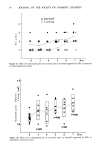
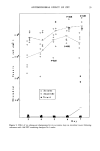
J. Soc. Cosmet. Chem., 33, 19-25 (January/February 1982) Analysis of 1,4-dioxane in ethoxylated compounds by gas chromatography/mass spectrometry using selected ion monitoring BRUCE A. WALDMAN, Union Carbide Corporation, Tarrytown Technical Center, Tarrytown, NY 10591. Received August 31, 1981. Synopsis A combined GAS CHROMATOGRAPHIC/MASS SPECTROMETRIC method for the analysis of 1,4-dioxane has been developed using SELECTED ION MONITORING of its molecular ion. The specificity obtained eliminates the need for extensive sample pre-treatments. Samples are diluted with an aqueous or methanolic solution of perdeuterotoluene (internal standard). Separation is accomplished by direct injection onto a Chromosorb 103 column. The peak area of 1,4-dioxane is ratioed to that of perdeuterotoluene and compared to a standard mixture. A detection limit comparable to the Birkel method of 0.5 mg/kg is readily obtained. Comparisons with data obtained from the Cosmetic Toiletry and Fragrance Association round robin study of 1,4-dioxane analysis, show good agreement between this method and the standard Birkel procedure for samples of Sodium Laureth Sulfate, Polysorbate 60, and PEG-8. Up to 15 determinations can be made in an eight-hour day (13 samples, 2 standards) with a relative precision of + 10% at a 1.0 mg/kg concentration. INTRODUCTION The Cosmetic Toiletry and Fragrance Association (CTFA) sponsored a round robin study to compare methods for the analysis of 1,4-dioxane in ethoxylated matrices (1). This study served to obtain an interlaboratory correlation of the accepted Birkel procedure (2) and to investigate new methodology. The types of ethoxylated compounds studied were Sodium Laureth Sulfate, Polysorbate 60 and PEG-8. The method described here was used in the study under the code-laboratory 18. The development of a combined Gas Chromatographic/Mass Spectrometric (GC/MS) method for 1,4-dioxane was begun to fulfill the need for a rapid, selective 1,4-dioxane analysis for both volatile and non-volatile samples. The Birkel method is labor intensive, restricted to non-volatile samples and capable of running only two or three samples per day. Direct injection methods are faster but generally require a specialized and dedicated GC system (3). Methods such as purge/trap GC and headspace GC have suffered from poor sensitivity and precision and show best utility on non-volatile samples. 19
20 JOURNAL OF THE SOCIETY OF COSMETIC CHEMISTS GC/MS analysis using selected ion monitoring eliminates the need for prior separation and concentration of 1,4-dioxane due to the excellent selectivity of detection. Dedicated equipment is not required the instrument is used unmodified. Sample analysis is rapid requiring 15-30 minutes per determination with no backflushing or specialized column treatment needed between determinations. A detection limit of 0.5 mg/kg can routinely be obtained. EXPERIMENTAL APPARATUS A Hewlett Packard 5992 B benchtop GC/MS was used throughout this study. The Hewlett Packard Flexible Disk Software was used for convenience but the standard tape software is satisfactory. The column used was 2 mm x ! mm glass, Chromosorb 103 (60/80). The porous polymer was pre-treated by Soxhlet extraction with acetone then toluene and vacuum dried. Operating conditions are listed in Table I. Table I Operation Conditions Gas Chromatography--Chromosorb 103 (60/80), 2mm x lmm glass column He Flow--25 cm3/min Initial Temperature--100øC Final Temperature--200øC Program Rate--8øC/min Injection Port--150øC Solvent Wait--8.0 min Run Time--11.0 min Mass Spectrometry Ion Monitored (amu) 88.00 98.00 Dwell Times (msec) 1000 100 Mass Window (amu) _+0.15 _+0.15 CHEMICALS The methanol used was HPLC grade obtained from J.T. Baker (Phillipsburg, NJ). Perdeuterotoluene (99+ %) was purchased from Aldrich Chemicals (Milwaukee, WI). 1,4-dioxane was purchased from Burdick & Jackson Laboratories Inc. (Muskegon, MI). Chromosorb 103, 60/80 mesh, (Johns Mansville Co.) was purchased from Supelco, Inc. (Bellefonte, PA). All water used was reagent grade obtained from a Millipore Milli-Q water system. PREPARATION OF STANDARD SOLUTIONS Calibration standards were prepared from a stock solution made by diluting 1.00 g of 1,4-dioxane to 100 ml with methanol. From this solution standards of 0.5, 1.5, 10 and 100 mg/l are made by dilution.
Purchased for the exclusive use of nofirst nolast (unknown) From: SCC Media Library & Resource Center (library.scconline.org)