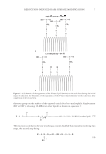
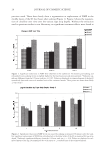
EPDME IMPROVES LAMELLAR LIPID STRUCTURE 47 To evaluate further the effect of EPDME on lipid membranes, we conducted experiments using liposomes. There are many reports of EPR studies on the fl uidity of liposome mem- branes (14,21–24), and the spectra that we obtained with 5-DSA were consistent with these reports (Figure 5). It was confi rmed that, although the lipid membrane structure was disrupted by SDS (the fl uidity is increased, as indicated by a decrease in S of ca. 0.007), pre-treatment with EPDME suppressed this effect (the reduction in S was only 0.003), as shown in Figure 6. Mizushima et al. (16) examined the moisture retention capacity of SC under various con- ditions and suggested that water in untreated SC hydrates the lipid layers and maintains the S value even under very dry external conditions. On the other hand, the amount of water in SC treated with SDS varied, depending on environmental humidity, with corre- sponding changes in the S value (16). It can be speculated that SDS disrupts lamellar structures by solubilizing the lipid components, releasing water of hydration as free wa- ter. Thus, the improvement in membrane structural order by EPDME in SDS-treated SC and liposomes in this study may be attributable to the ability of EPDME to provide bound water at the lipid layers. CONCLUSIONS EPR spectroscopy was used to examine changes in the order parameter of lipid structure in SC successively stripped from SDS-treated dry skin. Application of EPDME partially reversed the disruption of lipid structure due to SDS treatment. Similar improvement was found in SDS-treated liposomes. The low concentration of SDS used did not result in any decrease in TEWL, indicating that EPDME may preserve the ordered lamellar struc- ture of lipids by increasing the level of hydration. ACKNOWLEDGMENTS We thank Professor Noriyuki Kumazawa of Ibaraki University for providing liposomes, and Dr. Koichi Nakagawa of Fukushima Medical University and Dr. Mitsuhiro Denda of the Shiseido Research Center for helpful suggestions. REFERENCES (1) T. Ohmori, Y. Yamamura, K. Nakahara, R. Miyahara, K. Hosokawa, K. Maruyama, T. Okamoto, and H. Kakoki, Development of novel multifunctional cosmetic raw materials and their application. I. Characterization of a random copolymer of polyoxyethylene/polyoxypropylene dimethyl ether, J. Oleo Sci., 55, 365–375 (2006). (2) E. Yagi, K. Sakamoto, and K. Nakagawa, Depth dependence of stratum corneum lipid ordering: A slow-tumbling simulation for electron paramagnetic resonance, J. Invest. Dermatol., 127, 895–899 (2007). (3) E. Yagi, K. Nakagawa, and K. Sakamoto, Establishment of ex vivo stratum corneum lipid ordering analysis by electron spin resonance, J. Soc. Cosmet. Chem. Jpn., 42, 231–236 (2008). (4) J. Mizushima, Y. Kawasaki, M. Ino, K. Sakamoto, M. Kawashima, and H. I. Maibach, Effect of surfac- tant on human stratum corneum utilizing electron paramagnetic resonance spectroscopy, J. Jpn. Cosmet. Sci. Soe., 25, 130–135 (2001). (5) K. Nakagawa, J. Mizushima, Y. Takino, K. Sakamoto, and H. I. Maibach, Chain ordering of stra- tum corneum lipids investigated by EPR slow-tumbling simulation, Spectrochimica. Acta Part A, 63, 816–820 (2006).
