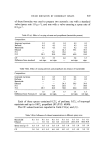
490 JOURNAL OF THE SOCIETY OF COSMETIC CHEMISTS 50 EFA deficiency ,, I I • I I I I 2 3 4 5 6 SSO dosoge 7 8 9 Weeks Figure 2. Simultaneous variations of (x) transepidermal water loss (TWL), (- - -) resistance at zero current and ( ) amplitude of the phoreographical response (SRV) expressed as percentages of the mean values obtained in control rats.
FATTY ACIDS AS REGULATORS OF CELL MEMBRANE FUNCTIONS 491 Chemical analysis Polyunsaturated fatty acid contents of the various lipid fractions of the epidermis are given in Table III. Table III. Determination of essential fatty acids (%) in various lipid fractions of rat epidermis during EFA-deficiency Control rats EFA-deficient rats FFA SE TG PL FFA SE TG PL Linoleic acid 2.9 2.7 6.9 5.2 1.9 1.1 2.3 2.6 Eicosatrienoic acid Trace Trace Trace Trace 0.3 1.7 0.3 3.3 Arachidonic acid 1.1 1.0 Trace 3.6 1.5 2.2 0.1 2.5 FFA, Free fatty acids TG, triglycerides SE, sterol esters PL, phospholipids. Linoleic acid: significant fall in triglycerides and phospholipids. Eicosatrienoic acid: rise in sterol esters and phospholipids. Arachidonic acid: fall in phospholipids (may not be significant). DISCUSSION For the interpretation of the various results, it must be kept in mind that each technique yields information relating to a different kind of cutaneous structure since the phoreographical response originates in the living epidermal cells whereas the water-loss is regulated by the stratum corneum. On the other hand it is obvious that, if SSO is administered orally, any change in the stratum corneum proceeds from a previous change in the living epidermal cells from which this layer is derived. EFA-deficiency primarily affects the living epidermal layers and, secondarily, the kera- tinized cells, after a latent period corresponding to the duration of the keratinization process, i.e. about 18-20 days. This appears clearly when comparing the time-dependent curves for AR and R. Very soon after starting the deficient diet, the phoreographical response undergoes modifications and disappears after 3 weeks, showing the first effects of the deficiency at the level of living epidermal cells. Skin resistance, on the contrary, shows practically no variation for 2 weeks a significant decrease occurred only after about 20 days which delay is consistent with the time required for the keratinization of the first de- ficient cells.
Purchased for the exclusive use of nofirst nolast (unknown) From: SCC Media Library & Resource Center (library.scconline.org)