleum jelly can vary sufficiently to cause subtle differences in the finished product in which it is used and, although a Yellow B.P. W/A Grade 45 or a White B.P. W/A Grade 40A or 40B may be specified, you may not always receive supplies derived from * Presented at the April 9, 1954, Meeting, London, England.
236 JOURNAL OF THE SOCIETY OF COSMETIC CHEMISTS REFERENCES (1) Butcher, E. O., "The Hair Cycles in the Albino Rat," dnat. Rec., 61, 5 (1934). (2) Butcher, E. O., "The Oxygen Consumption of the Skin During the Hair Cycle in the White Rat," rim. 7. Physiol., 138, 408 (1943). (3) Butcher, E. O., and Grokoest, A. W., "The Influence of Tissue Fluid on Hair Growth," Growth, 5, 175 (1941). (4) Butcher, E. O., "The Effects of Applications of Various Substances on the Epidermis of the Rat," it. Invest. Derrnatol., 16, 85 (1951). (5) Periman, A., "The Effect of Certain Lubricating Agents and Coarse Foods Upon the Cornification of the Oral Mucosa of the White Rat," 7. Dent. Res., 29, 1 (1950). (6) Harry, R. G., "Skin Penetration," Brit. 7. DermatoL & Syphilol., 53, 65 (1941). (7) Eller, J. J., and Wolff, S., "Permeability and Absorption of the Skin," drch. Dermatol. & Syphilol., 40, 900 (1939). (8) Calvery, H. O., Draize, J. H., and Lang, E. P., "The Metabolism and Permeability of Normal Skin," Phys. Reviews, 26, 495 (1946). (9) Butcher, E. O., "The Penetration of Fat and Fatty Acids Into the Skin of the Rat," 7. Invest. Dermatol., 21, 43 (1953). (10) MacKee, G. M., Sulzberger, M. B., Hermann, F., and Baker, R. L., "Histological Stud- ies on Percutaneous Penetration with Special Reference to the Effect of Vehicles," Ibid., 6, 43 (1945). (11) Johnston, G. W., and Lee, C. O., "A Radioactive Method of Testing Absorption from Ointment Bases," 7. rim. Pharm. dssoc., 32, 278 (1943). (12) Butcher, E. O., "Penetration of Radioactive Stearic Acid Into the Skin of the Rat," 7. Invest. DermatoL, 21, 243 (1953). (13) Burch, G. E., and Winsor, T., "Diffusion of Water Through Dead Plantar, Palmar, and Torsal Human Skin and Through the Nails," drch. Dermatol. & Syphilol., 53, 39 (1944). (14) Ralston, A. W., "Fatty Acids and Their Derivatives," New York, John Wiley & Sons, Inc. (1948), p. 78. (15) O'Brien, J.P., "The Effect of Lipoid Solvents on the Pores of the Skin," it. Invest. Der- matol., 15, 141 (1950). THE USE OF THE PENETROMETER IN THE DETERMINATION OF CONSISTENCY OF PETROLEUM JELLY* By R. T. DOBSON Chesebrough Manufacturing Co., Ltd., London, England THE OBJECT of this short talk is to explain to those not familiar with the penetrometer the working method to be employed with this apparatus and precautions which should be undertaken to ensure that repeatable and comparable results may be obtained which are indicative of differences in consistency between petroleum jellies from different sources. As many of you will be aware, the consistency of petroleum jelly can vary sufficiently to cause subtle differences in the finished product in which it is used and, although a Yellow B.P. W/A Grade 45 or a White B.P. W/A Grade 40A or 40B may be specified, you may not always receive supplies derived from * Presented at the April 9, 1954, Meeting, London, England.
Purchased for the exclusive use of nofirst nolast (unknown) From: SCC Media Library & Resource Center (library.scconline.org)