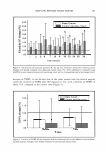
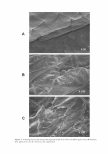
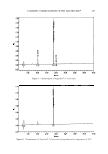
174 JOURNAL OF COSMETIC SCIENCE that skin lipids do not cover comeocytes effectively in postmenopausal women who are not on HRT. However, women who are on HRT show significantly improved lipid coverage of corneocytes, which is comparable with the younger subjects. This implies that HRT should improve the lipid coverage and skin condition of postmenopausal women. Caffeine Improves Barrier Function in :Male Skin J. M. Brandner, M. J. Behne, B. Huesing and I. Moll The influence of androgens, especially testosterone and its effector dihydrotestosterone, results in a constitutive disadvantage for male skin, e.g. reduced viability of hair at the scalp and reduced epidermal permeability barrier repair capacity. Dihydrotestosterone can act, among others, as an adenyl cyclase inhibitor. Caffeine on the other hand is an inexpensive and (in regular doses) harmless substance used in various cosmetic products, which can act as a phosphodiesterase inhibitor. To prove the hypothesis that caffeine as a phosphodiesterase inhibitor is able to override testosterone-induced effects on barrier function, we performed a double-blind placebo controlled study with healthy volunteers. In this study, 0. 5% caffeine in a hydroxyethylcellulose gel preparation (HEC) was applied on one forearm, HEC without caffeine on the other forearm of male and female volunteers for 7 days and transepidermal water loss (TEWL) was measured before and at the end of the treatment period. Basal TEWL did not differ significantly between male and female subjects but the application of caffeine significantly reduced TEWL in male skin compared with female skin. We conclude that caffeine is beneficial for barrier function in male skin. Effects of Environmentally Realistic Levels of Ozone on Stratum Comeum Function Q. C. He, A Tavakkol, K. Wietecha, R Begum-Gafur, S. A Ansari and T. Polefka The impact of troposphere ozone (03), the major oxidant in photochemical smog, on the overall wellbeing of skin is of considerable interest. To date, limited information is available on the impact of 03 on human skin. Using a specially designed 03 exposure chamber, we provide the first evidence that exposure of human skin to � (0.8 ppm, 2-h time-weighted average) significantly reduced vitamin E by 70% and concomitantly increased lipid hydroperoxides by 2.3 fold in the superficial stratum comeum (SC). Although the dose of � used here reduced the resident rnicroflora population by 50% and created a state of oxidative stress within the SC, it did not affect several key enzymes involved in SC homeostasis including the redox sensitive transglutaminase and the SC tryptic (KLKS) and chymotryptic (KLK7) proteases. Importantly, no signs of skin dryness or erythema were observed. We hypothesize that the limited effects of low doses of� on SC function is attributable to several factors including: (i) protection provided by the anti-oxidant defence syste (ii) inability of 03 to penetrate the SC and (iii) limited water available to catalyse the Criegee reaction. Although chronic exposure to 03 may produce a different outcome than that reported here, our data suggest that exposure to environmentally relevant doses of 03, at best, induces a moderate state of oxidative stress, without producing a visible clinical response. In our opinion, exposure of skin to lN radiation is a much more significant threat than exposure to ground level �. Natural Skin Surface pH is on Average Below 5, Which is Beneficial for its Resident Flora H. Lambers, S. Piessens, A Bloem, H. Pronk and P. Finkel Variable skin pH values are being reported in literature, all in the acidic range but with a broad range from pH 4.0 to 7.0. In a multicentre study (N = 330), we have assessed the skin surface pH of the volar forearm before and after refraining from showering and cosmetic product application for 24 h. The average pH dropped from 5.12 ± 0.56 to 4.93 ± 0.45. On the basis of this pH drop, it is estimated that the 'natural' skin surface pH is on average 4.7, i.e. below 5. This is in line with existing literature, where a relatively large number of reports (c. 50%) actually describes pH values below 5.0 this is in contrast to the general assumption, that skin surface pH is on average between 5.0 and 6.0. Not only prior use of cosmetic products, especially soaps, have profound influence on skin surface pH, but the use of plain tap water, in Europe with a pH value generally around 8.0, will increase skin pH up to 6 h after application before returning to its 'natural' value of on average below 5.0. It is demonstrated that skin with pH values below 5.0 is in a better condition than skin with pH values above 5.0, as shown by measuring the biophysical parameters of barrier function, moisturization and scaling. The effect of pH on adhesion of resident skin microflora was also assessed an acid skin pH ( 4-4.5) keeps the resident bacterial flora attached to the skin, whereas an alkaline pH (8-9) promotes the dispersal from the skin. Sunblocking Efficiency of Various TiOrLoaded Solid Lipid Nanoparticle Formulations1 E. Cengiz•, S. A. Wissingt, R. H Milllert and Y. Yazan• In this study, titanium dioxide (TiO2) was incorporated into solid lipid nanoparticle (SLN) formulations using both classical and novel preparation methods. The SLNs were investigated by evaluating their stabilities and physicochernical characteristics. UV-protection abilities of formulations were investigated using in vitro Transpore™ and Sun To See™ test methods. Results have been discussed by comparing the classical SLN formulation with the novel SLN, hybrid SLN (H-SLN) and the emulsion formulations. The results showed the superiority of the H SLN formulations compared with the classical SLN all SLN formulations were better when compared with the emulsion formulations considering the lN protection. Incorporation of TiO2 as a sunscreen agent into SLN formulations gives opportunity to produce stable and safe formulations with reduced amount but high UV-protection ability.
