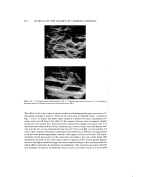
(A) (B) (C) Figure 2. SEMs of tip and root ends of an untreated human hair fiber: (A) tip end, 640 X, Fw = 0.041 mg (]3) -0.5 mm from tip, 640 X (C) toward the root end, 640 X, Fw = 0.330 mg
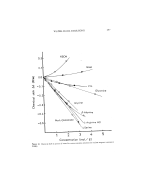
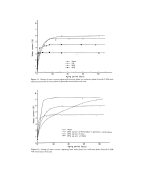
K_ERATIN FIBER SURFACE 281 I00 - E o 90 z 80- 0 REDUCTION o •. CONTACT ANGLE 0 = 90 ø OXIDATION 5 2 4 6 8 I0 12 TIME (min) Figure 3. Effect of oxidation and reduction treatments on human hair fiber wetrabiliry CRITICAL SURFACE TENSION OF HAIR The determination of the critical surface tension of keratins in various forms using al- cohol-water solutions has been achieved by several authors. A summary of these inves- tigations has been given by E1-Shimi and Goddard [13]. The method employed in this investigation of using n-butanol-water solutions is based on the work of Feldtman and McPhee [14] on wool. n-Butanol-water solutions cover- ing a surface tension range from 37 to 72.5 dyn/cm were used. In earlier measure- ments, the direction of immersion into the liquid with respect to hair scales was ignored. Later, wettability was found to depend on the scale direction of immersion [9], and therefore, measurements were carried out in both scale directions. Both advancing and equilibrium wetting forces were utilized to evaluate the corresponding values of cos 0. A plot of cos 0a versus %.v according to the Zisman approach [4], was found to be nonlinear, suggesting contributions from nondispersion interactions. A logarithmic plot of (1 + cos 0) versus %.v according to equation (8) is shown in Fig. 4 for a single hair fiber. As expected, the plots for the advancing and the equilibrium measurements are both linear. The slope of the line and the value of 7c (critical surface tension) at (1 + cos 0) equals 2, i.e., at a contact angle of 0 ø, were calculated for each of 5 fibers by linear regression analysis, and the average values are reported in Table II. The 3'ca values are close to the % of pure bulk water with respect to nonpolar liquids, which has been found to be -22 dyn/cm [6]. This supports the idea that conditioning the hair fibers at 65 per cent RH might have led to the adsorption of a multimolecular
Purchased for the exclusive use of nofirst nolast (unknown) From: SCC Media Library & Resource Center (library.scconline.org)