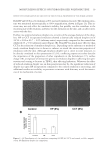
18-MEA DEPOSITION ON HAIR 35 angles, 70, 45, 25, 15, and 10 degrees, in a high-energy resolution mode with pass energy of 112 eV. RESULTS CHARACTERIZATION OF ALKALINE-COLOR-TREATED WEATHERED HAIR Surface properties of alkaline-color-treated weathered hair are shown in Figure 1. Since 18-MEA is covalently bound to the cuticle surface via a thioester linkage, it can be re- moved with alkaline treatments such as perming, coloring, and bleaching. It is well known that the reduction of 18-MEA affects surface properties of hair such as hydrophobicity and friction. Figure 1(A) shows the relative ion yield of 18-MEA versus the total ion yield on the outermost surface of hair measured by TOF-SIMS. In the case of alkaline-color-treated weathered hair, most of the 18-MEA has been removed. Figure 1(B) shows the hydropho- bic property of normal hair and alkaline-color-treated weathered hair. A higher value means that the surface is more hydrophobic, and a lower value means that the surface is more hydrophilic. The contact angle of normal hair was around 90°, which means that it was hydrophobic because of the presence of 18-MEA. On the other hand, that of alkaline- color-treated weathered hair was around 65°, which means that it was more hydrophilic because of the absence of 18-MEA and the oxidation of sulfur groups to sulfate. Figure 1(C) shows the dynamic friction coeffi cients of normal hair and alkaline-color-treated weathered hair. It shows that surface friction increased when 18-MEA was removed. Since it was confi rmed that the results obtained here correspond to previous knowledge, alkaline-color-treated weathered hair was used in the subsequent experiments. The objective for this study was to attach 18-MEA onto alkaline-color-treated weathered hair and to provide persistent hydrophobicity and low friction on an alkaline-color-treated weathered hair surface. In the following sections, contact angles after one instance of shampooing were measured in order to make sure that the damaged hair surface main- tained its hydrophobicity even after shampooing. Figure 1. Surface properties of alkaline-color-treated weathered hair. Relative ion yield of 18-MEA versus the total ion yield (A), contact angle (B), and dynamic friction coeffi cient (C) are presented. The bars repre- sent means for n=5 the whiskers represent the standard deviations. (a) Normal hair. (b) Alkaline-color- treated weathered hair.
JOURNAL OF COSMETIC SCIENCE 36 APPLICATION OF 18-MEA AS AN ACID FORM Contact angles of alkaline-color-treated weathered hair treated with 18-MEA as acid type are shown in Figure 2. When the alkaline-color-treated weathered hair was treated with 1 wt% of 18-MEA in chloroform, the contact angle became 90°, corresponding to that of normal hair (Figure 2c). That means the surface of the alkaline-color-treated weathered hair recovers hydrophobicity just after 18-MEA application. The contact angle decreased after shampooing (Figure 2d), however, meaning the surface reverts to being hydrophilic. This is because 18-MEA applied as an acid form does not have shampoo resistance. APPLICATION OF 18-MEA AS A SALT OR COMPLEX Contact angles of alkaline-color-treated weathered hair treated with 18-MEA salts or polymer complexes and subsequently shampooed are shown in Figure 3. The contact angles of all samples were almost the same as that of alkaline-color-treated weathered hair. These results indicate that these 18-MEA salts or complexes could not provide per- sistent hydrophobicity to an alkaline-color-treated weathered hair surface. Contact angles of alkaline-color-treated weathered hair treated with 18-MEA and long- chain tertiary amine or quaternary cationic surfactant complexes in conditioners, after one-time shampooing with a plain shampoo [15 wt% of sodium polyoxyethylene lauryl Figure 2. Contact angle of alkaline-color-treated weathered hair treated with 18-MEA as an acid form. The bars represent means for n=5 the whiskers represent the standard deviations. (a) Normal hair. (b) Alkaline- color-treated weathered hair. (c) Alkaline-color-treated weathered hair treated with 18-MEA as an acid form (1 wt% of 18-MEA in chloroform was applied). (d) Alkaline-color-treated weathered hair treated simply with 18-MEA as an acid form and shampooed. Figure 3. Contact angle of alkaline-color-treated weathered hair treated with 18-MEA salts or complexes after shampooing. The bars represent means for n=5 the whiskers represent the standard deviations. 1 wt% of 18-MEA salt or complex in water was applied. (a) Sodium salt. (b) Potassium salt. (c) Ammonium salt. (d) Monoethanol amine salt. (e) Cationic hydroxyethyl cellulose complex (polyquaternium-10). (f) Guar hydroxypropyltrimonium complex.
Purchased for the exclusive use of nofirst nolast (unknown) From: SCC Media Library & Resource Center (library.scconline.org)