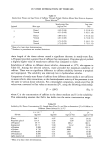
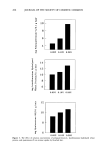
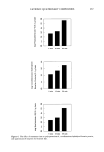
234 JOURNAL OF THE SOCIETY OF COSMETIC CHEMISTS in which the adsorption of polyquaternium-10 by harshly bleached hair continued over a week's time. This latter study served to demonstrate the porous nature of this damaged hair type and the slower diffusion into and adsorption of polymer within the fiber after quick initial adsorption at the immediate outer fiber surfaces. The influence of polyquaternium concentration was also studied by examining 0.10% HMW HEC on cationic adsorption from 0.05 % and 0.20% solutions of the polyquater- nium (Figure 3). Cationic uptake was less from 0.05% polyquaternium-10 solutions when 0.10% HMW HEC was included for both mildly and harshly bleached hair (p = 0.001 and p = 0.062, respectively). There were no differences in adsorbance relative to controls from 0.20% polyquaternium-10 solutions containing HMW HEC for either bleached hair type. Data for these results are found in Table II. Within the 45-minute time frame allowed for adsorption, polyquaternium-10 uptake depends on treatment solution concentration. Compare 2.8 vs 3.5 mg/g hair and 8.6 vs 9.1 mg/g hair in going from 0.05% to 0.20% in polyquaternium-10 (Table II). High-molecular-weight HEC can compete to some degree for adsorption sites with polyquaternium-10 when the latter is at low concentration, i.e. at 0.10% and less, but not at the higher 0.20% concentration. The degree of hair damage also influences competitive uptake. SUMMARY Nonionic cellulosic polymers influence the uptake of polyquaternium-10 by bleached hair. The direction and magnitude of this influence is dependent on both the severity of the bleach treatment and the type of nonionic cellulosic included. Mildly bleached hair shows decreased cationic uptake when high-molecular-weight "' 12 Z 10 O I1. 8 O Q 6 o , 4 Z 2 ":[ 0 ._1 o MILD HARSH BLEACHED HAIR TYPE 0.05% (W/V) POLYQUAT-10 0.20% (W/V) POLYQUAT-10 Figure 3. The effect of polyquaternium-10 concentration and 0.10% HMW HEC on cationic adsorption by bleached hair.
POLYQUATERNIUM- 10 UPTAKE 235 Table II Effect of Polyquaternium-10 Concentration and Addition of 0.10% HMW HEC on Polyquaternium-10 Uptake by Bleached Hair (Average N = 3) Mildly Harshly bleached hair bleached hair (mg/g) (mg/g) 0.05 % Polyquaternium- 10 control 0.05% Polyquaternium- 10/0.10% HMW HEC 0.20% Polyquaternium- 10 0.20% Polyquaternium- 10/0.10% HMW HEC 2.8 (0.1) a 8.6 (0.2) 2.2 (0.1) 8.0 (0.2) 3.5 (0.2) 9.1 (0.3) 3.7 (0.4) 9.5 (0.3) a Numbers in parentheses indicate standard deviation. HEC, HPMC, and HMHEC are included in a cationic treatment solution. This decrease is most likely a result of limited competitive adsorption of the nonionic cellulosic by the hair surface. Harshly bleached hair shows increased cationic adsorption when HPMC or HMHEC are included in cationic treatment solutions. High-molecular-weight HEC reduced polyquaternium-10 uptake for both hair bleach types when included in 0.05% cationic polymer solutions. There was no difference in cationic adsorption from 0.20% solutions containing HMW HEC for either hair bleach type. REFERENCES (1) A. L. L. Hunting, Shampoo thickeners, Cosmet. Toilerr., 97, 53-63 (1982). (2) A. L. L. Hunting, Encyclopedia of Hair Conditioner Ingredients (Micelle Press, Cranford, NJ, 1983), p. 250. (3) M. T. Clarke, Water-soluble cellulose ethers for hair care products, $eifen Ole Fette Wasche, 17, 684-687 (1990). (4) E. D. Goddard and W. C. Harris, An ESCA study of conditioning polymers on hair substrates,J, Soc. Cosmet. Chem., 38, 233-246 (1987). (5) E. D. Goddard, J. A. Faucher, R.J. Scott, and M. E. Turney, Adsorption of Polymer JR on keratinous surfaces--Part II,J. Soc, Cosmet. Chem., 26, 539-550 (1975). (6) Y. K. Kamath, C. J. Dansizer, and H.-D. Weigmann, Surface wettability of human hair. II. Effect of temperature on the deposition of polymers and surfactants, J. Appl. Polym. Sci., 30, 925-936 (1985). J. A. Faucher and E. D. Goddard, Influence of surfactants on the sorption of a cationic polymer by keratinous substrates, J. Colloid Interface Sci., 55, 313-319 (1976). J. A. Faucher, E. D. Goddard, and R. B. Hannan, Sorption and desorption of a cationic polymer by human hair: Effects of salt solutions, Text. Res. J., 47, 616-620 (1977). P. Finkelstein and K. Laden, The mechanism of conditioning with alkyl quaternary ammonium compounds,J. Appl. Polym. Symp., 18, 673-680 (1971). J. M. Hutter, M. T. Clarke, E. K. Just, J. L. Lichtin, and A. Sakr, Colloid titration: A method to quantify the adsorption of cationic polymer by bleached hair,J. Soc. Cosmet. Chem., 42, 87-96 (1991). E. D. Goddard, Substantivity through cationic substitution, Cosmet. Toiletr., 102, 71-80 (1987). Aqualon Company, Product Data Sheet #4032, Wilmington, DE, 1988. Aqualon Company, Product Data Sheet #56.001-USA, Wilmington, DE, 1990. (7) (8) (9) (10) (11) (12) (13)
Purchased for the exclusive use of nofirst nolast (unknown) From: SCC Media Library & Resource Center (library.scconline.org)