262 JOURNAL OF THE SOCIETY OF COSMETIC CHENHSTS TabLe II RF Values of the Oxidation Products of p-Aminophenol and Resorcinol(a) Band Color Relative Intensity RF x100 Brown (origin) Strong 0 Blue Light 7.35 Pink Strong 18.17 Green Medium 26.47 Brownish Red Medium 30.88 Brown Medium 32.35 Red Strong 37.64 Yellow Strong 38.82 (a) 1'1 mixture with hydrogen peroxide oxidant and sodium carbonate base '•. ::i 'i Chloroform' Ethylacetate' Methanol (6: 2:2) solvent system. Reactants Structure of Major Product NH 2 Para-phenylenediamine + .• N• .•NH 2 Hydrogen peroxide H2N N •,• NH 2 Para-phenylenediamine ,• + Resorcinol + Hydrogen peroxide •j•N•NH.•'• H2N'" • HO"- '"•"•'•O • 'XNH Para-phenylenediamine + 2,4 diaminoanisole + Hydrogen peroxide N•OMe H2 N-• •'"•./'H2N'" • "•NH Figure 1. Structure and color of major oxidation products Color on TLC :i: Ilue "!!
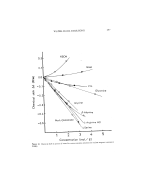
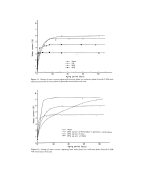
THIN-LAYER CHROMATOGRAPHY Table III THIN LAYER PLATES Source Adsorbent Coating Inert Backing 263 Brinkman Slica Gel a (Merck) Glass plate Mallinckrodt Slica Gel Glass fiber web Eastman Silica Gel Anal. tech. Alumina Acid Polyethylene terephthalate Glass plate Anal. tech. Alumina Neutral Glass plate Anal. tech. Alumina Basic Glass plate Brinkman Cellulose Glass plate Corning Glass powder Glass plate Varied Filter papers None a Analytical (.25 mm) and preparalive (2 mm) ! • FACTORS OF CHROMATOGRAPHIC SEPARATIONS :?•::Solutes.' The nature of the solutes to be analyzed is important to the success of obtaining :!!('an effective separation. Upon oxidation, PDA and allied amines given very complex i: :: :mixture of products. This is because oxidation of PDA involves the formation of a :highly reactive intermediate (32), which can undergo various reactions. Upon oxida- i: don, PDA gives quinonedimine, which on hydrolysis, gives quinone-monoimine, and i'i: on further hydrolysis, results in the formation of benzoquinone (33). •:::' Once formed, quinonediimine reacts rapidly with unreacted PDA and gives a major : products known as Bandrowski's base. As has been shown before in oxidative dyes, there are may couplers, other than primary intermediates, which undergo competitive :: reaction with quinonediimine to give a mixture of products (34). These are mostly in- dophenols and indamines and can be bound through nitrogen or oxygen. These are main products. In addition to these, various forms of one ring, two ring or poly-ring structures can form (25). Thus, selectivity in the reaction is very low. Even when a single precursor is used, one always ends up with 3 to 4 major components, and at least 5 to 6 minor components. While the nature of the solute plays a role, the amount of solvent is also important. In many instances, inversion of the bands was found, with a change in the amount of solute, fast-moving bands becoming slow-moving and vice- versa.
Purchased for the exclusive use of nofirst nolast (unknown) From: SCC Media Library & Resource Center (library.scconline.org)