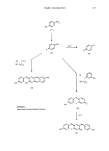
ANALYTICAL CHEMISTRY OF COSMETICS 417 This concern has recently been highlighted with respect to D & C Green (1,4-bis[(4-methylphenyl)amino]-9,10-anthracenedione), which is listed in the Code of Federal Regulations (CFR) for use in drugs and cosmetics. Because it is a certified dye, each commercially-prepared batch of this color is subject to FDA certification. This material is formed by reacting 1 mole of quinizarin with 2 moles of p-toluidine. D & C Green//16 has been shown to be safe for external use however, literature reports have demonstrated that p-toluidine is a carcinogen in mice (89). Residual amounts of reactants such as p-toluidine are commonly found in this color, and trace levels are unavoidably present even in highly purified reagent grade material. Until recently, there were no validated methods available for detecting trace levels of p-toluidine in D & C Green//16, thus the reluctance of the FDA to "permanently" list this color for use in consumer products. Several methods have since been reported (90,91) which can detect p-toluidine at the 500 ppb level and probably lower. The methods involve separation by HPLC followed by UV or fluorescence detection. This approach by the regulatory agencies of requiring analytical methodology for hazardous trace components in compounds shown to be safe is becoming standard, and the cosmetic analytical chemist will become more involved in developing trace analytical techniques for quality control of these raw materials. REFERENCES (1) L. R. Snyder and J.J. Kirkland, Introduction to Modern Liquid Chromatography, 2nd Edition (John Wiley & Sons, Inc., New York, 1979). (2) R. Namba, H. Nishiya, A. Shibamoto, Y. Morikawa, S. Tahara, and T. Mitsui, "Development of new automated analysis system of cosmetics by means of computer," IFSSC 12th International Congress, Paris, September 13-17, 1982. (3) Anionic Surfactants--Chemical Analysis, Surfactant Science Series, Vol. 8, J. Cross, Ed. (Marcel Dekker, New York, 1977). (4) J. Cross, Cationic Surfactants, E.Jungermann, Ed. (Marcel Dekker, New York, 1970), pp 419-482. (5) J. H. Jones, General colorimetric method for the determination of small quantities of sulfonated or sulfated surface active compounds,J. Assoc. O•c. Ag. Chemists, 28, 389-409 (1945). (6) G. P. Edwards, W. E. Ewers, and W. W. Mansfield, Determination of sodium cetyl sulfate and its solution in water, Analyst, 77, 205-207 (1952). (7) K. Burger, Methods for quantitative micro-determination and trace detection of surface active compounds. I. Detection and determination of very small amounts of anionics and cationics in aqueous solution, Z. Anal. Chem., 196, 15-21 (1963). (8) G. S. Buchanan and J. C. Griffith, Polarographic estimation of anionic detergents, J. Electroanal. Chem., 5, 204-207 (1963). (9) Laboratory Methods in Infrared Spectroscopy, 2nd Edition, R. G.J. Miller and B.C. Stace, Eds. (Heyden and Sons, Ltd., London, 1972). (10) D. Hummel, Identification and Analysis of Surface Active Agents by Infrared and Chemical Methods (Interscience Publishers, New York, 1962). (11) L.J. Bellamy, The Infrared Spectra of Complex Mokcuks, 2nd Edition (Methuen and Co., Ltd., London, 1958). (12) W. Brugel, An Introduction to Infrared Spectroscopy (Methuen and Co., Ltd., London, 1962). (13) N. B. Colthup, L. H. Daly, and S. E. Wiberley, Introduction to Infrared and Raman Spectroscopy (Academic Press, New York, 1964). (14) R. G. Sinclair, A. F. McKay, G. S. Myers, and R. N. Jones, The infrared absorption spectra of unsaturated fatty acids and esters,J. Am. Chem. Soc., 74, 2578-2585 (1952). (15) M. Aoki and Y. Iwayama, Determination of ionic surface active agents with dyes. IV. Applicability of fluorescein dyes and indicator, and stability of anionic detergents in solution, Yakugaku Zasshi (Tokyo), 80, 1749 (1960) (in Japanese). (16) W. E. Link, H. M. Hickman, and R. A. Morrissette, Gas-liquid chromatography of fatty derivatives. II.
