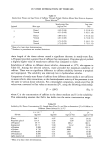
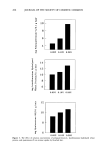
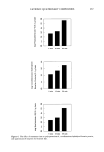
POLYQUATERNIUM- 10 UPTAKE 231 SUBSTRATE TREATMENT Approximately one gram of bleached hair was accurately weighed and placed in a 125-ml Erlenmeyer flask. About 20 g of the polyquaternium-10 or polyquaternium- 10/nonionic cellulosic polymer solution was accurately weighed and dispensed onto the hair using a syringe. The flask was tightly covered and placed in a 40øC shaker bath for 45 minutes. The solution was then decanted for concentration analysis by colloid titration (10). Cationic uptake for the two bleached hair types was determined by measuring solutions containing polyquaternium-10 before and after immersion of a hair tress. Differences in solution concentration were attributed to sorption of the polymer by the hair. Identical measurements were made for solutions containing polyquaternium-10 at the same con- centration but which also contained one of the nonionic cellulosic polymers. DATA ANALYSIS Statistical analyses were performed on an IBM-compatible, personal computer using the MINITAB © (State College, PA) statistical analysis software program. All data are reported as average values of n = 3 determinations, unless otherwise noted. Standard deviations are reported for all data and illustrated in the accompanying figures. Tests of differences in cationic polymer uptake between solutions containing nonionic cellulosic polymers with cationic polymer and control solutions of cationic alone were examined using a pooled t-test for the difference between two sample means. p-Values of 0.05 or less were noted and indicate significant differences in the data. RESULTS AND DISCUSSION COLLOID TITRATION Because the colloid titration method is susceptible to contaminants (11), the nonionic cellulosic polymers were first analyzed to assess their possible influence on titration endpoints. Titrations of 300-lxL aliquots of 0.10% nonionic cellulosic polymer solutions showed no difference in their equivalence points when compared to the normal indicator blank. This is not unexpected, since cellulose ethers are uncharged and should not participate in the titration. The titration endpoints determined in this method are therefore due solely to the presence of polyquaternium-10 in the various treatment solutions. Polyquaternium-10 uptake onto "mildly" and "harshly" bleached hair was measured from control solutions containing the cationic alone. These adsorptions measured 2.6 - 0.1 mg/g hair and 8.6 +-- 0.2 mg/g hair, respectively. Uptake was then determined from polyquaternium-10 solutions containing 0.10 w/v% of one of the four nonionic cellu- losics: LMW HEC, HMW HEC, HPMC, and HMHEC. Sorption data are found in Table I. Uptake by mildly bleached hair (Figure 1) from polyquaternium- 10 solutions containing HMW HEC was significantly less (p = 0.002) than the cationic control. There were also strongly directional and significant decreases in cationic adsorption from poly-
232 JOURNAL OF THE SOCIETY OF COSMETIC CHEMISTS Table I Effect of Added Nonionic Cellulosic Polymers on Polyquaternium-10 Uptake by Bleached Hair (Average N = 3) Mildly Harshly bleached hair bleached hair (mg/g) (mg/g) 0.10% Polyquaternium- 10 0.10% HMW HEC/0.10% Polyquaternium-10 0.10% LMW HEC/0.10% Polyquaternium- 10 0.10% HMHEC/0.10% Polyquaternium-10 0.10% HPMC/0.10% Polyquaternium-10 2.6 (0.1) a 8.6 (0.2) 1.8 (0.2) 7.3 (0.2) b 2.8 (0.2) 8.5 (0.2) 2.2 (0.2) 9.7 (0.3) 2.4 (0.1) 11.4 (0.8) a Numbers in parentheses indicate standard deviation. b Polyquaternium-10 uptake control = 7.3 (0.7). quaternium-10 solutions containing either HPMC or HMHEC (p = 0.06 and p = 0.025, respectively), but not from those containing LMW HEC. HEC adsorbs slightly onto the surface of a hair fiber, even though the polymer is uncharged (7). This behavior is apparently extended to solutions containing cationic polymer, where the nonionics can compete with the latter for adsorption sites on hair. In keeping with general trends noted for the effect of molecular weight on polymer adsorption, HMW HEC, once adsorbed, would be less easily displaced than LMW HEC. This phenomenon would explain the relative effectiveness in modifying the adsorption of polyquaternium- 10. '%', 2 z rr 1 0 o TREATMENT SOLUTION •'•[] POLYQUAT-10 '•[] POLYQUAT-10AND ONLY NONIONIC CELLULOSIC POLYMER ALL SOLUTIONS ARE 0.1% ON/V) IN NONIONIC POLYMER AND/OR POLYQUATERNIUM-10 Figure l. The effect of nonionic cellulosic polymers on polyquaternium-l0 adsorption by mildly bleached hair.
Purchased for the exclusive use of nofirst nolast (unknown) From: SCC Media Library & Resource Center (library.scconline.org)