HEMP-SEED AND OLIVE OILS 235 EVALUATION OF THE PHOTOSTABILITY OF CHLOROPHYLL Chlorophyll is a photosensitive molecule that may undergo structural changes on ex posure to light, possibly influencing lipoperoxidation. The formation of conjugated double bonds may be accelerated under the influence of free radicals derived from the photodegradation of chlorophyll. We thus evaluated its photostability by irradiating hemp-seed and extra-virgin olive oils under UV A and under visible light for increasing durations of time. At each scheduled time the irradiated oil samples were examined spectrophotometrically. Oil samples were placed in Pyrex containers 10 cm from the UVA or OSRAM (solar spectrum) lamp. Spectrophotometric analysis was done after 30, 90, and 180 minutes of irradiation, as described above. The radiation intensity emitted by the UV A lamp was measured, as for the UVB lamp, and was 1.89 x 10-- 4 W cm- 2 • Standard solar radiation intensity is 1.1 x 10- 3 W cm- 2 (12), slightly above that of the UVA lamp used. DETERMINATION OF VITAMIN E IN HEMP OIL Vitamin E (tocopherol) is a lipophilic compound contained in small amounts in the non-saponifiable matter of oils. Tocopherols are efficient antioxidants if present in the optimal ratio versus PUFAs (the tocopherol/fatty acid ratio should be above 0.8). Vi tamin E content was determined by HPLC under the following conditions: • Column: Supersphere 100-RP 18 (length 5 cm, internal diameter 4.6 cm) • Eluent: ethanol/water: 92/8 • Flow: 1.2 ml/min • Detector: UV (A. = 295 nm) • Retention time: 12 min Two samples of the 1998 hemp-seed oil and two of the 1999 batch were dispersed in methanol at a 1:2 ratio, stirred on vortex, and centrifuged at 6000 rpm for 10 minutes to promote passage of tocopherols into the alcoholic phase. A calibration curve versus the standard reference substance (a-tocopherol) was made to determine concentration. Standard solutions containing three different concentrations of a-tocopherol were analyzed by HPLC under the above conditions. The calibration curve was linear, indicating low standard error and high correlation coefficients within the concentration range. Oil samples were then analyzed by HPLC under the above condi tions. FORMULATIVE STUDIES DETERMINATION OF APP ARENT VISCOSITY The viscosity of the emulsions was determined at 25 ° C ± 0.1 °C using a Brookfield viscometer with a small SC 029 adapter chamber. The determinations were performed at 5 s- 1 shear stress on 13 g of each sample.
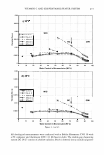
236 JOURNAL OF COSMETIC SCIENCE RHEOLOGICAL RUNS (13-15) In order to reveal any structuring or destructuring of the systems, flux rheograms were determined on 13 g of each sample, in steady-state conditions at 25 ° C ± 0.1 °C, using a Brookfield viscometer with a small SC 029 adapter chamber. Shear stress values were determined at increasing and decreasing shear rates, with each shear rate maintained for one minute. pH DETERMINATION pH values were determined on each sample at room temperature before and after heating to 40°C for 24 h. CENTRIFUGE TEST An accelerated test of emulsion stability was performed by centrifuging a small amount of each sample in an Eppendorf® centrifuge at 3000 and 4000 rpm, checking for outcrop or phase separation every 10 minutes. PREPARATION OF EYE GEL-EMULSION WITH VEGETABLE OILS The emulsion was prepared employing (a) as lipid, hemp-seed, olive, or extra-virgin olive oils and (b) as rheological modifier with emulsifier activity, Carbopol 1382® (acrylates/ Cl0-30 alkyl acrylate crosspolymer) neutralized with a 10% NaOH aqueous solution. The polymer was dispersed in the aqueous phase, heated to 60°C under stirring with Ultra Turrax T 25 homogenizer. The lipid phase was then added to the aqueous phase, homogenizing until the system reached room temperature. An aliquot (0.272%) of 10% NaOH aqueous solution was added to the emulsion until it became homogeneous. PREPARATION OF SPRAYABLE AFTER-SUN FLUID CREAMS (MILK) WITH VEGETABLE OILS Recent research has focused on sprayable cosmetic products, whose functional and sen sory characteristics meet market demands. These products are generally emulsions with high viscosity, though they are sprayable using a device intended for liquids. Fluid sprayable creams meet consumer demands for cosmetics that are easy to apply. The emulsions were prepared employing, as lipid, the hemp-seed, olive, or extra-virgin olive oils and, as rheological modifier, Pemulen TR-1 ® (acrylates/Cl0-30 alkyl acrylate cross polymer) neutralized with 18% NaOH aqueous solution. The emulsifiers employed in their preparation were Polysorbate 20 (Tween 20®), Polysorbate 40 (Tween 40®), Peg- 40-hydrogenated castor oil (Cremophor RH®40), methyl glucose sesquistearate (20) OE (Glucamate SS E20®), and LRI® solubilizer. The gels were initially obtained by dis persing the polymer in cold water and homogenizing with Ultra Turrax T25 for about one minute. The system was then neutralized by adding an aqueous solution of NaOH under mild stirring. 0/W emulsions were subsequently obtained by slowly adding the emulsifiers and oils to the aqueous phase under homogenization. The sprayable emul sions were then characterized through pH determination, test of centrifugation, and studies of viscosity and rheological behavior, following the methods described above. Some
Purchased for the exclusive use of nofirst nolast (unknown) From: SCC Media Library & Resource Center (library.scconline.org)