418 JOURNAL OF THE SOCIETY OF COSMETIC CHEMISTS Analysis of fatty alcohol mixtures by gas-liquid chromatography, J. Am. Oil. Chem. Soc., 36, 300 (1969). (17) T. H. Liddicoet and L. H. Smithson, Analysis of surfactants using pyrolysis-gas chromatography, J. Am. Oil. Chem. Soc., 42, 1097 (1975). (18) J. Torrnquist, Quantitative analysis of polyethylene glycol monododecyl ethers by gas chromatogra- phy after silylation, Acta Chemica Scandinavica, 23, 1935-1942 (1969). (19) S. I. Hakomori, A rapid permethylation of glycolipid polysaccharide catalyzed methylsulfonyl carbanion in dimethylsulfoxide,J. Biochem., 55, 205-208 (1964). (20) K. Sj8berg, A stable solution of methylsulfinyl carbanion, Tetrahedron Letters, 51, 6383-6384 (1966). (21) G. Schomburg et al., Gas chromatographic analysis with glass capillary columns, J. Chrom., 122, 55-72 (1976). (22) I.E. Rosenberg and E. Fu, Unpublished research. (23) I.E. Rosenberg andJ-S. Wang, Unpublished research. (24) H. J. Vonk et al., Modern analytical methods for ethoxylated surfactants, T. Mezhdunar. Kongr. Poverkhn.- Akt. Veshehestrum, 1,435-449(1977). (25) E. Julia-Dan(•s and A.M. Casanovas, Application of mass spectroscopy to the analysis of nonionic surfactants, Tenside Deterg., 16, 317-323 (1979). (26) C. K. Cross and A. C. Mackay, Analysis of alkyl ethoxylates by NMR, J. Am. Oil Chem. Soc., 50, 249-250 (1973). (27) H. Walz and H. Kirschnek, Nuclear resonance spectroscopy as a valuable complement to infrared and ultraviolet analysis of surface active compounds, Proc. 3rd Intern. Congr. Surface Active Substances, Koln, 3, 92-98 (1960). (28) A. R. Greif, Jr. and ?. W. Flanagan, The characterization of non-ionic surfactants by NMR,J. Am. Oil Chem. Soc., 40, 118-120 (1963). (29) M. M. Crutchfield, R. R. Irani, and J. T. Yoder, Quantitative application of high resolution proton magnetic resonance measurements in the characterization of detergent chemicals, J. Am. Oil Chem. Soc., 41,129-132 (1964). (30) C. C. Hinckley, Paramagnetic shifts in solution of cholesterol and the dipyridine adduct of trisdipivalomethanatoeuropium (III). A shift reagent, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 91, 5160-5162 (1969). (31) J. K. M. Sanders and D. H. Williams, A shift reagent for use in nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy. A first order spectrum of n-hexanol, Chem. Commun., 422-423 (1970). (32) J. K. M. Sanders and D. H. Williams, Tris(dipivalomethanato)europium. A paramagnetic shift reagent for use in nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy,J. Am. Chem. Soc., 93,641-645 (1971). (33) G. E. Stolzenberg, R. G. Zaylskie, and P. A. Olson, Nuclear magnetic resonance identification of O,P-isomers in an ethoxylated alkylphenol nonionic surfactant as tris(2,2,6,6-tetramethylheptane- 3,5-dione)europium III complex, Anal Chem., 43,908-912 (1971). (34) C. P. Terweij-Groen, S. Heemstra, andJ. C. Kraak, Distribution mechanism of ionizable substances in dynamic anion exchange systems using cationic surfactants in high performance liquid chromatogra- phy,J. Chromatogr., 161, 69-82 (1978). (35) K. Nakamura, Y. Morikawa, and I. Matsumoto, Rapid analysis of ionic and non-ionic surfactant homologs by high performance liquid chromatography,J. Am. Oil Chem. Soc., 58, 72-77 (1981). (36) A. Nozawa and T. Ohnuma, Improved high performance liquid chromatographic analysis of ethylene oxide condensation by their esterification with 3,5-dinitrobenzoyl chloride, J. Chromatogr., 187, 261-263 (1980). (37) K. Nakamura and Y. Morikawa, Separation of surfactant mixtures and their homologs by high pressure liquid chromatography,J. Am. Oil Chem. Soc., 59, 64068 (1982). (38) J. F. K. Huber et al., Rapid separation and determination of nonionic surfactants of the polyethylene glycol-monoalkyl phenyl ether- type by column liquid chromatography, Anal Chem., 44, 105-110 (1972). (39) K. Aitzetmuller, Application of moving-wire detectors for the liquid chromatography of fats and fatty acid derived oleochemicals,J. Chrom. Sci., 13,454-461 (1975). (40) J.J. Kirkland, Analysis of sulfonic acids and salts by gas chromatography of volatile derivatives, Anal Chem., 32, 1388 (1960). (41) T. Nagai, S. Hashimoto, I. Yamane, and A. Mori, Gas chromatographic analysis for alpha-olefin sulfonates,J. Am. Oil Chem. Soc., 47, 505 (1970). (42) L. D. Metcalf, The direct gas chromatographic analysis of long chain quaternary ammonium compounds,J. Am. Oil Chem. Soc., 40, 25 (1963).
Purchased for the exclusive use of nofirst nolast (unknown) From: SCC Media Library & Resource Center (library.scconline.org)