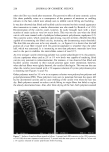
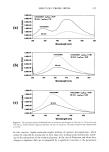
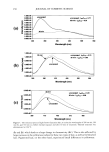
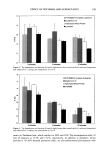
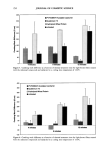
248 JOURNAL OF COSMETIC SCIENCE --ClinCH Ha CH•--• C--O I NH PVP/DMAPA Acrylates Copolymer O O C HT'-C-- O--( C H 2 ) 1-•--C H 3 II I C 17 H3-•--C-- N H--(C H2)•-- •--C H3 CH 3 c, © Quaternium 70 Figure 1. Chemical structures of PVP/DMAPA acrylates copolymer and quaternium 70. and hydrolyzed wheat protein. At these temperatures, 12 min exposure of intact hair results in a 27.5% (132øC) and 50.0% (152øC) loss of Trp. The data in Figures 2 and 3 indicate that modified hair undergoes a slower Trp decomposition as compared to untreated hair. For example, hair modified with quaternium 70 and subjected to 12 min of curling iron exposure at 132 øC undergoes a Trp loss of approximately 22%, providing (27.5% - 22%/27.5% x 100% = 20%) a 20% thermal protection factor. The effect of all treatments was similar, with the protective effect ranging from 10% to 20% and evident even after the shortest exposure times (4 min). We conducted similar experi-
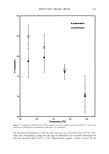
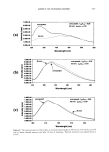
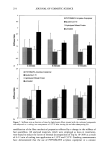
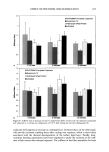
EFFECT OF POLYMERS AND SURFACTANTS 249 9O 8O 75 7O 65 [] PVP/DMAPA Acrylates Copolymer [] Quaternium 70 [] Hydrolyzed Wheat Protein [] untreated 12 minutes Figure 2. Trp degradation as a function of time for light-brown hair treated with the indicated compounds and subjected to a curling iron temperature of 132øC. 8o :r• PVP/DMAPA Acrylates Copolymer [] Quaternium 70 [] Hydrolyzed Wheat Protein [] untreated 6o 55 5o -4 •.•==•..•.• .:• .. .-.-v•........• .:•: ... 4 minutes 8 minutes 12 minutes Figure 3. Trp degradation as a function of time for light-brown hair treated with the indicated compounds and subjected to a curling iron temperature of 152øC. ments on Piedmont hair, which resulted in 40% and 65% Trp decomposition after 10 rain of exposure at 132øC and 152øC, respectively. In addition to polymers, which provided a 10-20% thermal protection effect, we also administered pretreatment with
Purchased for the exclusive use of nofirst nolast (unknown) From: SCC Media Library & Resource Center (library.scconline.org)