513 SIMPLIFIED SALT-ASSISTED SOLVENT EXTRACTION methanol of chromatographic grade were purchased from Fisher Scientific Chemical Division (Fair Lawn, NJ, USA). Other chemicals were of analytical grade. PROPOSED METHOD Preparation of mixed standards solutions. Two standard stock solutions containing the target compounds was prepared employing methanol as solvent. From this solution, working standard solutions were daily prepared in the same solvent. The concentrations are as follows: 1. Standard solution 1: 0.0943 mg/mL for R1, 0.2034 mg/mL for Rg1, 0.0788 mg/mL for Re, 0.2085 mg/mL for Rb1, 0.1337 mg/mL for Rd. 2. Standard solution 2: 0.1161 mg/mL for R1, 0.2394 mg/mL for Rg1, 0.0464 mg/mL for Re, 0. 4165 mg/mL for Rb1, 0.2714 mg/mL for Rd. All these solutions were stored at 4°C and brought to room temperature before the solutions were used. Sample preparation. For sample preparation, 5 g (±2 mg) toothpastes and 1 g (±2 mg) anhydrous magnesium sulfate were added to 50 mL centrifuge tubes. Twenty mL methanol was added and the tubes were vortex mixed for about 20 s until the paste was dispersed in methanol (no deposition was found at the bottom of the centrifuge tube), followed by ultrasonic extraction for 30 min at 35 Hz, centrifugation at 4,000 rpm for 5 min, then the supernatant was poured into the evaporating dish. The previous extraction was repeated once, and the supernatant was combined twice and evaporated by water bath. After the evaporating dish was cooled, it was redissolved in methanol to 10 mL with constant volume, centrifugation set at 6,000 rpm for 10 min, filtered by 0.22 μm microporous membrane, and then the continued filtrate was taken to obtain the test solution. Compound R1 R2 R3 Formula Molecular weight notoginseng R1 H Glc(2- 1)Xyl Glc C47H80O18 933.13 ginsenoside Rg1 H Glc Glc C42H72O14 801.01 ginsenoside Re H Glc(2- 1)Rha Glc C48H82O18 947.15 ginsenoside Rb1 Glc(2- 1)Glc H Glc(6- 1)Glc C54H92O23 1109.29 ginsenoside Rd Glc(2- 1)Glc H Glc C48H82O18 947.15 OH OR 3 R 1 O R 2 Figure 1. Core structure of the ginsenosides referenced in this work. The abbreviations for the functional groups are as follows: Glc glucose, Rha rhamnose, Xyl xylose.
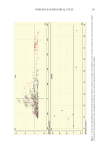
514 JOURNAL OF COSMETIC SCIENCE Chromatographic analysis. Ten μL of the standard or sample solution were injected into the column set at 30°C. The elution was performed at 1 mL min−1 flow rate with an acetonitrile and water mixture as mobile phase, in gradient elution mode. Detection wavelength for signal monitoring was fixed at 203 nm and runtime was set at 76 min. The elution gradient program is shown in Table I. RESULTS AND DISCUSSION STUDY OF THE CHROMATOGRAPHIC VARIABLES Different mobile phase composition, pH, and solvents may affect the analysis process, such as retention time, resolution factor, peak shape, and so on. Especially when toothpaste matrixes are complex, many impurities cause peaks to overlap. The commonly used raw materials in toothpaste, such as benzyl alcohol, sorbitol, and glycerol, all contain benzene ring, conjugated double bond, or other transition forms, and are absorbed in the UV region. Although their maximum absorption wavelength is not 203 nm, it will still affect the separation and detection, especially when their polarity is close to that of saponins. So we chose gradient elution. Acetonitrile and H 2 O are the most commonly used mobile phases for saponins separation (10–11), different ration determines different elution capacity. Figure 2 shows typical HPLC chromatograms of notoginseng R1, ginsenoside Rg1, Re, Rb1, and Rd. Figure 2A is the chromatogram of standards. Figure 2B is the chromatogram of toothpastes containing notoginseng R1, ginsenoside Rg1, Re, Rb1, and Rd after extraction. STUDY OF THE SAMPLE PREPARATION VARIABLES In the preparation of toothpaste samples, a liquid–liquid extraction was carried out using methanol as extraction solvent and magnesium sulfate as assist. The effect of the extraction solvent and auxiliary extraction methods were studied. We studied various solvent/water blends, including methanol/water (100%, 85%, 50%, v/v), ethanol/water (100%, 85%, 50%, v/v), water, and water-saturated n-butanol. 100% methanol and 100% ethanol both provided higher recovery than others, but ethanol reduced the separation of peak ginsenoside Rg1 and Re, and resolution was below 1.5. Water-saturated n-butanol extraction followed by 70% ethanol/water eluting column chromatography also provided a recovery with above 85%, but its precision was too poor, Table I Elution Gradient Program t/min H2O/% Acetonitrile/% 0 81 19 17 81 19 60 64 36 70 64 36 70.1 10 90 75 10 90 75.1 81 19 76 81 19
Purchased for the exclusive use of nofirst nolast (unknown) From: SCC Media Library & Resource Center (library.scconline.org)