ABSTRACTS 175 Vol. 28, No. 6, 2006 Review Article The Riddle of Genuine Skin Microrelief and Wrinkles P. Quatrcaoo7., L. Thirion, C Picrard-Franchimont and G.E. Pictard Wrinkles result &om distinct structural changes occmring in specific parts of the dennis and subcutaneous tissue. There is a need for evidenced-based cosmetology identifying and quantifying the different aspects of wrinkling. Histology allows to detect specific changes associated with particular types of wrinkles. Four main types of wrinkles can thus be recognized, including the atrophic crinkling rhytids, the permanent elastotic creases, the dynamic expression lines, and the gravitational folds. Each type usually develops on specific skin regions exhibiting distinct microanatomical characteristics. Whereas skin microrclief, expression lines and skin folds appear clearly marked at the histological level, only little dermal changes arc identified under other reducible or permanent wrinkles compared with the skin immediately adjacent to them. Distinguishing different types of wrinkles brings more precision to the clinical practice. This is of importance because the different types of wrinkles respond differently to cosmetic, dermatological and surgical treatments. Review Article Stratum Corneum Keratin Structure, Function and Formation - a Comprehensive Review L. Norlen A comprehensive review on stratum corneum keratin organization, largely based on the recently published cubic rod-packing and membrane templating model [J. Invest. Dennatol., 123, 2004, 715], is presented. Keratin is the major non-aqueous component (wt/wt) of stratum corneum. As 90-100% of the stratum comeum water is thought to be located intracellularly one may presume that keratin also is a major factor (together with filaggrin-derived free amino acids) determining stratum comeum hydration level and water holding capacity. This water holding capacity depends in turn on the structural organization of the corneocyte keratin intermediate filament network. The cubic rod-packing model for the structure and function of the stratum comeum cell matrix postulates that comeocyte keratin filaments are arranged according to a cubic-like rod-packing symmetry. It is in accordance with the cryo electron density pattern of the native corneocyte keratin matrix and could account for the swelling behaviour and the mechanical properties of mammalian stratum comeum. The membrane templating model for keratin dynamics and for the formation of the stratum comeum cell matrix postulates the presence in viable epidermal cellular space of a highly dynamic small lattice parameter (30 nm) membrane structure with cubic-like symmetry, to which keratin is associated. It further proposes that membrane templating, rather than spontaneous self-assembly, is responsible for keratin intennediate filament formation and dynamics. It is in accordance with the cryo-electron density patterns of the native keratinocyte cytoplasmic space and could account for the characteristic features of the keratin network formation process, the d yna mic properties of keratin intennediate filaments, the close lipid association of keratin, the insolubility in non-denaturating buffers and pronounced polymorphism of keratin assembled in vitro, and the measured reduction in cell-volume and hydration level between stratum granulosum and stratum corneum. Skin Color and Makeup Strategies of Women from Different Ethnic Groups L. Caisey, F. Grangeat, A. Lemasson, J. Talabot and A. Voirin The development of a world-wide makeup foundation range requires a thorough understanding of skin color features of women around the world. To understand the cosmetic needs of women from different ethnic groups, we measured skin color in five different groups (French and American Caucasian, Japanese, African-American, and Hispanic-American) and compared the data obtained with women's self-perception of skin color, before or after applying their usual foundation product. Skin color was measured using a spectro-radiometer and a spheric lighting device with CCD camera ensuring a highly reliable imaging and data acquisition. The diversity of skin types involved in the study lead to define a large, continuous color space where color spectra from various ethnic groups overlap. 'Three types of complexion - dark, medium, or light - were distinguished in each group. Only Japanese women did not identify with this lightness scale and considered it makes more sense to classify their skin according to a pink-ocher-beige color scale. The approach however revealed the great variety of skin colors within each ethnic group and the extent of unevenness. A fairly good agreement appeared between women's self perception and data from color measurements but in Hispanic-American gro up. Data recorded, after foundation was applied, showed overall consistency with makeup strategy as described by volunteers except for the latter gro up whose approach looked more uncertain and variable. The findings of the study demonstrate the advantage of combining qualitative and quantitative approach for assessing the cosmetic needs and expectation'i of women from different ethnic origin and cultural back gro und.
Purchased for the exclusive use of nofirst nolast (unknown) From: SCC Media Library & Resource Center (library.scconline.org)