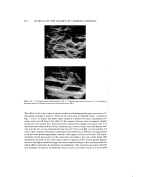
WATER-IN-OIL EMULSIONS 289 aqueous solution of the amino acids was measured by a MK-A type Karl Fischer ap- paratus •* at 35øC measuring point: 1 cm above the interface (constant). (7) Optical Microscopy.' Emulsion particles were observed by means of phase-contrast and polarizing microscopies magnification 400 x. (8) Electron Microscopy,' Specimens were exposed to the saturated osmium tetroxide at- mosphere for 72 h at 4øC, then dehydrated with ethanol and finally embedded in epoxy resin Epon 812. The specimens were sectioned at 500 • thickness by a LKB III type ultramicrotome equipped with a diamond knife and observed under the Hitachi HU- 12A EM. (c). Inorganic-Organic Property Balance (lOB).' The authors make reference to this con- cept in order to correlate the results of the experiment. Fujita (5) proposed the idea of the inorganic-organic property as a tool for predicting the various properties of or- ganic substances. From the physical properties, such as boiling point, refractive index, etc., he gave an empirically specific number to each inorganic and organic property which corresponded to each functional group. Those surfactants capable of forming gels with an aqueous solution of amino acids or their salts are shown in Table I. Table II Table I Classification of the Surfactants Applicable to Gel Formation Appearance X-Ray Surfactant Diffraction Spacing (_•,) Trade Name Common Name RT lOB Pattern d• d• d=/d• Sunsoft O-30B a Glycerol L 0.39 C 33.8 70.7 2.09 monooleate Arlacel 186 b Glycerol L 0.47 C 33.8 73.9 2.18 monooleate G-ElS Glycerol L 0.42 C 33.8 70.7 2.09 monoisostearate POEM O-72-D c Diglycerol L 0.66 C 32.3 67.7 2.10 dioleate DIG-EIS • D•glycerol L 0.47 C 33.0 67.7 2.05 diisostearate PE-EIS Pentaerythritol L 0.53 C 31.5 67.7 2.15 diisostearate Arlacel 83 b Sorbitan L 0.63 C 34.3 73.9 2.15 sesquioleate Emalex e POE (2.4) sorbitol L 0 49 C 33.8 70.7 2.09 EG2854-ol tetraoleate L: Liquid S: Solid, C: Clear I' Indistinct N: No peak. aTaiyo Kagaku Co., Ltd. (62 Akahori, Yokkaichi, Mie, Japan). bKao Atlas Co., Ltd. (1-I Kayaba, Nihonbashi, Chuoku, Tokyo, Japan). CRiken Vitamin Oil Co., Ltd. (3-8-10 Nishikanda, Chiyodaku, Tokyo,Japan). dMatsumoto Trading Co., Ltd. (3-1 Nihonbashihoncho, Chuoku, Tokyo, Japan). e5 Nihon Emulsion Co., Ltd. (5-32-7 Minami, Koenji, Suginamiku, Tokyo, Japan). rSurfactants synthesized by the authors. *Kyoto Denki, 68 Kisyoinshinden, Minamiku, Kyoto, Japan.
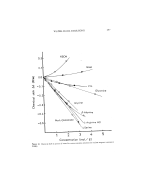
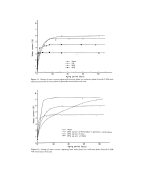
290 JOURNAL OF THE SOCIETY OF COSMETIC CHEMISTS Table II Classification of the Surfactant Lacking the Function of Gel Formation Trade Name Appearance X-Ray Surfactant D•ffracrion Common Name RT lOB Pattern d• Spacing d: d_,/d, G-di-nC8 t Glycerol dioctanoate L 0.58 I 24.2 G-tri-nC• t Glycero[ trioctanoate L 0.33 I 28.0 G-mono-brCa r Gls, cerol mono 2- L 1.24 I 28.5 ethylhexanoate G-d•-brC8 t Glycerol di-2- L 0.6l N -- ethylhexanoate G-tri-brC• r Glycerol rri-2- L 0.35 N -- ethylhexanoate DIG-MO" Diglycerol monooleate L 0.80 I 38.2 DIG-TRO" Diglycerol trioleate L 0.26 I 29.3 DIG-TEO a Diglycerol tetraoleate L 0.17 I 27.7 TENOS ©• Gtycerol monostearate S 0.64 C 58.7 SPAN © 85 • Sorbitan trtoleate L 0.31 C 29.6 Nikkol ©z Batylalcohol S 0.23 C 28.0 GM- 181S monoisostearate Hostaphat ©h Trioleyl phosphate L 0.23 I 32.2 KO-300 Emalex ©e Eths, le neglycol L 0.40 I 30.5 EG-O monooleate EG-OPG-O e Propyleneglycol L 0.38 I 27.4 monooleate EG-O 300 dio • Propyleneglycol L 0.54 I (-) 300 dioleate EG-O 503 • POE(3)oleylethel L 0.57 N -- Nikkol ©• MYO-2 POE(2)oleate L 0.53 N -- POEM ©c O- 105 POE(5)glycerol L 1.03 N -- monooleate (-) (-) (-) -- 86.6 (-) (-) (-) 5%6 44.5 (-) (-) (-) (-) (-) (-) (-) -- 2.27 (-) (-) (-) 2.01 1.59 (-) (-) (-) (-) •Taiyo Kagaku Co, Ltd. (62 Akahori, Yokkaichi, Mie, Japan). OKao Atlas Co., Lid (1-1 Kayaba, N•honbasM, Chuoku, Tokyo, Japan) CRiken Vitamin Oit Co, Ltd. (3-8-10 Nishikanda, Chiyodaku, Tokyo, Japan). dMatsumoto Trading Co., Ltd. (3-1 NihonbasMhoncho, Chuoku, Tokyo, Japan). •5 N•hon Emulsion Co., Ltd. (5-32-7 Minamt, Koenj•, Suginamiku, Tokyo, Japan). •Nippon Fine Chemical Co., Ltd. (4-4-26 Honzanminami, Higashinodaku, Kobe, Japan). "Nikko Chemicals Co., Ltd. (1-4-8 Bakurocho, Nihonbashi, Chuoku, Tokyo, Japan). hHoechst Dyestuffs & Chemicals Co., Ltd. (Frankfurt, Germany). indicates those surfactants which did not produce a suitable gel. The various physical properties of the gel which were evaluated are shown in Figs. 3 to 17 and Tables III to IV. GEL EMULSIFICATION METHOD Materials.' A standard gel was formulated with Sunsoft O-30B and an aqueous solution of monosodium L-glutamate monohydrate. Other surfactants used are shown in Table I. Squalane (special reagent grade) was used as the oil phase. For the formulation of the creams, materials readily available commercially were used.
Purchased for the exclusive use of nofirst nolast (unknown) From: SCC Media Library & Resource Center (library.scconline.org)