JOURNAL OF COSMETIC SCIENCE 48 (6) E. J. Shimshick and H. M. McConnell, Lateral phase separation in phospholipid membranes, Biochemis- try, 12, 2351–2360 (1973). (7) M. Ge, S. B. Rananavare, and J. H. Freed, ESR studies of stearic acid binding to bovine serum albumin, Biochim. Biophys. Acta, 1036, 228–236 (1990). (8) G. Imokawa, S. Akasaki, Y. Minematsu, and M. Kawai, Importance of intercellular lipids in water- retention properties of the stratum corneum: Induction and recovery study of surfactant dry skin, Arch. Derm. Res., 282, 45–51 (1989). (9) Y. Kawasaki, D. Quan, K. Sakamoto, and H. I. Maibach, Electron resonance studies on the infl uence of anionic surfactants on human skin, Dermatology, 194, 238–242 (1997). (10) A. W. Fulmer and G. J. Kramer, Stratum corneum lipid abnormalities in surfactant-induced dry scaly skin, J. Invest. Dermatol., 86, 598–602 (1986). (11) M. Fartasch, Ultrastructure of the epidermal barrier after irritation, Microsc. Res. Tech., 37, 193–199 (1997). (12) J. A. Bouwstra, A. de Graaff, G. S. Gooris, J. Nijsse, J. W. Wiechers, and A. C. van Aelst, Water distri- bution and related morphology in human stratus corneum at different hydration levels, J. Invest. Derma- tol., 120, 750–758 (2003). (13) J. Caussin, G. S. Gooris, H. W. W. Groenink, J. W. Wiechers, and J.A. Bouwstra, Interaction of lipo- philic moisturizers on stratum corneum lipid domains in vitro and in vivo, Skin Pharmacol. Physiol., 20, 175–186 (2007). (14) W. L. Hubbell and H. M. McConnell, Molecular motion in spin-labeled phospholipids and membranes, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 93, 314–326 (1971). (15) J. Mizushima, Y. Kawasaki, T. Tabohashi, T. Kitano, K. Sakamoto, M. Kawashima, R. Cooke, and H. I. Maibach, Electron paramagnetic resonance study, Int. J. Pharm., 197, 193–202 (2000). (16) J. Mizushima, Y. Kawasaki, K. Sakamoto, M. Kawashima, R. Cooke, and H. I. Maibach, Electron para- magnetic resonance: A new technique in skin research, Skin. Res. Technol., 6, 100–107 (2000). (17) J. Mizushima, Y. Kawasaki, T. Kitano, K. Sakamoto, M. Kawashima, R. Cooke, and H. I. Maibach, Electron paramagnetic resonance study utilizing stripping method on normal human stratum corneum, Skin Res. Technol., 6, 108–111 (2000). (18) R. H. Crepeau, S. Saxena, S. Lee, B. R. Patyal, and J. H. Freed, Studies on lipid membranes by two- dimensional Fourier transform ESR: Enhancement of resolution to ordering and dynamics, Biophys. J., 66, 1489–1504 (1994). (19) D. E. Budil, S. Lee, S. Saxena, and J. H. Freed, Nonlinear-least-squares of slow-motion EPR spectra in one and two dimensions using a modifi ed levenberg, J. Magn. Reson. Ser. A., 120, 155–189 (1996). (20) A. O. Barel and P. Clarys, In vitro calibration of the capacitance method (Corneometer CM 825) and conductance method (Skicon-200) for the evaluation of the hydration state of the skin, Skin Res. Technol., 3, 107–113 (1997). (21) S. Ohnishi and T. Ito, Clustering of lecithin molecules in phosphatidylserine membranes induced by calcium ion binding to phosphatidylserine, Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun., 51, 132–138 (1973). (22) R. Simona, F. S. Raymond, and M. Giacomo, ESR as a valuable tool for the investigation of the dy- namics of EPC and EPC/cholesterol liposomes containing a carboranyl- nucleoside intended for BNCT, Biochim. Biophys. Acta, 1712, 81–91 (2005). (23) C. Fini, V. D. Tuoung, M. Aliante, A. Floridi, and S. Cannistraro, Reconstitution of 5′-nucleotidase of bull seminal plasma in spin-labeled liposomes, J. Membrane Biol., 142, 137–144 (1994). (24) M. Dariusz, P. Marian, and E. Grzegorz, The infl uence of tin compounds on the dynamic properties of liposome membranes: A study using the esr method, Cell. Molec. Biol. Lett., 11, 56–61 (2006).
Purchased for the exclusive use of nofirst nolast (unknown) From: SCC Media Library & Resource Center (library.scconline.org)