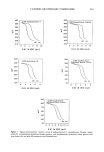
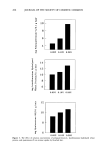
268 JOURNAL OF THE SOCIETY OF COSMETIC CHEMISTS 10 rain, 23øC 10 min, 35øC 10mln. 23øC 10 min, 35øC o o 12 10 - 8 - to min, 23øC 10 min 35'C Figure 5. The effect of temperature on the sorption of quaternium-26, stearalkonium chloride, and laurdimonium hydrolyzed wheat protein by bleached hair.
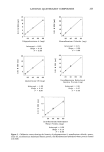
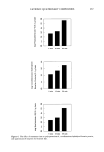
CATIONIC QUATERNARY COMPOUNDS 269 NV T P1X P•X BIX B•X 11 lO 9 8 7 6 5 4 2 1 o NV T P1X P2X B1X B2X Figure 6. The effect of condition and cysteic acid content of hair on stearalkonium chloride and laurdi- monium hydrolyzed wheat protein sorption (NV = normal virgin hair T = tinted hair P IX, 2X -- one-time, two-time permed hair B1 X, 2X = one-time, two-time bleached hair). bleach. Other indications of hair damage may be obtained from the measurement of cysteic acid content which, in a study of the effects of reactive chemical processes on hair, was shown to be pronounced at the cuticle layer of the hair (17). Two examples are displayed in Figure 6: uptake of stearalkonium chloride and laurdimonium hydrolyzed wheat protein at various hair conditions. As the hair became more damaged (increase of wt% cysteic acid), the amount of cationic compounds adsorbed to hair increased. This phenomenon has been well recognized (11,13,19). By the same token, hair with oxi- dative damage adsorbs cationic compounds more readily than hair with reductive dam- age. The results suggest a phenomenon in which the cationic ammonium compounds are
Purchased for the exclusive use of nofirst nolast (unknown) From: SCC Media Library & Resource Center (library.scconline.org)