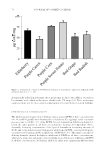
PROPERTIES OF ANTHOCYANIN-PIGMENTED LIPSTICK FORMULATIONS 71 that of the lipstick base alone when analyzed by one-way ANOVA (p value 0.05). Inter- estingly, when the inhibitory percentages of the lipstick formulas were analyzed against that of their respective ACN extract in methanol, no signifi cant differences were found at all three concentrations. These results may be suggesting that the ACNs are behaving in a similar manner to their reducing behavior in solution. The free radical scavenging ca- pacity of each formula extract, expressed as IC50 values, is shown in Figure 4. The antioxidant activity in order from highest activity found was as follows: the purple corn formula (4.87 ± 0.28 μg/mg), elderberry formula (13.35 ± 0.21 μg/mg), purple sweet potato (13.44 ± 0.01 μg/mg), red radish (14.49 ± 1.30 μg/mg), purple carrot (28.59 ± 2.65 μg/mg), red grape skin (31.18 ± 0.68 μg/mg), and, fi nally, the base lipstick Figu re 3. UV absorbance of ACN–lipstick formulations compared with the lipstick base in ethanol. Results are means (n = 8 ± SD). Tabl e I Calculated In Vitro UVB SPF Values Determined from Ethanolic Extracts of ACN–Lipstick Formulations Compared with the Lipstick Base Lipstick formulation Calculated UVB SPF Base 8.19 Elderberry 13.85 Purple carrot 11.27 Purple corn 11.62 Purple sweet potato 14.44 Red grape 11.39 Red radish 15.84 Calculations based on absorbance values in the UV wavelength range of 290–320 nm.
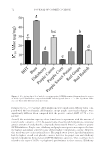
JOURNAL OF COSMETIC SCIENCE 72 formula (46.72 ± 0.67 μg/mg). All formulations were signifi cantly different when com- pared with the base formula. All formulas, except purple carrot and red grape, were signifi cantly different when compared with the positive control, BHT (25.78 ± 2.66 μg/mg). Overall, the antioxidant capacity values found were in agreement with the amount of total phenolic content (r = 0.97). In general terms, those lipstick formulations containing greater amounts of total phenolic compounds demonstrated lower IC50 values or greater DPPH inhibition. Purple corn, elderberry, and purple sweet potato were expected to have the highest antioxidant activity because of their higher total phenolic content. However, this trend was not consistent in all cases. The purple sweet potato lipstick formulation had the highest overall total phenolic content however, the purple corn and elderberry lipstick formulations showed greater DPPH inhibition capacities. This could have been related to the types of ACNs or polyphenols predominant in those extracts. Elderberry Figu re 4. IC50 (μg/mg lipstick) of radical scavenging against DPPH determined from methanolic extracts of ACN–lipstick formulations compared with BHT and the lipstick base (n = 5 ± SD). Signifi cant differ- ences are denoted by different letters above bars.
Purchased for the exclusive use of nofirst nolast (unknown) From: SCC Media Library & Resource Center (library.scconline.org)