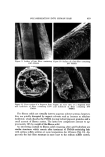
POLYMERIZATION INTO HUMAN HAIR 411 Z 0 3O 2O I0 I I I I I TGA 5 I0 15 20 25 Na H SO• I 30 t (MINUTES) Figure 2. Influence of the reduction step on add-on These data also show a faster initial rate of polymerization with the TGA system than with the bisulfite system, consistent with the faster rate of reduc- tion of disulfide bonds in hair by TGA. The reaction of TGA with human hair has been shown to be diffusion-controlled (5). Therefore, these data show the importance of step 1, i.e., diffusion of the reducing agent into the fibers, to the overall polymerization reaction. Step 2, the chemical reaction of the disulfide bond with TGA is faster than diffusion and, therfore, of lesser importance to the kinetic scheme however, the extent of this disulfide scission is the prime factor that controls the rate of penetration of monomer and initiator into the fibers, and controls the amount of polymer add-on as shown in Fig. 2 and in the scanning electron micrographs.
412 JOURNAL OF THE SOCIETY OF COSMETIC CHEMISTS 01- o o ,t IO I, I 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 I/2 (MINUTES) Figure 3. A•-o• •. po]ymeHz•tio• •me tm•e• co•st•t •e•ucfio• co•t•o•s Lengthy rinses prior to the polymerization step were not required with either TGA or bisulfite as reducing agent. A short 2-rain rinse under the tap was employed, providing reproducible results with a minimum of solution polymerization. Steps 4-9, Additional Aspects of Diffusion Rate Control Experiments were conducted measuring polymer add-on at different poly- merization times. Results from these experiments are plotted in Fig. 3. The initial part of this curve shows a retardation effect, possibly an inhibition time, followed by a reaction linearly related to the square root of time, consistent with diffusion rate control into a cylinder of infinite length (6). Considering the entire reaction sequence, only steps 1, 4, and 6 involve diffusion. The previous section describes how step 1 affects the rate of poly- merization i•l thc fibers. The roles of CHP and MMA concentrations on this reaction are illustrated graphically in Fig. 4 and 5. These plots show that the
Purchased for the exclusive use of nofirst nolast (unknown) From: SCC Media Library & Resource Center (library.scconline.org)