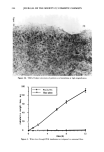
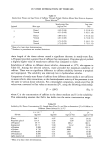
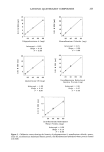
CATIONIC QUATERNARY COMPOUNDS 261 Table I General Information of Tested Quaternary Compounds Material CTFA adopted name % Solid pH Source Celquat L-200 Polyquaternium-4 90-95 5-6 Nat'l Starch • Carsoquat SDQ-85 Stearalkonium Chloride 85-90 5-6 Lonza 2 Ceraphyl 65 Quaternium-26 53-63 5-6 Van Dyk 3 Hydrotriticum QL Laurdimonium 28-32 4-6 Croda 4 hydrolyzed wheat protein Croquat WKP Cocodimonium 28-32 4-5 Croda 4 hydrolyzed keratin protein National Starch and Chemical Company, Specialty Polymer, Finderne Avenue, Bridgewater, NJ 08807. Lonza, 17-17 Rt 208, Fair Lawn, NJ 07410. Van Dyk, Main and William Sts., Belleville, NJ 07109. Croda Inc., 183 Madison Avenue, New York, NY 10016. of octoxynol-9 in water (Rohm & Haas), and distilled water (total volume 100 ml) was titrated by a Brinkman Potentiograph E536 connected to a Dosimat E535 that dispenses a standard 0.0 ! M sodium dodecylsulfate (SDS E. Merck) at a rate of 3.5 ml/minute. The change in the potential was monitored by a surfactant electrode, Model 93-42, obtained from Orion Research. From the potentiogram, the endpoint was determined as the point of steepest slope by a tangent template. All solutions were titrated at a pH of 2-3. PREPARATION OF CALIBRATION CURVES Solutions containing 10, 20, 40, and 80 mg (corrected for average percent solid) of cationic compound were prepared in triplicate and titrated with 0.01 M SDS solution as described above. It was not necessary to correct for a blank since the titration does not yield any endpoint (no neutralization process occurs). The calibration curves were ob- tained by plotting the weight (mg) of cationic compounds vs the volume (ml) of standard SDS solution used in the titration. SUBSTANTIVITY STUDY Unless otherwise noted, the procedure to measure the substantivity of quaternary com- pounds is as follows: 0.1 g of bleached hair was added to a 40-ml solution of quaternary compound that was then placed in a 35øC shaker bath for 30 minutes. At the end of the treatment time, the solution was decanted and the hair was rinsed (3 X 20 ml) with distilled water. The combined solution (100 ml) was titrated with 0.01 M SDS solution as described above. An untreated sample (without hair) was subjected to the same conditions. All experiments were performed in triplicate. The average of three deter- minations was obtained, and the quantity of the quaternary compound in the titrated solutions was calculated from the appropriate calibration curve. The calculated differ- ence in the amount of cationic compound present in the untreated and treated solutions represents the cationic uptake by the hair sample. The effect of the rinse on the desorption of cationic compounds from the hair is not
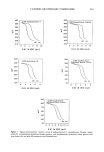
262 JOURNAL OF THE SOCIETY OF COSMETIC CHEMISTS definitive. The amount of the quaternary compound found in the rinse (about 1% of the adsorbed quantity) may not result from the desorption, but instead from the residual solution adhering to the hair tress. HAIR SAMPLES AND CHEMICAL TREATMENTS Light brown, normal virgin (NV) quality European hair (DeMeo Brothers, New York) was used as received throughout the study. Virgin hair tresses were bleached with Levitation Bleach TM powder (Redken Laboratories, Inc.) mixed with 9% hydrogen per- oxide. The tresses were saturated with bleach, covered with plastic film, and incubated at 35øC for 45 minutes. The hair tresses were then rinsed under a stream of distilled water for five minutes and air dried (B 1 x). The same procedure was repeated on the B 1 x hair to obtain two-time bleached hair (B2 x). The permanent waving procedure utilized a commercial alkaline permanent wave, Perm Art TM (Redken Laboratories, Inc.). Reduction of hair samples was accomplished by saturating hair with a solution containing 9% thioglycolic acid (pH 9.5) at 30øC for 15 minutes. The tresses were then rinsed under a stream of distilled water for three minutes and blotted dry. These reduced tresses were saturated with neutralizing solution (2% hydrogen peroxide) for five min- utes, rinsed with distilled water for five minutes, and air dried (PIX). The same procedure was repeated on the P 1 x hair to obtain two-time permed hair (P2 x). Tinted hair (T) was obtained by using a commercial cream color (Deco Color TM 6RU, Redken Laboratories, Inc.) mixed with 6% hydrogen peroxide. Hair tresses were saturated with the color at 38øC for 45 minutes, then rinsed under a stream of distilled water for five minutes and air dried. AMINO ACID ANALYSIS Hair samples were hydrolyzed in sealed evacuated tubes with 6N HCI at 110øC for 48 h. The hydrolysates were then analyzed on a Beckman 121M or 6300 amino acid analyzer following a previously reported procedure (17). RESULTS AND DISCUSSION To illustrate the versatility and the efficiency of the new method, a variety of quaternary compounds were tested (Table I). Since the present procedure is an aqueous titration, the quaternary compounds should be water-soluble. However, water-insoluble or dispersible compounds can also be used if they are solubilized in mixed solvent systems such as water-alcohol mixtures. In the present study, a 0.01 M SDS solution was used as the titrant because it is a designated standard for the Orion surfactant electrode. Also, in the potentiometric titration of quaternary ammonium compounds, one of the main criteria for a successful quantitative analysis is the presence of a sufficiently large potential decrease at the endpoint. The titration curves should display a pronounced inflection at the endpoint such that the point of steepest slope can be obtained accurately and reproducibly. Typical potentiometric titration curves obtained for the tested cationic compounds are shown in Figure 1. All of the curves in Figure 1 show a suitable potential decrease and
Purchased for the exclusive use of nofirst nolast (unknown) From: SCC Media Library & Resource Center (library.scconline.org)