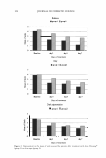
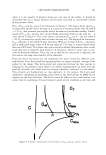
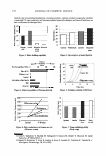
202 JOURNAL OF COSMETIC SCIENCE o_ i� •- II .Cl .c :c.e .E II 45% 40% 35% 30% 25% 20% • '";- 15% = 10% 5% 0% 1 % Extrapone Honeysuckle (0.0008% Ollorogenic acid*) 1 % Extrapone A.leraria (0.0017% A.lerarin*) 1 % Extrapone Sophora (0.00103% Rutin*) * Concentration of the major component in 1.0 % Extrapone Figure 1: IL-I alpha inhibition ofTCM Extracts and the respective major components. 90% 0% 0.1 % Exlrapone Honeysuckle (0.00008% Chlorogenic acid*) 0.1% Exlrapone Pueraria (0.00017% Puerarin*) 0.1% Exlrapone Sophora (0.000103% Rutin*) * Concentration of the major component in 0.1 % Extrapone Figure l: Antioxidant capacity ofTCM Extracts and the respective major components. Conclusion Extracts from the TCM plants Japanese honeysuckle (Lonicera japonica), kudzu (Pueraria /obata) and Japanese pagoda tree (Sophora japonica) exhibit potent anti-irritant activity in human epidermal keratinocytes. The anti- irritant activity of these extracts does not correlate with their radical scavenging activity. Moreover, only a small part of the anti-irritant and anti-oxidant activity of the extracts could be ascribed to the respective major ingredients. Thus, the presence of several ingredients in a botanical extract is apparently essential for optimal efficacy. References [I) Ye, J., Garg, A., Calhoun, C., Feingold K.R., Elias, P.M., and Ghadially, R. Exp. Dermato/. 11, 209-16 (2002) [2] zur Muhlen, A., Klotz, A., Weimans, S., Veeger, M., Thomer, B., Diener, B., and Hermann. M. Skin Pharmaco/. Physiol. 17, 167-75 (2004) [3] Ashida, Y., M. Ogo and M. Denda Br. J. Dermatol. 144, 238-43 (2001) [4) Seo J.Y., Kim E.K., Lee S.H., Park K.C., Kim K.H., and Chung J.H. Mech. Ageing Dev. 124, 903-10 (2003)
2005 ANNUAL SCIENTIFIC MEETING 203 SALICYLIC Acrn PROTECTS THE SKIN FROM UV DAMAGE Thomas Mammone, Ph.D., David Gan, Earl Goyarts, and Daniel Maes, Ph.D. Estee Lauder Companies, Melville, NY Abstract Aspirin (acetyl salicylate) has long been used as an analgesic. Salicylic acid has previously been reported to have anti- inflammatory properties. These activities include inhibiting activity of cox-I, cox-2, and NF-kb. In addition, salicylic acid has also been shown in some systems to induce Hsp70. We have demonstrated that salicylic acid inhibits UVB-induced NF-kb activation in keratinocytes. In addition, salicylic acid was also found to induce Hsp 70 in keratinocytes and increase keratinocytc survival to UVB toxicity. In living skin equivalents, salicylic acid was found to reduce UVB induced sunburn cell formation, as well as increase the removal of UVB induced TI dimer formation in living skin equivalents. Given these protective properties of salicylic acid, we propose the use of salicylic acid as a topical therapeutic to protect the skin from sun damage. Introduction Willow Bark has been used for centuries in Europe and China, and is still used today for its multiple medicinal properties. The medicinal ingredient, salicylic acid has long been used in modem medicine, initially as an analgesic. Today, aspirin (acetyl salicylate) is taken as an analgesic, anti-inflammatory, blood thinner, and as preventative medicine for heart disease. Salicylic acid has been reported as a cox-2 inhibitor (Wu, 2003) as well as an inhibitor of NF-kb activity (Kwon, 2003, and Constanzo, 2003), which would explain in part, its analgesic properties. In skin care, salicylic acid is used for acne treatment and for skin desquamation. However, it has also been reported that salicylic acid activates the binding of the HSF-1 transcription factor to the heat shock response element upstream of the Hsp70 gene in mammalian cells (Jurivich, 1992) Recently, it was reported that sodium salicylate was found to induce heat shock proteins in mammalian cells (Ishihara, 2003). As heat shock proteins such as Hsp70 have been shown to be cytoprotective, it is likely that salicylic acid may be useful as a protective agent in skin. Methods NF-kb activation assay: Normal Human Epidennal Keratinocytes (NHEK) were grown on 100mm plates to 50% confluence in the absence of hydrocortisone. These NHEK were then treated with 0, or I mM salicylic acid for 6hrs. The keratinocytes were then treated with 0-25mJ/cm2 UVB. NF-kB p65 was isolated from NHEKs with the Trans-AM NF-kB p65 kit (Active Motif). The kit contains an ELISA plate with oligonucleotides containing an NF-kb consensus-binding site for sequestering NF-kB present in NHEK nuclear extracts. Detection of the NF-kb protein is via a primary antibody and conjugated secondary antibody. Following the addition of substrate, the enzymatic reaction is allowed to proceed for up to 10 minutes before measuring the absorbance on a spectrophotometer at 450nm. Hsp70 protein determination: NHEK were grown to 75% confluency in 6 well plates before being treated with different doses of salicylic acid (0-lOOmg/ml). These treatments were carried out for 24 hours. Following the post incubation, the keratinocytes were harvested and pelleted. The Hsp70 ELISA kit from StressGen was used to quantify the levels ofHsp70 in the NHEK samples. UVB Viability Assay: NHEK were grown to 75% con fluency in 6 well plates before being treated with different doses of salicylic acid (0-1 OOmg/ml). Follwing a 6 hour pre-incubation, the NHEK were exposed to 30, 60, and 90mJ/cm2. The MTS survival assay was done l 8hrs post UVB treatment. Host-cell reactivation assay: Fibroblasts from a 31 year-old donor (ATCC) were incubated with liposomes containing the pSEAP DNA reporter (SV40 promoter fused to an alkaline phosphatase reporter). Cells were plated in 24 well plates and grown for 24 hours prior to exposure with liposomes loaded with reporter DNA. Fibroblasts were treated for 24hrs prior to transfection and 48hrs after transfection with salicylic acid. The DNA reporter-incorporated liposomes were then transfected into the fibroblasts. DNA damage was inflicted with UVB irradiation equivalent to 200,400, 600, 800, 1000 or 1500 mJ/cm2. The positive control cells were treated with liposomes containing reporter DNA, but not exposed to UVB. Untreated cells did not receive reporter DNA. The vector- encoded alkaline phosphatase is heat stable at 65oC. To each well, 97 ml of assay buffer was added and incubated for 5 min at room temperature prior to adding 3 ml of lmM MUP. The plate was incubated for 60 min in the dark at room temperature before measuring the fluorescence (excitation: 360 nm and emission: 460 nm).
Purchased for the exclusive use of nofirst nolast (unknown) From: SCC Media Library & Resource Center (library.scconline.org)