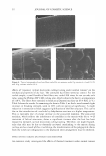
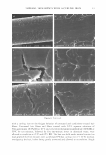
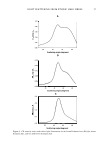
Table I Radiation's Frequency and Wavelength (1): Planck's Equation* Applies, and It Describes the Indirect Proportionality Between the Wavelength of the Radiation** and the Energy That Is Associated With It (the longer the wavelength, the lower the energy) Wavelength, A (m) 10- 12 - 10-10 10-10 - 10-3 (= 10 nm) 10- 3 (10 nm) - 3.8 x 10- 7 (380 nm) 3.8 x 10-7 (380 nm) -7.8 x 10-7 (780 nm) 7.8 X 10-7 - 10-4 10- 4 - 10-2 10-2 - ... * See Appendix I. Radiation )'-rays X-rays UV VIS Infrared Microwaves Radio waves Frequency, v (Hz or s- 1 ) 3 X 1020 - 3 X 10 18 3 X 10 18 - 3 X 10 16 3 X 10 16 - 7.8 X 10 1 4 7 .8 X 10 1 4 - 3.8 X 10 1 4 3.8 X 10 1 4 3 X 10 1 2 - 3 X lQ lO 3 X 10 1 0 - ... Energy of 1 mol of photons* (KJ mol- 1 ) 11.95 X 107 -11.95 X 105 11.95 X 105 - 11.95 X 103 11.95 X 103 - 314 314 - 153 153 - 1.19 1.19 - 1.19 X 10-2 1.19 X 10-2 - •.. ** Very often, the UV radiation is referred to as "UV light" this is strictly speaking inaccurate, as the definition of light implies that it is visible to the human eye. UV radiation is not visible therefore, it is a radiation rather than a light. m 1-Tj 1-Tj m n ,.., 0 C � u ,.., 5 0 z ::r: � ,.., � C n ,.., C � m \0 ---J
98 Bond C-H C-N C=O C-0 S-S 0-H S-H C-C C=C C-S JOURNAL OF COSMETIC SCIENCE Table II Bond Dissociation Energies (BDE) (4,5) Bond dissociation energy (KJ mol- 1 ) 413 293 707 335 213 463 364 348 619 259 It is important to note that although the BDE gives a good idea of the strength of a chemical bond, in practice, solvation can weaken bonds and cause great deviation from the value reported in this table. Solvation occurs when the "bonds" (molecules) are in a chemical environment where secondary chemical bonds are formed, e.g., H-bonds. As for substrate degradation, the IR portion of the energy contributes to increase the temperature of the substrate.a The energy associated with IR radiation is low compared to UV radiation. When the hair structure is considered, both melanin and the proteins compete for the absorption of light between 254 and 345 nm (7). As this article will review some of the most recently published papers on this subject, it will become clear that although it is not immediately perceived, UV damage to hair fibers plays an integral role in the overall aspects of hair damage. UV-RADIATION SOURCES, SOLAR SIMULATOR SYSTEMS Solar simulators are standard equipment for weathering studies. Although natural light is, in most part, readily available, the seasonal variability and the fact that it is available for only half of the day is a drawback. In addition, solar simulators can be set up to expose the sample to light of greater intensity than natural light. Two major factors need to be considered when using an artificial light source: 1. Correlation between natural solar radiation (visible and non-visible) and the artificial light source. Does the exposure to the artificial radiation produce the same effects on the test material as the exposure to natural radiation does? 2. Acceleration factor (if applicable): How many hours in natural light are equivalent to one hour of radiation exposure in the instrument (or vice versa)? A publication by Q-Panel (3) clearly describes the many aspects of establishing the correlation of real sunlight to artificially generated light and UV radiation. a Q-Panel, private communication.
Purchased for the exclusive use of nofirst nolast (unknown) From: SCC Media Library & Resource Center (library.scconline.org)