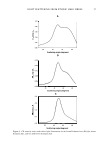
2 JOURNAL OF COSMETIC SCIENCE the ultimate stabilization of 1-ascorbic acid in the aqueous phase has not been reported in the literature. The degradation processes of 1-ascorbic acid are very complex and contain a number of oxidation/reduction and intermolecular rearrangement reactions (13). Scheme 1 shows well the degradation pathway of 1-ascorbic acid in the aqueous solution. Dehydro-1- ascorbic acid, an oxidation form of 1-ascorbic acid, is highly unstable in an aqueous solution, which may convert to a variety of species, such as 2,3-diketo-L-gulonic acid, 1-xylosome, etc. (14, 15 ). An important clue in the degradation process is chat the degradation is initiated by the ionization of the hydroxy groups in the 1-ascorbic acid molecule. The control of ionization may provide us a potential route that can protect fundamentally the degradation of 1-ascorbic acid in the aqueous system. In our previous studies, we developed stable w/o/w double emulsions by two-step emulsification method (16). In those studies it was shown chat the stable w/o/w double emulsions produced can be used as a useful tool for the stabilization of water-soluble, unstable 1-ascorbic acid. In the present contribution, 1-ascorbic acid located in the internal aqueous phase of w/o/w double emulsions was stabilized, controlling the pH and ionization property. The effectiveness was then evaluated according co the experimental parameters. EXPERIMENT AL MATERIALS 1-ascorbic acid (99.9% assay, Shinyo Pure Chemicals, Japan), magnesium sulfate (MgSO4 , Aldrich Chemical Co., USA), and sodium hydroxide (NaOH, Aldrich) were all of reagent grade and used without any further purification. In the preparation of w/o/w double emulsions, the lipophilic primary surfactant was Arlacel P135, a polyethylene glycol (30) dipolyhydroxystearate (Uniquema Americas). The hydrophilic secondary surfactant was Synperonic PE/F 127, an echoxylaced propylene oxide copolymer (ICI, France). Puresyn 4, a hydrogenated polydecene (ExxonMobil Chemical) and xanthan gum (Kelco Biopolymers) were used as oil and emulsion stabilizers, respectively, in the preparation of w/o/w double emulsions. PREPARATION OF w/o/w DOUBLE EMULSIONS The double emulsions were produced by two-step process (17-19). In the first step, L-ascorbic acid was dissolved in water together with MgSO 4 . The adjustment of pH was OH OH I I H OH 2CHC ):: 0 '( 0 .:_:_ H OH 2CHC ti 0 ----+ HO OH O 0 COOH I C=O I C=O I ____. HC-OH I HO-yH CH20H CHO I C=O I HC-OH I HO-yH CH20H L-Ascorbic acid Dehydro-L-ascorbic acid 2,3-diketo-L-gulonic acid L-xylosome Scheme 1. Schematic representation of the degradation of L-ascorbic acid in aqueous solution.
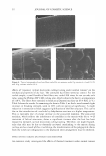
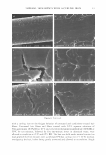
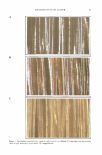
STABILIZATION OF 1-ASCORBIC ACID 3 carried out by adding 10 wt% NaOH solution to the 1-ascorbic acid/MgSO 4 aqueous solution. The total amount of internal aqueous phase was compensated by adding water. Then the primary water-in-oil (w/o) emulsions were prepared by adding slowly the 1-ascorbic acid/MgSO 4 aqueous solution to the oil phase composed of Puresyn 4 and Arlacel P135 at a high temperature (70° ± 5 ° C) while emulsifying at 7000 rpm for 5 min with an MX-5 homogenizer (Nihonseiki Co., Japan). The primary w/o emulsions produced were continuously cooled to room temperature. In the second step, the primary w/o emulsions produced in the first step were reemulsified at 4000 rpm in the aqueous phase containing Synperonic PE/F 127. About 20 g/min was a suitable speed for the primary w/o emulsions. After another 5 min of homogenization, the w/o/w double emulsions produced were stabilized sterically with the aid of a xanthan gum. The w/o/w double emulsions containing 1-ascorbic acid in the internal aqueous phase were then sealed in polyethylene plastic tubes and stored at 40°C. The composition for the pro duction of w/o/w double emulsions is summarized in Table I. OM OBSERVATION Microscopic analysis was carried out to visualize the morphology of w/o/w double emulsions with an optical microscope (OM) (Nikon Microphot FXA). After 1/10 (w/w) dilution of the double emulsions in DDI water, the droplet morphology was captured with a digital camera at room temperature. HPLC MEASUREMENT To determine the concentration of 1-ascorbic acid in the w/o/w double emulsions, HPLC measurements were carried out. After dissolving completely 1 g of w/o/w double emulsions containing 1-ascorbic acid in 10 ml of methanol, the total volume was adjusted to 100 ml by adding DDI water. Ultrasound was applied to the diluted emulsions for 20 min to break up the droplets perfectly. The HPLC sample solutions Table I Standard Composition for w/o/w Double Emulsions Emulsification step Ingredient Concentration (wt%) Primary w/o emulsion" w/o/w double emulsion6 a 75° ± 5°C 7,000 rpm 5 min. b 25 ° ± 5°C 4,000 rpm 5 min. Puresyn 4 Arlacel P 13 5 DDI water MgS04 1-ascorbic acid NaOHc DDI water Synperonic PE/F 127 Primary emulsion Xanthan gumd c Sodium hydroxide aqueous solution was added to adjust pH of internal aqueous phase. l 1 g/dl aqueous solution. 15.5 2 29 (variable) 0.5 3 (variable) Variable 39 1 50 10
Purchased for the exclusive use of nofirst nolast (unknown) From: SCC Media Library & Resource Center (library.scconline.org)