STRUCTURE AND PERMEABILITY OF HUMAN NAIL 379 used to enhance penetration of the antifungal drugs itraconazole (1%) and miconazole nitrate (2%) through the human nail. AC and other sulfhydrl (-SH)-containing amino acid derivatives were considered to be responsible for cleaving the disulfide linkages (-S-S-) in the keratin matrix, whereas urea was added to break the hydrogen bonds and thus facilitate the cleavage of the disulfide linkages. The reaction sequence between the cystine linkages in keratin and cysteine (containing the -SH group) is shown in Figure 6. The enhanced penetration of the antifungals into the nail was demonstrated by nail swelling tests and drug partitioning tests (5,45). The swelling test was used as an indicator of rate and extent of drug uptake by the nail, and the partitioning test was used as a measure of drug migration into the nail. These tests were performed by immersing nail clippings in the test formulation at 32øC for two days, rinsing off the adherent formulation after this period, examining the weight gain, and analyzing for drug content by HPLC (after digestion of the nails). The results from the swelling and partitioning studies for 1% itraconazole formulations containing various cysteine derivatives (5%) and urea (10%) are shown in Table V. In addition to the cysteine derivatives and urea, the formulations tested contained salicylic acid (5%), and the vehicle comprised a mixture of propylene carbonate, propylene glycol, and water. The results in Table V are expressed as swelling and partitioning enhancement factors. The swelling enhancement factor was defined as the ratio of percent weight gain of the test nail sample (with enhancer) to that of the control nail sample (without enhancer). Similarly, the parti- tioning enhancement factor was defined as the ratio of drug concentration in the test nail sample to that in the control nail sample. Table V shows that a promising result was seen for the formulation containing 1% itraconazole, 5% AC, and 10% urea, which resulted in significant nail swelling (threefold greater than control) and drug uptake into the nail (93.6-fold higher than the control without enhancer). In the same set of studies (45), the effect of enhancers (AC and urea) on the i, vitro nail permeation of itraconazole and miconazole nitrate was demonstrated. The permeation studies were conducted using nail diffusion cells of area 0.1202 cm •, wherein the nail separated the donor and receptor compartment. To simulate actual use conditions, the donor chamber was re-dosed with fresh drug formulation at predetermined times (after removing the formulation from a previous application). The receptor fluid used was 20% aqueous hydroxypropyl-lB-cyclodextrin, to ensure that sink conditions were maintained. The amount of drug permeated (in the receptor) and the amount of drug in the nail, as Nail -- S--S--Nail + 2HS-CH:-CH(NH,)-COOH Cysteine 2Nail -- SH + HOOC-CH(NH2)-CH2 • -- S -- CH2-CH(NH:•)-COOH Cystinc Figure 6. Chemical reaction sequence between nail kerntin and sulfhydryl containing amino acid (cysteine). Adapted from reference 5.
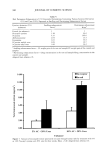
380 JOURNAL OF COSMETIC SCIENCE Table V Nail Permeation Enhancement of 1% Itraconzole Formulations Containing Various Cysteine Derivatives (5%) and Urea (10%), Expressed as Swelling and Partitioning Enhancement Factors Cysteine derivative (5%) Swelling enhancement Partitioning enhancement (enhancer) factor • factor 2 Control (no enhancer) 1 1 N-acetyl-l-cysteine 3.18 93.6 1-Cysteine 4.57 105.0 dl-Homocysteine 2.04 23.5 Cysteamine 3.03 56.5 1-Cysteine methyl ester 2.09 30.7 1-Cysteine ethyl ester 1.82 26.2 • Swelling enhancement factor = (% weight gain of the test nail sample)/(% weight gain of the control nail sample). 2 Partitioning enhancement factor = (drug concentration in the test nail sample)/(drug concentration in the control nail sample). Adapted from reference 45. 14.00 12.00 10.00 8.00 6.00 4.00 2.00 0.00 5% AC + 20% Urea [] In receptor ß In nail 10% AC + 20% Urea Enhancer Figure 7. Amount of miconazole nitrate penetrated into and through human nails by treatment with 5% or 10% N-acetyl cysteine and 20% urea for three weeks. Mean e S.D. Adapted from reference 45.
Purchased for the exclusive use of nofirst nolast (unknown) From: SCC Media Library & Resource Center (library.scconline.org)