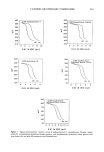
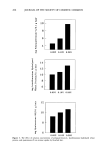
POLYQUATERNIUM- t0 UPTAKE 233 Polyquaternium-t0 adsorption by harshly bleached hair from solutions containing either HMW HEC or LMW HEC was not significantly different from that of cationic control solutions (Figure 2). In light of these results, the lower uptake by mildly bleached hair of cationic due to HMW HEC, HPMC, and HMHEC in the treatment solutions (Figure t) at first seems anomalous. However, adsorption of cationic onto the less damaged surface of this hair is already low compared to that of the more harshly bleached hair (Figure 2). Small decreases caused by competitive adsorption of the nonionic would then be larger relative to the total amount of polyquaternium-t0 adsorbed. The increase in cationic uptake by harshly bleached hair (but not mildly bleached hair) in the presence of HPMC and HMHEC is noteworthy. The explanation may well be a rate effect occasioned by the surface activities specific to these two polymers rather than one involving direct interactions with the polyquaternium and/or hair. The surface activities of HPMC and HMHEC are 60-65 dynes/cm @ 0.1% (12) and 46-5 t dynes/ cm @ 0.1% (13), respectively. As described previously (t0), the contact time of bleached hair tresses with treatment solutions was standardized to 45 minutes. After 45 minutes, adsorption of polyquater- nium-t0 onto mildly bleached hair from 0.1% treatment solutions of the polyquater- nium alone was largely complete at 2.6 mg/g longer treatments of up to 180 minutes resulted in only a 0.9 mg/g increase to 3.5 mg/g. On the other hand, harshly bleached hair had adsorbed considerably more polyquaternium in the interval between 45 and 180 minutes (at 8.6 and 12.6 mg/g, respectively). As such, HPMC and HMHEC may speed the approach of the polyquaternium to equilibrium adsorption by lowering the interfacial surface tension between the solution bulk and hair surface, and thus facilitate phase transfer of the polyquaternium-t0 to the hair surfaces. This mechanism seems especially reasonable in light of earlier studies (7) ,',- 12 8 10 I,LI o ½ 8 •o 6 =' 4 :=, 2 ._1 .o 0 TREATMENT SOLUTION • POLYQUAT-10 ONLY POLYQUAT-10 AND NONIONIC CELLULOSlC POLYMER ALL SOLUTIONS ARE 0.1% ON/V) IN NONIONIC AND/OR POLYQUATERNIUM-10 Figure 2. The effect of nonionic cellulosic polymers on polyquaternium-10 adsorption by harshly bleached hair.
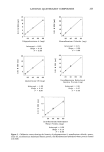
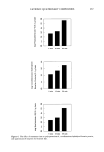
234 JOURNAL OF THE SOCIETY OF COSMETIC CHEMISTS in which the adsorption of polyquaternium-10 by harshly bleached hair continued over a week's time. This latter study served to demonstrate the porous nature of this damaged hair type and the slower diffusion into and adsorption of polymer within the fiber after quick initial adsorption at the immediate outer fiber surfaces. The influence of polyquaternium concentration was also studied by examining 0.10% HMW HEC on cationic adsorption from 0.05 % and 0.20% solutions of the polyquater- nium (Figure 3). Cationic uptake was less from 0.05% polyquaternium-10 solutions when 0.10% HMW HEC was included for both mildly and harshly bleached hair (p = 0.001 and p = 0.062, respectively). There were no differences in adsorbance relative to controls from 0.20% polyquaternium-10 solutions containing HMW HEC for either bleached hair type. Data for these results are found in Table II. Within the 45-minute time frame allowed for adsorption, polyquaternium-10 uptake depends on treatment solution concentration. Compare 2.8 vs 3.5 mg/g hair and 8.6 vs 9.1 mg/g hair in going from 0.05% to 0.20% in polyquaternium-10 (Table II). High-molecular-weight HEC can compete to some degree for adsorption sites with polyquaternium-10 when the latter is at low concentration, i.e. at 0.10% and less, but not at the higher 0.20% concentration. The degree of hair damage also influences competitive uptake. SUMMARY Nonionic cellulosic polymers influence the uptake of polyquaternium-10 by bleached hair. The direction and magnitude of this influence is dependent on both the severity of the bleach treatment and the type of nonionic cellulosic included. Mildly bleached hair shows decreased cationic uptake when high-molecular-weight "' 12 Z 10 O I1. 8 O Q 6 o , 4 Z 2 ":[ 0 ._1 o MILD HARSH BLEACHED HAIR TYPE 0.05% (W/V) POLYQUAT-10 0.20% (W/V) POLYQUAT-10 Figure 3. The effect of polyquaternium-10 concentration and 0.10% HMW HEC on cationic adsorption by bleached hair.
Purchased for the exclusive use of nofirst nolast (unknown) From: SCC Media Library & Resource Center (library.scconline.org)