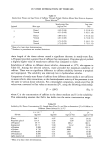
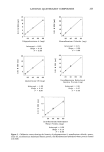
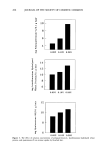
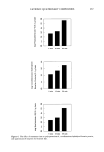
270 JOURNAL OF THE SOCIETY OF COSMETIC CHEMISTS attracted by the anionic sulfonate group of the cysteic acid at the outer layer of the hair fiber. Relative comparison of the substantivity of the cationic compounds can also be made on the basis of their equivalent weight. Quaternary molecules having higher equivalent weight exhibit better substantivity. In the present study, an apparent equivalent weight of the compounds tested can be readily calculated from the calibration curves (Figure 2) by the following equation: Equiv wt (mg/mequiv) = slope x Ns•)s where slope = slope of the appropriate calibration curve (mls•)s/mg cationic compound) Ns•)s = normality of SDS titrant (0.01 mequiv/ml) Table II shows the calculated equivalent weights obtained from the potentiometric titration method under the tested conditions. These values may not represent the "true" equivalent weight of the cationic compounds since their titration is based on the assumption of a complete 1:1 ion pair interaction. For example, the calculated value for stearalkonium chloride is 357 mg/mequiv whereas the theoretical value is 423 mg/ mequiv. Among other factors, titratable impurities in the commercial grade samples are possibly accountable for such a discrepancy. Table II also shows the quantitative uptake of the quaternary compounds by bleached hair that was treated at 35øC for 30 minutes with a 0.05% solution of the cationic compound. The calculated equivalent weights display an order of stearalkonium chloride • cocodimonium hydrolyzed keratin protein quaternium-26 laurdimonium hy- drolyzed wheat protein polyquaternium-4. This trend is similar to the order of the substantivity of these compounds to hair, i.e., stearalkonium chloride • cocodimonium hydrolyzed keratin protein quaternium-26 laurdimonium hydrolyzed wheat pro- tein. Polyquaternium-4, having the highest equivalent weight, displays the lowest substantivity. This anomaly is not well understood. However, the high rate of increase in substantivity of polyquaternium-4 at higher concentration and longer treatment time is noted (Figures 3,4). Thus, even though a standardized method for the study of the Table II Comparison of the Calculated Equivalent Weight and the Substantivity of Tested Compounds Material Calculated Substantivity using equivalent weight 0.05% solution (mg/mequiv) (mg/0.1 g hair) Stearalkonium chloride Cocodimonium hydrolyzed keratin protein Quaternium-26 Laurdimonium hydrolyzed wheat protein Polyquaternium-4 357 8.65 37O 8.43 526 9.25 714 10.09 833 4.62
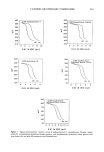
CATIONIC QUATERNARY COMPOUNDS 271 substantivity of cationic compounds has not been developed, based on the present experimental conditions laurdimonium hydrolyzed wheat protein exhibits the greatest substantivity, followed by quaternium-26, stearalkonium chloride, and cocodimonium hydrolyzed keratin protein. The bulk of the present study was performed on aqueous solutions of the quaternary ammonium compounds used neat. Interference by other components (cationic, anionic, or amphoteric) present in formulated products have not yet been fully assessed. How- ever, a potentiometric titration curve of a commercial aqueous-based protein hair con- ditioner (CAT TM , Redken Laboratories, Inc.) shows no apparent interference encoun- tered in titration of a quaternized protein in a complex formulation. The result from this 450 400 350 300 ' •5o 200 150 100 ,too 3õ0 300 250 200 50 i i lO 15 I I I I I 0 2 4 8 8 0.01 M $D$ (ml) I 0 5 (A) I 20 ml of titrant Figure 7. Potentiometric titration curves of a commercial protein conditioner with 0.01 M SDS as titrant (A) and 0.01 M STPB as titrant (B). The titration curve of the neat botanical quatemized protein used in this conditioner is also shown (inset).
Purchased for the exclusive use of nofirst nolast (unknown) From: SCC Media Library & Resource Center (library.scconline.org)