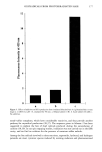
206 JOURNAL OF COSMETIC SCIENCE V• and V2 derived from the spectral reflectance data of the skin indicate the amount of melanin in the stratum basale and that above the stratum basale, respectively. The authors have devised a method for separating coloring caused by melanin at different depths from the skin surface and for displaying the degree of coloration at each depth as a separate im- age. The average brightness of a pigmented region was calculated based only on the melanin compo- nent and defined as the average pigmentation den- sity. To represent the brightness-related frequency distribution of pixels in a digitized image, a new method employing two parameters was developed. Using this method to display the melanin profile in skin, it is possible to represent the pigmentation condition in images having equal average pigmen- tation densities but different frequency distributions of brightness. Key words: spectral reflectance, melanin, pigmented skin, evaluation, principal component analysis The Effects of Oligosaccharide-Carrying Poly- mers to Skin Cell and Its Cosmetic Applications Hideo Kuroda, Ai Oba, Michio Ochiai, Masao Shaku, POLA R&D Institute of Fundamental Tech- nology, POLA Corporation We examined the biological properties of oligo- saccharide-carrying styrene homopolymers. In cell cultures, of four oligosaccharide species, only lac- tose-carrying polymer (PVLA) increased fibroblast cell attachment. And PVLA showed biological ac- tivities as substratum like an extracellular matrix, that promoted cell proliferation, collagen and gly- cosaminoglycan (GAG) synthesis. In animal skin, PVLA not only increased epidermal cell mitotic ac- tivity, but also improved recovery of UVB induced photoaged skin surface textures. Moreover, after 1 month usage of 1% PVLA contained cream on faces of middle-aged women, their skin elasticity was in- creased significantly. Therefore, we considered PVLA was an effective ingredient for anti-aging cos- metics. Key words: lactose-carrying styrene homopolymer, PVLA, extracellular matrix, collagen, glycosamino- glycan, keratinocyte, fibroblast cell, cell prolifera- tion, skin elasticity, anti-aging A New Method for Direct and Instantaneous Measurement of Skin Texture Koichi Shimoto**, Tsunenori Honda*** Fundamental Research Laboratories, Research & De- velopment Division, KOSE Corporation**, Faculty of Engineering, Tokyo University of Agriculture and Technology*** Objective measurement and evaluation of skin sur- face conditions is important in developing effective cosmetics. Three-dimensional (3D) depiction of skin characteristics such as wrinkles and skin texture is crucial to this evaluation. In recent years, many methods based on image processing for measuring skin surface characteristics have been proposed. However, conventional methods have many prob- lems. Some measure only skin replicas and some require keeping test subjects for long periods of time. There is clearly a lack of quick and accurate means of measuring important skin surface charac- teristics. A new and unique method for accurately measuring the 3D characteristics of human skin directly and instantaneously is proposed here. This method involves direct measurement of the skin. From multiple monocular gray images recorded under various optical conditions, 3D shapes of the skin texture are reconstructed through image processing that is derived from integration of nor- mals over the entire surface. With conventional methods, it is impossible to accurately reconstruct the complex shapes and varying complexions of hu- man skin. However, our proposed method enables reconstruction of the complex 3D shapes from theoretical solutions based on vector equation. When the object is multi-colored, this method per- mits reconstruction of the shape from estimation of reflectance using new restricting conditions based on surface free energy. To increase the speed of measurements, a new method was devised to simul- taneously process multiple images recorded in color, categorizing them by wavelength, using our new equation to avoid the problems in color of ob- jects. A new measurement system has been con- structed from our theory and tested on different specimens. The new device required only 0.03 s for each image recording and the average square error of reconstruction was only 0.0026. Clearly, this method offers significant advantages over conven- tional methods. Key words: direct measurement, human skin, tex- ture, 3D shape, color image Preparation of Ultra Fine Emulsion by Phase Inversion Temperature (PIT) Emulsification Yoshikazu Konno, Yoshio Sugaya, Midori Hirobe, Emi Hokao, Product Research Laboratory, KOSE Corporation
ABSTRACTS 207 Phase inversion temperature (PIT) emulsification is the method which use the change of the balance for hydrophilic-hydrophobic of nonionic surface active agent. In this study emulsions were assembled ac- cording to PIT emulsification with POE (n) sorbitol tetraoleate (n: 30, 60) and POE (20) hydrogenated castor oil as emulsifier, and were subjected to evalu- ation of particle size and storage stability. Thus in order to obtain ultra fine emulsion with less than 200 nm in diameter, the combination of emulsifier and oil is important. Stability of ultra fine emulsion prepared with POE (20) hydrogenated castor oil was good on the other hand prepared with POE (n) sorbitol tetraoleate (n: 30, 60) depended on oils. We could obtain ultra fine and stable emulsion with mixture of the emulsifiers for various oils. Key words: phase inversion temperature, emulsifi- cation, ultrafine emulsion, POE (30) sorbitol tetra- oleate, POE (60) sorbitol tetraoleate, POE (20) hy- drogenated castor oil, particle size, storage stability, emulsifier, oil
Purchased for the exclusive use of nofirst nolast (unknown) From: SCC Media Library & Resource Center (library.scconline.org)