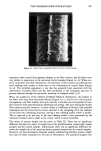
NITROSOALKANOLAMINE DETERMINATION 135 METHOD Dissolve the amine (1 g) in methanol/water (1:1, 10 ml), add internal standard NEHPA (50 •xl) and three drops of indicator solution. Add ion exchange resin in small portions to the stirred mixture until the solution, after first turning red, becomes colorless. Transfer the suspension quantitatively into glass column and elute with methanol/water (1:1, 100 ml). Take down in a vacuum rotary evaporator (40øC) and take up residue in chloroform/acetone (5:1, 10 ml). Transfer quantitatively to clean-up column, wash the column with the same solvent (40 ml). Elute nitrosamines with acetone (50 ml). Rotate down (5 ml), transfer quantitatively into a receiver, and remove solvent by nitrogen stream. SILYLATION Add MSHFBA (150 •zl) to residue and allow to stand 45 min at room temperature. Make up to 0.5 ml with i-octane. Treatment of standard (50 ng NDELA and 50 ng NEHPA): remove solvent under nitrogen and derivatize in the same way. GC CONDITIONS Column: 6% OV 275 on Volaspher A2 (80- 100 mesh ASTM) (2 mm X 3 m) silanized glass. Carrier gas: He (20 ml/min). Injector: 200øC. Temperature programme: initial temperature, 1 min, 150øC, at 2ø/min to 170øC and then at 10ø/min to 220øC. Pyro- lyzer temperature: 400-500øC. Volume injected: 5 •zl. RESULTS AND DISCUSSION Artifact formation represents a great problem when analyzing alkanolamines, especially secondary amines. Inorganic (Kieselguhr) or organic (ion exchange resin XAD2) mate- Q. _1 'I- UJ Z Z 0 5 10 15 20min Figure l. Gas chromatogram with contaminants NBHPA and NDELA and internal standard NEHPA.
136 JOURNAL OF THE SOCIETY OF COSMETIC CHEMISTS rials are especially critical because traces of NOx adsorbed to these sorbents lead to nitrosamine formation. Removal of the amine by adsorption to a cation exchange resin prevents artifact formation. Subsequent clean-up on a silica gel 40-column represents an efficient further purification step. Analysis of high purity DEA by this method did not show detectable NDELA contamination (5 ppb), which proves that artifact for- mation is inhibited. For trimethylsilylation, the conditions described were found to be appropriate heating in a closed system to 80øC did not improve the yields. A gas chromatogram as obtained from a typical diethanolamine sample is illustrated in Figure 1. Baseline separation of internal standard (NEHPA-TMS) and contaminating nitrosamine (NDELA-TMS) is obtained. To test the reproducibility of the analytical procedure, a sample of DEA was analyzed ten times. An average NDELA content of 279 }xg/kg _ 11 }xg/kg (SD = standard deviation) was found. The average recovery of the internal standard was 89 - 8% (SD). The determination limit was 5 }xg/kg in our hands. Preliminary results of a first collab- orative study indicate that this limit might not be reached in all instances, depending on analytical experience and sensitivity of the Thermal Energy Analyzer. Therefore, a range of 5- 15 }xg/kg is given. As can be seen from Table I, most of the alkanolamines analyzed are contaminated with the corresponding nitrosamines. This is in agreement with results obtained earlier with a series of secondary alkylamines (14). The finding that specific samples showed no detectable contaminations demonstrates that nitrosamine formation obviously can be reduced or prevented by maintaining appropriate conditions for production and/or storage of the corresponding amines. To examine possibilities for removal of nitrosa- mine contamination, DEA contaminated with 280 ppb NDELA was treated overnight with Ni/A1 alloy (0.5 g of the amine, diluted in 10 ml water, 150 mg of alloy). This treatment resulted in a 90% reduction of the NDELA content. ACKNOWLEDGMENTS This study was supported by the German Ministry for Youth, Family, Women and Health (Kap. 1502, title 53201). We thank Miss B. Weber for competent technical assistance. Table I Contamination of Alkanolamines With NDELA and NBHPA NDELA (•g/kg) NBHPA (•g/kg) DEA 1 DEA 2 DEA 3 DEA 4 TEA MEA 1 BHPA 1 BHPA 2 BHPA 3 91 1460 279 5 5 41 465 36 13
Purchased for the exclusive use of nofirst nolast (unknown) From: SCC Media Library & Resource Center (library.scconline.org)