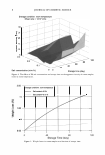
44 JOURNAL OF COSMETIC SCIENCE DETERMINATION OF TYROSINASE-INHIBITORY ACTIVITY The tyrosinase-inhibitory activity of the ether crude extract was determined by spec trophotometry with a modified method (5 ,6). The sample solutions of A. incisus extract or a positive control, kojic acid (analytical grade, Lot No. 08325 34, Sigma-Aldrich, Steinheim, Germany), were prepared by dissolving the crude extract or kojic acid in dimethylsulfoxide (DMSO, analytical grade, Lot No. 0320064, Sigma Chemical Co. Ltd., Missouri). For each concentration of the sample solution, fours well were desig nated as A, B, C, and D. Each contained a reaction mixture (180 µl) as follows: (A) 20 µl of 426 units/ml of mushroom tyrosinase (analytical grade, Lot No. 023K7024, Sigma-Aldrich), 140 µl of 20 mM phosphate buffer (pH 6.8), and 20 µl of DMSO (B) 160 µl of 20 mM phosphate buffer (pH 6.8) and 20 µl of DMSO (C) 20 µl of 426 units/ml of mushroom tyrosinase solution, 140 µl of 20 mM phosphate buffer (pH 6.8), and 20 µl of the sample solution (D) 160 µl of 20 mM phosphate buffer (pH 6.8) and 20 µl of the sample solution The mixed solution was incubated at room temperature for 10 min, and then 20 µl of 0.85 mM 3,4-dihydroxyphenylalanine (L-DOPA, analytical grade, Lot No. 023K7024, Sigma-Aldrich) was added to each well. After incubation at 25°C for 20 min, an amount of DOP Achrome produced in each well was measured with an absorbence at 490 nm by using a Spectra Count® microplate reader (Perkin Elmer, Inc., Massachusetts). Tyrosinase-inhibitory activity was calculated by using the following equation: %Tyrosinase inhibition= [(A-B) - (C-D)/(A-B)] x 100 where A = an absorbance of the mixture well (A), B = an absorbence of the mixture well (B), C = an absorbence of the mixture well (C), and D = an absorbence of the mixture well (D). IC 50 , the 50% inhibition of tyrosinase activity was calculated as the concentration of test samples that inhibit 50% of tyrosinase activity under experimental conditions. This study was performed in triplicate. DETERMINATION OF ANTIOXIDANT ACTIVITY We used 2,2-diphenyl-l-picrylhydrazyl (DPPH, analytical grade, Lot No. 083K0830, Sigma-Aldrich) to measure the free-radical scavenging activity of the extract, comparing it to positive controls including butylhydroxytoluene (BHT, analytical grade, Lot No. 78H0689, Merck, Danstadt, Germany) and L-ascorbic acid (ACS reagent, Lot No. 60780, Riedel-deHaen, Seelze, Germany). The degree of DPPH decoloration indicated the scavenging efficiency of the added sample solution. This DPPH assay was performed in triplicate under a modified method (7 ,8). The sample solutions of the tested samples including A. incisus ether extract, BHT, and L-ascorbic acid were prepared by dissolving each of them with DMSO, methanol, and deionized water, respectively. The reaction mixture consisted of 150 µl of DPPH (0.2 mM, stored at -20°C until use) and 75 µl of the sample solution. This sample solution was replaced with methanol, DMSO, or deionized water for use as a blank solution. The mixture was vortex-mixed for 15 sec and left to stand for 30 min. After incubation, the absorbence of the remaining DPPH was measured at a wavelength of 515 nm by using
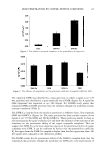
BREADFRUIT EXTRACT AS SKIN LIGHTENER 45 the Spectra Count® microplate reader. The radical scavenging activity was calculated as a percentage of DPPH decoloration using the following equation: %Radical scavenging activity= [1-(A5/AB)] X 100 where A5 = an absorbence of DPPH with the tested sample and AB = an absorbence of DPPH without the tested sample. EC50 , the equivalent concentration to give the 50% effect, was determined by log-probit analysis using six to ten different final concentrations of the samples. DETERMINATION OF MELANOGENESIS-INHIBITORY ACTIVITY B16-Fl (ATCC No. CRL-6323) mouse melanoma cells were purchased from the Ameri can Type Culture Collection (Lot No. 2634963, Virginia). This cell line was isolated from the melanocyte of mouse strain C57BL/6J B16Fl melanoma cells were initially cultured in a 25-cm2 flask (3.2 x 106 cells/ml) with DMEM (analytical grade, Lot No. 054K8302, Sigma-Aldrich, Missouri) supplemented with 10% fetal bovine serum (FBS, analytical grade, Lot No. 40f3634K, Gibco, Paisley, UK) in air containing 5% CO2 and at a temperature of 37°C. The medium was changed every two days. The passage numbers of 5 to 8 were used in this study. Before being tested, the cell suspension was transferred from the 25-cm2 flask into a 24-well plate (1 x 105 cells/well) and kept in an incubator (5% CO 2 and temperature of 3 7°C) overnight for complete adherence of the cells on the plate. After 24 hr of cultivation, the old medium was replaced with 1.0 ml of new DMEM medium con taining the various concentrations of A. incisus extract or artocarpin dissolved in DMSO. At the final concentration, the amount of DMSO used was not more than 0.1 % (v/v). The control cells were treated with 0.1 % (v/v) DMSO. Kojic acid and hydroquinone were used as positive controls in this study. A melanin content assay was performed by using a modified method (9) with triplicate run. After treatment for three days, the treated cells were harvested by using trypsin ization (Tyrpsin-EDTA, analytical grade, Lot No. 1212385, Gibco Canada Ltd., On tario, Canada) and washed twice with phosphate buffer saline. The samples were air dried and dissolved in 200 µl of 1 N NaOH containing 10% of DMSO (99.5% GC plant cell culture tested, CAS No. 67685, Merck, Shuchardt, Germany). The obtained solu tions were heated at 80 ° C for 1 hr and then cooled at room temperature. The absorbence of melanin was measured at a wavelength of 490 nm by using the Spectra Count® microplate reader. The melanin content per cell was calculated by comparing it to the absorbence of the control adjusted to 100%. DETERMINATION OF CELL VIABILITY Before being tested, B16Fl melanoma cells were initially cultured and treated as in the above procedure. After treatment for three days, the cell proliferation was measured by directly counting the number of cells treated with trypan blue. A hemocytometer was used for counting viable cells that were not stained with blue dye (trypan blue solution, R&D grade, Lot No. 55K2342, Sigma Chemical Co, Ltd.). The microscopic technique
Purchased for the exclusive use of nofirst nolast (unknown) From: SCC Media Library & Resource Center (library.scconline.org)