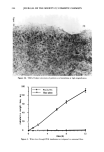
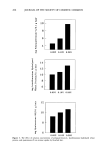
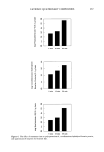
j. Soc. Cosmet. Chem., 43, 229-235 (September/October 1992) The influence of nonionic cellulosic polymers on the uptake of polyquaternium-10 by bleached hair JACQUELINE M. HUTTER, MARY T. CLARKE, ERNST K. JUST, J. L. LICHTIN, and ADEL SAKR, University of Cincinnati College of Pharmacy, Cincinnati, OH (J. M.H., J. L. L., A.S.), and Aqualon Company, Wilmington, DE (M.T.C., E.K.J.). Received December 11, 1992. Synopsis The influence of nonionic cellulosic polymers on polyquaternium- 10 cationic hydroxyethylcellulose uptake by bleached hair was examined. Colloid titration was used to measure cationic polymer concentrations before and after immersion of hair tresses in treatment solutions. Cationic polymer uptake by mildly bleached hair decreased somewhat when high-molecular-weight hy- droxyethylcellulose (HMW HEC), hydroxypropyl methylcellulose (HPMC), and hydrophobically modified HEC (HMHEC) were included in polyquaternium-10 treatment solutions. There were no differences in polyquaternium-10 uptake by mildly bleached hair when low-molecular-weight HEC (LMW HEC) was included in treatment solutions. HPMC and HMHEC significantly increased the adsorption of polyquaternium-10 by harshly bleached hair. There were no significant differences in uptake of this cationic polymer when either HMW HEC or LMW HEC were included in treatment solutions for this hair type. INTRODUCTION Nonionic cellulosic ethers are widely used in hair care formulations for their viscosity modifying properties. A viscous hair care product is important for several reasons (1): (a) a thin product is difficult to transfer from its container (b) the consumer often equates thickness with a more concentrated or effective product (c) stability may be enhanced when the formulation is viscous and (d) a more viscous formulation frequently facilitates the manufacturing process. Cellulose ethers are also film-forming materials and serve to stabilize foam and improve the "feel" of a formulation (2). Several types of cellulose ethers are available. These vary in the number and nature of substituent groups attached to the cellulose backbone. These substituent groups, in turn, dictate the solubilities and compatibilities of the polymers (3). Nonionic cellulosic Jacqueline M. Hutter's current address is Helene Curtis Industries, 4401 West North Avenue, Building 3E, Chicago, IL 60639. 229
230 JOURNAL OF THE SOCIETY OF COSMETIC CHEMISTS polymers commonly used in hair products include hydroxyethylcellulose (HEC) and hydroxypropyl methylcellulose (HPMC). Long-chain alkyl groups can be also incorpo- rated onto HEC to yield a hydrophobically modified HEC (HMHEC). Shampoo formulations often contain cationic polymers to provide hair conditioning. The efficacy of a conditioning shampoo is directly related to the amount of cationic polymer deposited on the hair surface (4). It is well known that cationic polymer deposition is decreased when surfactants are included in a formulation. This interference is most marked in the presence of anionic surfactants, but amphoteric, or cationic, surfactants, as well as nonionic surfactants (5), may also decrease the deposition of cationic polymer. Other factors such as treatment temperature (6), cationic polymer concentration (7), and added electrolytes (8) have been examined and found to influence cationic polymer uptake. However, nothing has been reported on the effects of added cellulose ethers, which are ingredients common in hair care products, on cationic polymer deposition. This paper presents the results of work examining the influence of nonionic cellulosic polymers on the uptake of polyquaternium-10 by bleached hair. EXPERIMENTAL HAIR TRESS PREPARATION Medium-dark brown, 8-inch-long virgin quality European hair (DeMeo Bros., New York, NY) was washed and bleached in a formulation of 3% hydrogen peroxide (9). Two bleach conditions were chosen, 30 minutes at 32øC and 4 hours at 40øC. This yielded hair with two degrees of damage. CELLULOSIC POLYMERS Polyquaternium-10 (UCARE © Polymer JR 400, Amerchol, Edison, NJ) solutions of 0.05, 0.10, and 0.20 w/v% were prepared in a 0.001 M buffer of mono- and dibasic sodium phosphate (10). In addition, polyquaternium-10 solutions of the above concen- trations were prepared to contain 0.10 w/v% concentrations of nonionic cellulosic polymers. The nonionic cellulosics added were high-molecular-weight hydroxyethylcel- lulose (HMW HEC, NATROSOL © 250 HHR) medium viscosity (lower molecular weight) hydroxyethylcellulose (LMW HEC, NATROSOL © 250 MR) hydroxypropyl methylcellulose (HPMC, BENECEL © MP 943 PR) and hydrophobically modified hydroxyethylcellulose (HMHEC, NATROSOL © Plus CS, Grade 330). All nonionic cellulosic polymers were supplied by Aqualon, a Hercules Incorporated Unit (Wilming- ton, DE). COLLOID TITRATION The uptake of cationic polymer from treatment solutions by hair was determined by a colloid titration method discussed elsewhere (10). System parameters described previ- ously were identical in this study.
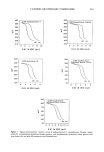
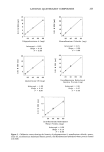
Purchased for the exclusive use of nofirst nolast (unknown) From: SCC Media Library & Resource Center (library.scconline.org)