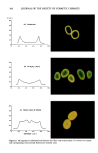
ETHOXYLATION OF HYDROXY ACIDS 321 Table II Ethoxylation of Coco Alcohol With One Mole of Ethylene Oxide Moles of EO Area % EO Contribution Designation [Value A] [Value B] [Value (A) (B)] NO EO 0 54.8 0.000 EO 1 1 19.6 0.196 EO 2 2 10.2 0.204 EO 3 3 6.8 0.204 EO 4 4 5.5 0.220 EO 5 5 2.1 0.105 EO 6 6 0.7 0.042 EO 7 7 0.2 0.014 EO 8 8 0.1 0.008 Total 100.0% Total calculated moles added 0.993 Unlike the kinetics observed with the ethoxylation of fatty alcohols, the base-catalyzed reaction of ethylene oxide with fatty acids is divided into two stages. The first is a stage in which negligible product forms. Slowly, the reaction of the acid and ethylene oxide begins after an induction period to give mostly ethylene glycol monoester. In the second stage, after the addition of about one mole, the reaction rate increases (8). Clearly, the existence of an induction period in the ethoxylation process indicates that the reaction is one of a fatty acid and ethylene oxide, rather than a fatty alcohol and ethylene oxide. As seen in Figure 2, the ethoxylation of fatty alcohols will not occur to an appreciable extent without a catalyst. The catalyst can be either acidic or, more typically, alkaline. Alkaline catalysts generally produce fewer by-products. One of the by-products that is made in the ethoxylation of fatty alcohols is polyethylene 0 0.5 1 1.5 2 2.5 3 3.5 -• Stearic Acid + Stearyl Alcohol Reaction Condition 1. Temperature 150 C 2. Initial Pressure 45 psig 3. Catalyst 0.1 % KOH Time At Reaction Condition (in H .... Figure 1. Moles of ethylene oxide added versus time.
322 JOURNAL OF THE SOCIETY OF COSMETIC CHEMISTS 1.2 . 0••.7_:: .. 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 Time At Reaction Condition •,n. .... • Figure 2. Ethoxylation rate (no catalyst). -•- Hyrdoxy Stearic AcH "•- Lactic Acid -z-- Stearic Acid -u- Stearyl Alcohol Reaction Condition 1. Temperature 150 C 2. Initial Pressure 45 psig 3. No Catalyst glycol. This by-product concentration will be increased by having water present in the fatty material before ethoxylation. Published data (9,10) indicates that the concentrations of PEGs are as follows: Hydrophobe NaOH catalyst Moles EO Ethoxylate PEG Cetyl/stearyl alcohol 1.0 5.0 96.0% 4.0% Lauryl alcohol 1.0 10.0 93.3 % 6.7 % Lauryl alcohol 1.0 20.0 91.8% 8.2% Lauryl alcohol 1.0 50.0 88.5 % 11.5 % FATTY ACID ETHOXYLATION Fatty acids when reacted with ethylene oxide produce complex mixtures of hydroxy esters. Unlike the products formed by the ethoxylation of fatty alcohols which are ethers, esters are formed when ethylene oxide is reacted with fatty acids. In addition to the oligomeric species that form during the reaction of a fatty acid with ethylene oxide, there is an added complication. That complication is the formation of diester. ESTER PRODUCTS Mono ester R - C(O) - O - CH2CH2OH Diester R - C(O) - O - CH2CH2OC(O) - R
Purchased for the exclusive use of nofirst nolast (unknown) From: SCC Media Library & Resource Center (library.scconline.org)