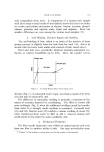
772 JOURNAL OF THE SOCIETY OF COSMETIC CHEMISTS COTSWOLD WOOL ,,••n and Stott] 0 I I • -' 0 1 2 3 l pH Figure 2. The swelling of wool (21) and hair (23) in aqueous HC1 a mixture of proteins, and a total analysis represents an average value. The cuticle contains more cystine than the cortex (15), and there are differences in other amino acids, also (16) the para-cortex of wool con- tains more sulfur than the ortho-cortex (13). It is therefore to be ex- pected that hair, with a higher ratio of cuticle to cortex and a cortex which is wholly para in nature, should differ significantly in its amino Table I Tensile Properties of Merino Wool and Hair at 21øC Property At 65% R.H. (24) In pH7 Buffer (25) Hair Wool Hair Wool Initial modulus, mg cm -2 Stress at yield point, mg cm -2 Stress at 20% extn., mg cm -2 Extension to post-yield, % Post-yield modulus, mg cm -'2 Extension at break, % Stress at break, mg cm -2 55 1.16 . . . . . . ß . . 37 2.0 31 0.62 ß . . 2O 1 1 21 12 0.52 0.45 27 29 5.3 3.4 51 41 1.7 0.8 Table II Dye Uptake of Different Fibers (7) Diffusion Coefficient Fiber Half-Dyeing Time (Hr) (Arbitrary Units) Human hair A 56 7.5 Human hair B 44 7.8 Human hair M 47 8.5 Human hair N 54 8.7 80's Merino wool 1.8 10.7 56's Down wool 2.0 17.4
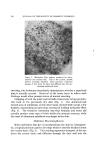
HAIR AND WOOL 778 acid composition from wool. A comparison of a human hair sample with those from several breeds of wool indeed shows the hair to be richer in cystinc and proline and poorer in alaninc, leucine, tyrosine, phenyl- alaninc, glutamic and aspartic acids, lysine and arginine. Real, but smaller, differences are seen among the various wool samples (17). 3. Acid Binding, g/Ioisture Regain and Swelling The acid-binding of hair, which is an index of the number of basic groups present, is slightly lower for hair than for wool (18) this is in accord with the lower basic amino acid content of hair, noted above. Wool and hair have practically identical moisture-adsorption iso- therms at relative humidities up to 95%. Here, the regain* curves Hookean region I I I I I i I i i I _ _11 yield region Post.yield region STRAIN Figure & A typical keratin fiber stress-strain curve diverge (Fig. 1) in saturated water vapor, wool had a regain of 33-34% (19) and hair of about 30% (20). The difference in saturation swelling is probably a function of the extent of restraint imposed by crosslinking. The effect is shown still more strikingly (Fig. 2) when the additional swelling caused by transfer from water to a strongly acidic medium is examined: Cotswold wool (21) and 64's Merino wool (22) exhibit a volume swelling of about 6% when transferred from water to HC1 at pH 1, whereas human hair swells about 3•% under the same conditions (23). 4. g/Iechanical Properties The fiber tensile properties vary within an animal species and even from one fiber to another within a lock. One may nevertheless state * "Regain" is the moisture content based on the dry weight of the material.
Purchased for the exclusive use of nofirst nolast (unknown) From: SCC Media Library & Resource Center (library.scconline.org)