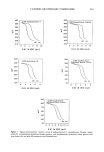
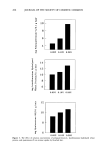
CATIONIC QUATERNARY COMPOUNDS 271 substantivity of cationic compounds has not been developed, based on the present experimental conditions laurdimonium hydrolyzed wheat protein exhibits the greatest substantivity, followed by quaternium-26, stearalkonium chloride, and cocodimonium hydrolyzed keratin protein. The bulk of the present study was performed on aqueous solutions of the quaternary ammonium compounds used neat. Interference by other components (cationic, anionic, or amphoteric) present in formulated products have not yet been fully assessed. How- ever, a potentiometric titration curve of a commercial aqueous-based protein hair con- ditioner (CAT TM , Redken Laboratories, Inc.) shows no apparent interference encoun- tered in titration of a quaternized protein in a complex formulation. The result from this 450 400 350 300 ' •5o 200 150 100 ,too 3õ0 300 250 200 50 i i lO 15 I I I I I 0 2 4 8 8 0.01 M $D$ (ml) I 0 5 (A) I 20 ml of titrant Figure 7. Potentiometric titration curves of a commercial protein conditioner with 0.01 M SDS as titrant (A) and 0.01 M STPB as titrant (B). The titration curve of the neat botanical quatemized protein used in this conditioner is also shown (inset).
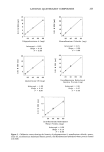
272 JOURNAL OF THE SOCIETY OF COSMETIC CHEMISTS titration indicates, with 5% error, the actual level of the cationic protein present in this hair conditioner. Also, Figure 7 illustrates the high potential jump at the endpoint of the titration curve of this conditioner. This curve is similar to the one, shown in the inset, of the quaternized protein, a main ingredient in the tested conditioner. Moreover, it is noteworthy that the potential jump of this titration curve was enhanced when sodium tetraphenylborate (STPB) was used as the titrant a similar observation has been reported (16). As a final note, the present titration method can be adapted to measure the equivalent weights of quaternary ammonium compounds and to determine the total charge on the surface of the hair fiber. The apparent equivalent weight of the cationic compounds calculated from the calibration curves is shown in Table II. However, further studies in such areas as pH effects, stability, molecular weight, and determination of the degree of quaternization of the ammonium compounds are needed to evaluate such concepts. ACKNOWLEDGMENTS The support of Paula and John Meehan of Redken Laboratories, Inc., is appreciated. The technical assistance of A. Edward Newsom, John N. Bruzas, Ivy L. P. Mai, and Diana C. Toro is acknowledged. REFERENCES (1) (2) (3) (4) (5) (6) (7) (8) (9) (10) (11) (12) (13) (14) c. R. Robbins, Chemical and Physical Behavior of Human Hair (Springer-Verlag, New York, 1988), pp. 196-224. R. J. Bouthilet and A. Karler, Cosmetic effect of substantive proteins, Proc. Sci. Sect. Toilet Goods Assoc., 44, 27-31 (1965). R. J. Crawford and C. R. Robbins, A replacement for Rubine dye for detecting cationics on keratin, J. Soc. Cosmet. Chem., 31, 273-278 (1980). Y. K. Kamath, C. J. Dansizer, and H.-D. Weigmann, Surface wettability of human hair. I. Effect of deposition of polymers and surfactants, J. Appl. Polym. Sci., 29, 1011-1026 (1984). H.-D. Weigmann, Y. K. Kamath, S. B. Ruetsch, P. Busch, and H. Tesmann, Characterization of surface deposits on human hair fibers, J. Soc. Cosmet. Chem., 41, 379-390 (1990). E. D. Goddard and W. C. Harris, An ESCA study of the substantivity of conditioning polymers on hair substrates, J. Soc. Cosmet. Chem., 38, 233-246 (1987). H. J. White, Jr., and D. L. Underwood, The use of radiotracers to study absorption by hair, J. Soc. Cosmet. Chem., 7, 198-204 (1956). J. A. Faucher and E. D. Goddard, Influence of surfactants on the sorption of a cationic polymer by keratinous substrates, J. Colloid. Interf. Sci., 55, 313-319 (1976). E. D. Goddard, J. A. Faucher, R. J. Scott, and M. E. Turney, Sorption of polymer JR on keratinous surfaces--Part II, J. Soc. Cosmet. Chem., 26, 539-550 (1975). G. V. Scott, Spectrophotometric determination of cationic surfactants with Orange II, Anal. Chem., 40, 768-773 (1968). G. V. Scott, C. R. Robbins, and J. D. Barnhurst, Sorption of quaternary ammonium surfactants by human hair, J. Soc. Cosmet. Chem., 20, 135-152 (1969). L. K. Wang and W. W. Shuster, Polyelectrolyte determination at low concentration, Ind. Eng. Chem. Prod. Res. Dev., 14, 312-314 (1975). J. M. Hutter, M. T. Clarke, E. K. Just, J. L. Lichtin, and A. Sakr, Colloid titration: A method to quantify the adsorption ofcationic polymer by bleached hair, J. Soc. Cosmet. Chem., 42, 87-96 (1991). B. J. Birch and D. E. Clarke, Surfactant-selective electrodes, Anal. Chim. Acta, 67, 387-393 (1973).
Purchased for the exclusive use of nofirst nolast (unknown) From: SCC Media Library & Resource Center (library.scconline.org)